|
Toxeus Magnus
''Toxeus magnus'' is a species of jumping spider of the genus ''Toxeus''. It is endemic to Taiwan and Southeast Asia. The species was originally classified as a part of the genus ''Myrmarachne'' in 1933 by Saitō in his work ''Notes on the spiders from Formosa'', but it was later reclassified as ''Toxeus'' by the Polish arachnologist Jerzy Prószyński in November 2016. The species is notable for being a non-mammalian animal that nurses its offspring through a form of lactation. ''Toxeus magnus'' is exceptional because of its social behaviour. Of the nearly 48,000 known different species of spiders only around 120 are known to be able to tolerate the company of others (including their own siblings) for more than three weeks, and only around 30 species of spiders are known to engage in life-long social lives. Lactation ''Toxeus magnus'' nurses its offspring for about 38 days, although they are able to forage on their own after 21 days. While the species was first classified in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Spider Catalog
The World Spider Catalog (WSC) is an online searchable database concerned with spider taxonomy. It aims to list all accepted families, genera and species, as well as provide access to the related taxonomic literature. The WSC began as a series of web pages in 2000, created by Norman I. Platnick of the American Museum of Natural History. After his retirement in 2014, the Natural History Museum of Bern took over, converting the catalog to a relational database A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for .... As of November 22, 2024, 52'487 species are listed, after an average discovery rate of three new species per day. The order Araneae has the seventh-most species of all orders. The WSC's existence makes spiders the largest taxon with an online listing that is updated regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ..., fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is almost pure sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salticidae
Jumping spiders are a group of spiders that constitute the family (biology), family Salticidae. , this family contained over 600 species description, described genus, genera and over 6,000 described species, making it the largest family of spiderscomprising 13% of spider species. Jumping spiders have some of the best visual perception, vision among arthropods — being capable of stereoptic color vision — and use sight in courtship, hunting, and navigation. Although they normally move unobtrusively and fairly slowly, most species are capable of very agile jumps, notably when hunting, but sometimes in response to sudden threats or crossing long gaps. Both their book lungs and Invertebrate trachea, tracheal system are well-developed, and they use both systems (bimodal breathing). Jumping spiders are generally recognized by their eye pattern. All jumping spiders have four pairs of eyes, with the Anatomical terms of location, anterior median pair (the two front middle eyes) being pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Milk
Crop milk is a secretion from the lining of the crop of parent birds in some species that is regurgitated to young birds. It is found among all pigeons and doves where it is also referred to as pigeon milk. Crop milk is also secreted from the crop of flamingos and the male emperor penguin, suggesting independent evolution of this trait. Unlike in mammals where typically only females produce milk, crop milk is produced by both males and females in pigeons and flamingos; and in penguins, only by the male. Lactation in birds is controlled by prolactin, which is the same hormone that causes lactation in mammals. Crop milk is a holocrine secretion non- sex specific in response to brooding unlike in mammals where milk is an apocrine secretion. Crop milk contains both fat and protein, as with mammalian milk, but unlike mammalian milk, it contains no carbohydrates. Pigeon milk Crop milk bears little physical resemblance to mammalian milk, though in pigeons it is compositionally s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophic Egg
A trophic egg is an egg (biology), egg whose function is not reproduction but nutrition; in essence, the trophic egg serves as food for offspring hatched from viable eggs. In most species that produce them, a trophic egg is usually an Fertilization, unfertilised egg. The production of trophic eggs has been observed in a highly diverse range of species, including fish, amphibians, spiders and insects. The function is not limited to any particular level of Parental investment, parental care, but occurs in some Subsociality, sub-social species of insects, the spider ''Amaurobius_ferox, A. ferox'', and a few other species like the frogs ''Leptodactylus fallax'' and ''Oophaga'', and the catfish ''Bagrus meridionalis''. Parents of some species deliver trophic eggs directly to their offspring, whereas some other species simply produce the trophic eggs after laying the viable eggs; they then leave the trophic eggs where the viable offspring are likely to find them. The Lamniformes, mackerel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized as an independent person capable of giving consent and taking responsibility, generally implies sexual maturity (certain disorders of sexual development notwithstanding), but depends on other criteria, defined by specific cultural expectations. Most multicellular organisms are unable to sexually reproduce at birth (animals) or germination (e.g. plants): depending on the species, it may be days, weeks, or years until they have developed enough to be able to do so; in addition, certain cues may trigger an organism to become sexually mature. These may be external, such as drought, or fire, that triggers sexual maturation of certain plants, or internal, such as percentage of body fat (certain animals). Internal cues are not to be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophilidae
The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true fruit flies because they are frugivorous, and include apple maggot flies and many pests. The best known species of the Drosophilidae is ''Drosophila melanogaster'', within the genus ''Drosophila'', also called the "fruit fly." ''Drosophila melanogaster'' is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. Many fundamental biological mechanisms were discovered first in ''D. melanogaster.'' The fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, '' Drosophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigastric Furrow
The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata (sections or segments), eight jointed legs, no wings or antennae, the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps, simple eyes, and an exoskeleton, which is periodically shed. Spiders also have several adaptations that distinguish them from other arachnids. All spiders are capable of producing silk of various types, which many species use to build webs to ensnare prey. Most spiders possess venom, which is injected into prey (or defensively, when the spider feels threatened) through the fangs of the chelicerae. Male spiders have specialized pedipalps that are used to transfer sperm to the female during mating. Many species of spiders exhibit a great deal of sexual dimorphism. External anatomy Spiders, unlike insects, have only two main body parts ( tagmata) instead of three: a fused head and thorax (called a cephalothorax or prosoma) and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
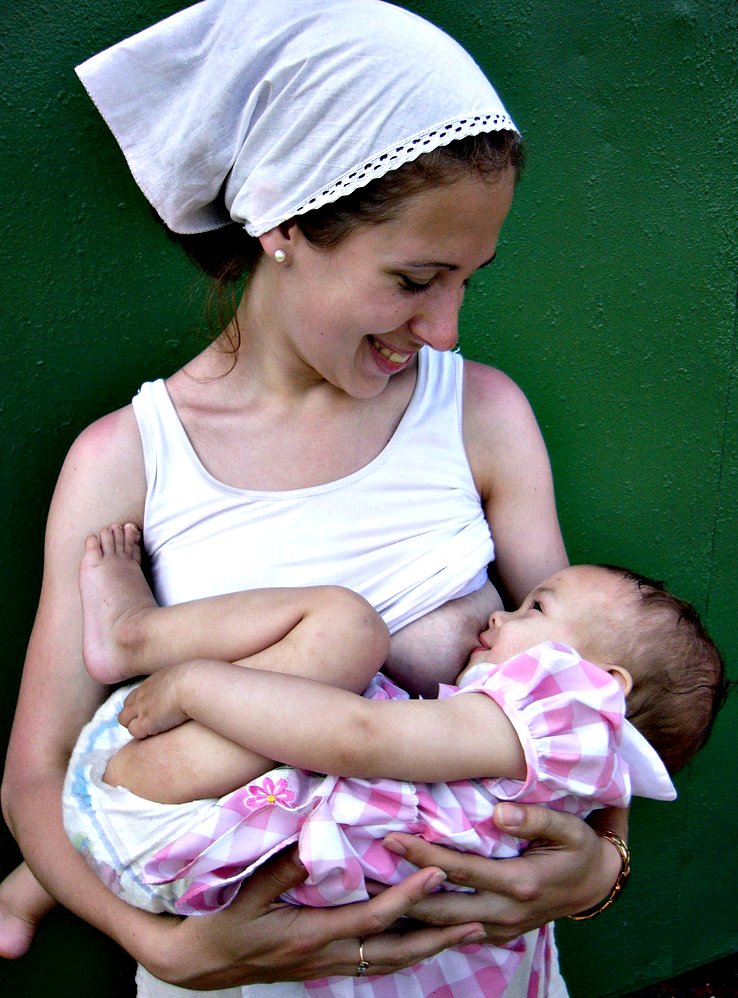
Cow's Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibodies and immune-modulating components that strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or formula) should have two servings of milk products a day, and more than six billion people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
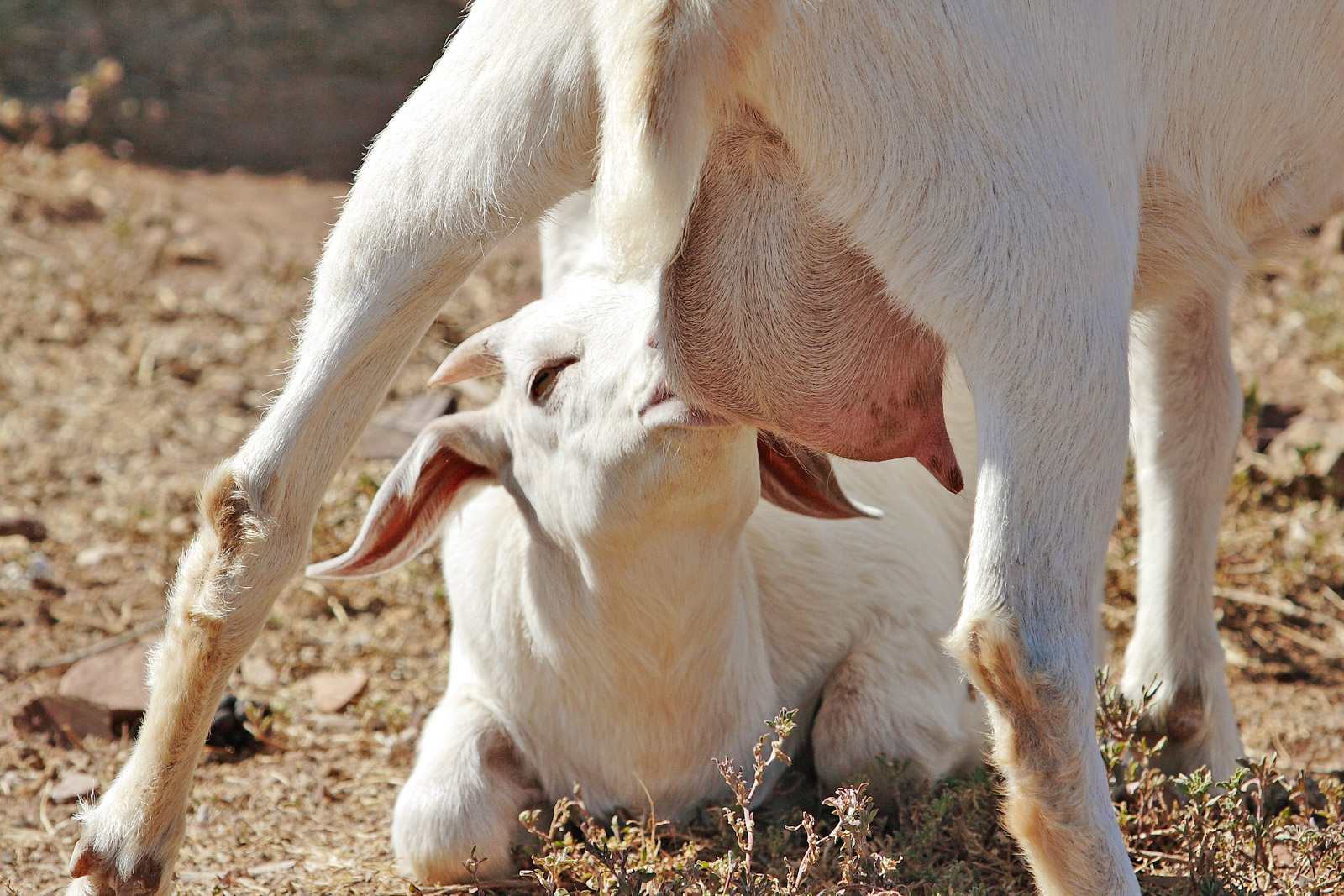
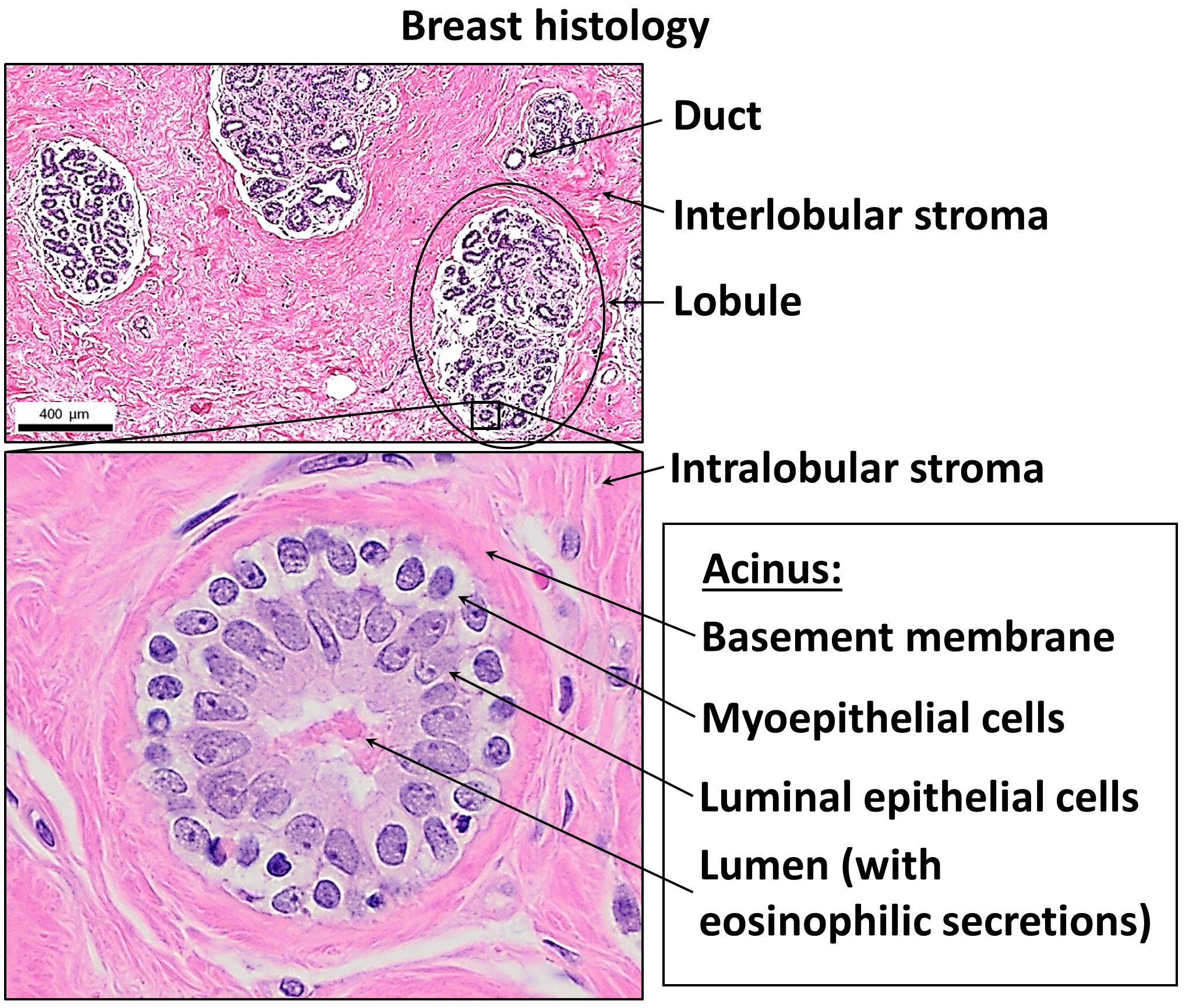
Mammary Glands
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats) to feed young offspring. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: monotremes, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of monotremes, their mammary glands are modified sebaceou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from (Genitive case, gen. ), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ''-ose'' used to name sugars. The compound is a white, water-soluble, non-Hygroscopy, hygroscopic solid with a mildly sweet taste. It is used in the food industry. Structure and reactions Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose, which form a β-1→4 Glycosidic bond, glycosidic linkage. Its systematic name is β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose. The glucose can be in either the α-pyranose form or the β-pyranose form, whereas the galactose can have only the β-pyranose form: hence α-lactose and β-lactose refer to the anomeric form of the glucopyranose ring alone. Detection reactions for lactose are the Alfred Wöhlk, Wöhlk and William Fearon, Fearon tests. They can be used to detect the different lactose content o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of lactating mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfeeding, breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Milk contains many nutrients, including calcium and protein, as well as lactose and saturated fat; the enzyme lactase is needed to break down lactose. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. The first milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies and immune-modulating components that milk immunity, strengthen the immune system against many diseases. As an agricultural product, Milking, milk is collected from farm animals, mostly cattle, on a dairy. It is used by humans as a drink and as the base ingredient for dairy products. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC recommends that children over the age of 12 months (the minimum age to stop giving breast milk or Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |