|
Torpedo (genus)
''Torpedo'' is a genus of rays, commonly known as electric rays, torpedo rays, or torpedoes. They are slow-moving bottom-dwellers capable of generating electricity as a defense and feeding mechanism. The naval weapon known as the torpedo was named after this genus, whose own name is derived from the Latin word meaning 'numb' or 'paralysed', presumably the sensation one would feel after experiencing the ray's electric shock. Taxonomic history Peter Forsskål validly published the genus name ''Torpedo'' in 1775, predating the use of the genus name ''Torpedo'' by Duméril in 1806, meaning that ''Torpedo'' Duméril, 1806 (often cited in catalogs) is a junior homonym of Forsskål's name and cannot be used. Forsskål included only a single species, '' Raja torpedo'' Linnaeus, 1758, thereby making it the type species of the genus. While Forsskål's description indicated that he had misinterpreted Linnaeus' name and ascribed it to another electric fish (currently known as ''Malapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Forsskål
Peter Forsskål, sometimes spelled Pehr Forsskål, Peter Forskaol, Petrus Forskål or Pehr Forsskåhl (11 January 1732 – 11 July 1763) was a Sweden, Swedish exploration, explorer, oriental studies, orientalist, natural history, naturalist, and an Apostles of Linnaeus, apostle of Carl Linnaeus. Early life Forsskål was born in Helsinki, now in Finland but then a part of Sweden, where his father, the priest , was serving as a Lutheran clergyman, but the family moved to Sweden in 1741 when the father was appointed to the parish of :sv:Tegelsmora församling, Tegelsmora in Uppland and the Archbishop of Uppsala, archdiocese of Uppsala. As was common at the time, he enrolled at Uppsala University at a young age in 1742, but returned home for some time and, after studies on his own, rematriculated in Uppsala in 1751, where he completed a Theology, theological degree the same year. Linnaeus's disciple In Uppsala Forsskål was one of the students of Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus, but appare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill Slit
Gill slits are individual openings to gills, i.e., multiple gill arches, which lack a single outer cover. Such gills are characteristic of cartilaginous fish such as sharks and rays, as well as deep-branching vertebrates such as lampreys. In contrast, bony fishes have a single outer bony gill covering called an operculum. Most sharks and rays have five pairs of gill slits, but a few species have 6 or 7 pairs. Shark gill slits lie in a row behind the head. The anterior edge of a gill slit is motile, moving outward to allow water to exit, but closing to prevent reverse flow. A modified slit, called a spiracle, lies just behind the eye, which assists the shark with taking in water during respiration and plays a major role in bottom–dwelling sharks. Spiracles are reduced or missing in active pelagic sharks. While the shark is moving, water passes through the mouth and over the gills in a process known as "ram ventilation". While at rest, most sharks pump water over their gil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scribonius Largus
Scribonius Largus Designatianus ( – ) was the court physician to the Roman emperor Claudius. Around 47 AD, at the request of Gaius Julius Callistus, the emperor's freedman, he drew up a list of 271 prescriptions (''Compositiones''), most of them his own, although he acknowledged his indebtedness to his tutors, to friends, and to the writings of eminent physicians. Certain traditional remedies are also included. The work has no pretensions to style, and contains many colloquialisms, and has been cited by Peter Suber as a forerunner of Open Access. The greater part of it was transferred without acknowledgment to the work of Marcellus Empiricus (c. 410), ''De Medicamentis Empiricis, Physicis, et Rationabilibus'', which is of great value for the correction of the text of Largus. See the edition of the ''Compositiones'' by S. Sconocchia (Teubner 1983), which replaced the well-outdated edition of G. Helmreich (Teubner 1887). ''Compositiones'' makes the earliest known allusion t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrin
Agrin is a large proteoglycan whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis. Agrin is named based on its involvement in the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis. In humans, this protein is encoded by the ''AGRN'' gene. This protein has nine domains homologous to protease inhibitors. It may also have functions in other tissues and during other stages of development. It is a major proteoglycan component in the glomerular basement membrane and may play a role in the renal filtration and cell-matrix interactions. Agrin functions by activating the MuSK protein (for Muscle-Specific Kinase), which is a receptor tyrosine kinase required for the formation and maintenance of the neuromuscular junction. Agrin is required to activate MuSK. Agrin is also required for neuromuscular junction formation. Discovery Agrin was first identified by the U.J. McMahan laboratory, Stanford University. Mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
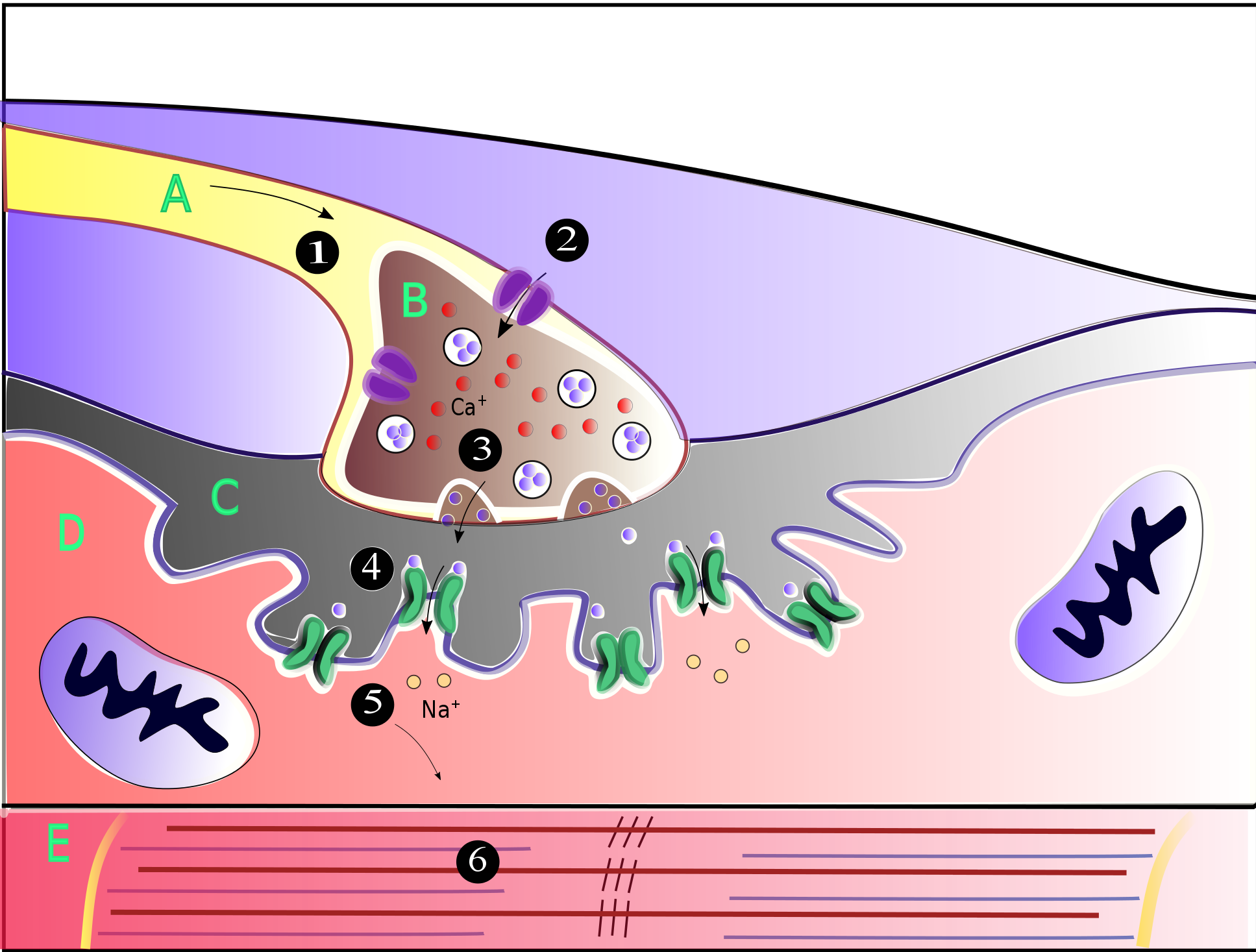
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction. Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. In the neuromuscular system, nerves from the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system are linked and work together with muscles. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-gated calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmins) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, those negatively charged electrons flow through the circuit and reach the positive terminal, thus causing a redox reaction by attracting positively charged ions, or cations. Thus, higher energy reactants are converted to lower energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential
Electric potential (also called the ''electric field potential'', potential drop, the electrostatic potential) is defined as electric potential energy per unit of electric charge. More precisely, electric potential is the amount of work (physics), work needed to move a test charge from a reference point to a specific point in a static electric field. The test charge used is small enough that disturbance to the field is unnoticeable, and its motion across the field is supposed to proceed with negligible acceleration, so as to avoid the test charge acquiring kinetic energy or producing radiation. By definition, the electric potential at the reference point is zero units. Typically, the reference point is Earth (electricity), earth or a point at infinity, although any point can be used. In classical electrostatics, the electrostatic field is a vector quantity expressed as the gradient of the electrostatic potential, which is a scalar (physics), scalar quantity denoted by or occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Organ (biology)
An Torpediniformes.html" ;"title="electric ray (Torpediniformes">electric ray (Torpediniformes) showing location of paired electric organs in the head, and electrocytes stacked within it In biology, the electric organ is an organ (biology), organ that an electric fish uses to create an electric field. Electric organs are derived from modified muscle or in some cases nerve tissue, called electrocytes, and have evolved at least six times among the Elasmobranchii, elasmobranchs and teleosts. These fish use their electric discharges for navigation, communication, mating, defence, and in strongly electric fish also for the incapacitation of prey. The electric organs of two strongly electric fish, the torpedo ray and the electric eel, were first studied in the 1770s by John Walsh, Hugh Williamson, and John Hunter. Charles Darwin used them as an instance of convergent evolution in his 1859 ''On the Origin of Species''. Modern study began with Hans Lissmann's 1951 study of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Torpedo
The Gulf torpedo (''Torpedo sinuspersici'') or variable electric ray, is a species of electric ray in the family Torpedinidae. It is found in the Indian Ocean, but may represent a species flock of several local endemic species. It is distinguishable from other ''Torpedo'' species in its range by its ornate dorsal coloration. Another common name, marbled electric ray, is not to be confused with '' Torpedo marmorata''. Distribution and habitat The Gulf torpedo is the most widespread of the electric rays in the western Indian Ocean, with a patchy range extending to South Africa, Somalia, the Red Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Persian Gulf, Sri Lanka, and the Andaman Sea. There are also less reliable reports of it occurring elsewhere, including Madagascar, the Seychelles, and the Laccadive Islands. Recorded for the first time in 2002 in Mediterranean Sea, its presence needs to be clarified due to its strong resemblance with '' Torpedo marmorata'', a species well established there.Guide o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |