|
Tooth Painting
Teeth blackening or teeth lacquering is a custom of dyeing one's teeth black. It was most predominantly practiced in Southeast Asian and Oceanic cultures, particularly among Austronesian, Austroasiatic, and Kra–Dai-speaking peoples. It was also practiced in Japan prior to the Meiji era, as well as in India. It was also performed among some groups in the Americas, most notably among the Shuar people of northern Peru and Ecuador. Teeth blackening is usually done during puberty. It was seen as a sign of maturity, beauty, and civilization. A common belief is that blackened teeth differentiated humans from animals. Teeth blackening is often done in conjunction with traditions of tooth sharpening and dental evulsion, as well as other body modification customs like tattoos. Teeth blackening and filing were regarded with fascination and disapproval by early European explorers and colonists. The practice survives in some isolated ethnic groups in Southeast Asia and Oceania but has mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woman From Akha Tribe
A woman is an adult female human. Before adulthood, a female child or Adolescence, adolescent is referred to as a girl. Typically, women are of the female sex and inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and women with functional uteruses are capable of pregnancy and giving childbirth, birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, ''SRY'' gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Sex differences in human physiology, Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. An adult woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. These characteristics facilitate childbirth and breastfeeding. Women typically have less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Teeth
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are Dental prosthesis, prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing Human tooth, teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the Human mouth, oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable (removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some of which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants (fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they fit onto the Human mandible, mandibular arch or on the maxilla, maxillary arch. Medical uses Dentures can help people via: * Chew, Mastication: chewing ability is improved by the replacement of edentulous (lacking teeth) areas with denture teeth. * Aesthetics: the presence of teeth gives a natural human physical appearance, appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
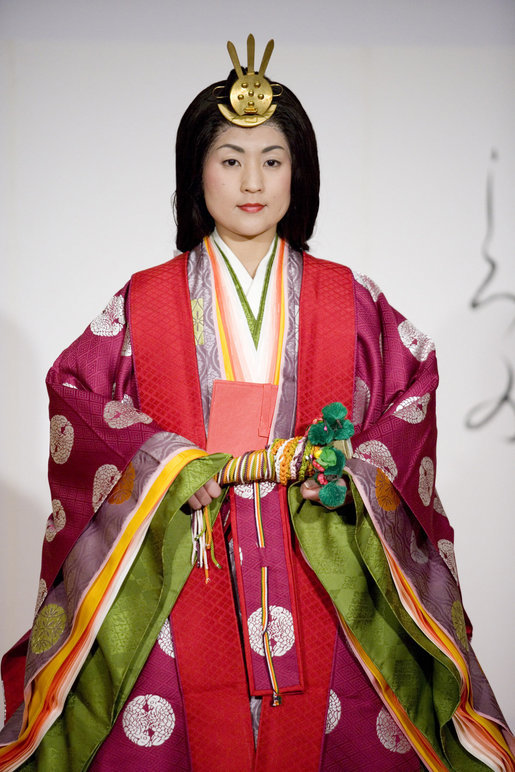
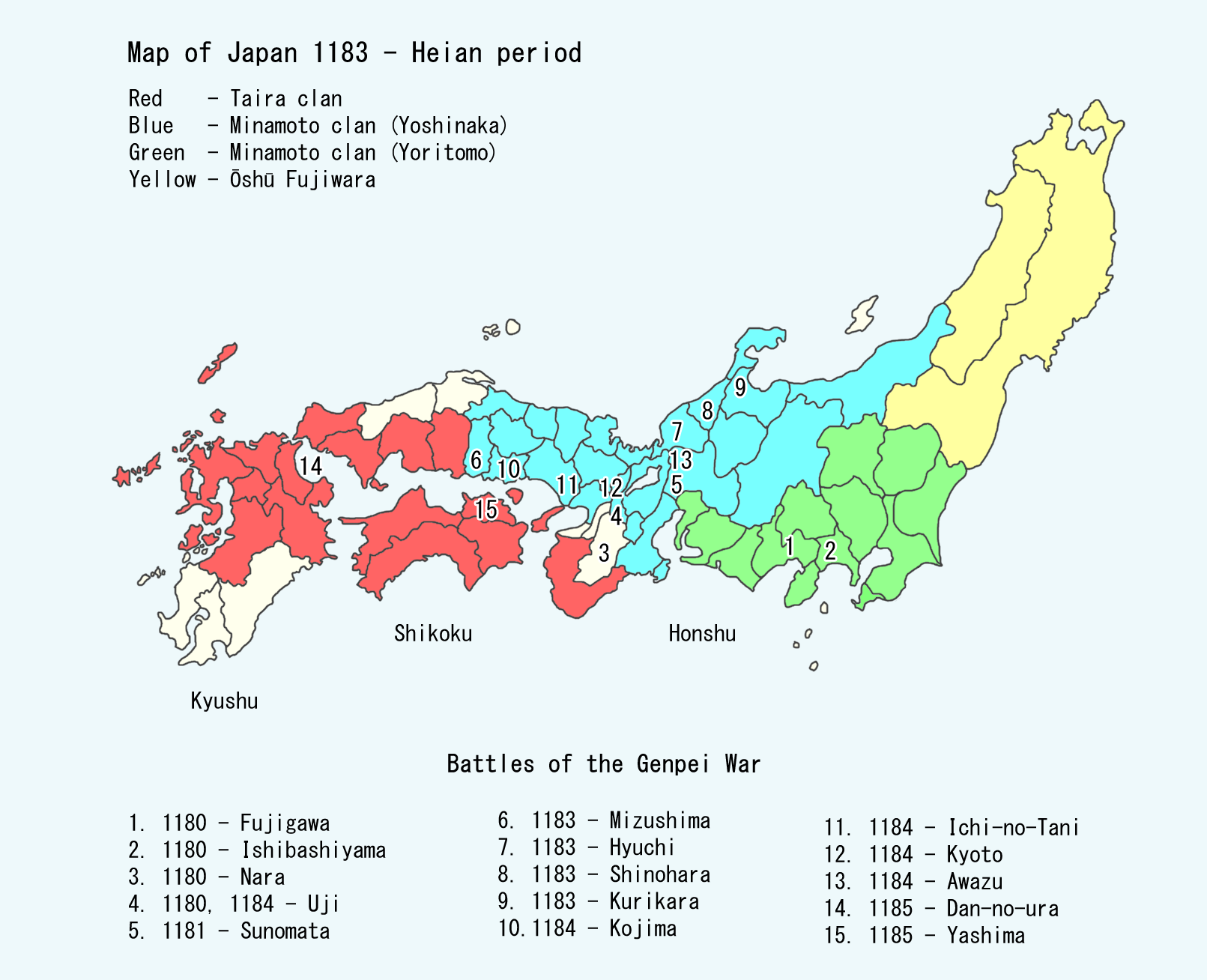
Taira Clan
The was one of the four most important Japanese clans, clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period, Heian period of History of Japan, Japanese history – the others being the Minamoto clan, Minamoto, the Fujiwara clan, Fujiwara, and the Tachibana clan (kuge), Tachibana. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the Emperor of Japan, emperors they descended from: Emperor Kanmu, Kanmu Heishi, Emperor Ninmyō, Ninmyō Heishi, Emperor Montoku, Montoku Heishi, and Emperor Kōkō, Kōkō Heishi, the most influential of which was the Kanmu Heishi line. In the twilight of the Heian period, the Taira controlled the boy emperor Emperor Antoku, Antoku (himself the grandson of the powerful ''Kugyō'' Taira no Kiyomori) and had effectively dominated the Imperial capital of Heian-kyō, Heian. However, they were opposed by their rivals the Minamoto clan (the Genji), which culminated in the Genpei War (1180–1185 AD). The five-year-long war concluded with a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genpuku
is a public holiday in Japan held annually on the second Monday of January under the Happy Monday System. It is held in order to congratulate and encourage all those who have already reached the age of maturity between April 2 of the previous year and April 1 of the current year, and to help them realise that they have become adults. Festivities include held at local and prefectural offices, as well as after-parties among family and friends. Overview On June 13, 2018, the age of maturity was lowered for the first time since it was established. According to the new law, which came into force in 2022, a citizen is considered an adult with the onset of full 18 years. Note that Coming of Age Day and the ceremony itself are not directly linked to changes in the legal status of young people. For example, adult status becomes effective on the 18th birthday, with some exceptions; both men and women can marry and are released from parental authority. At the same time, they are rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a period in Japanese history when the Chinese influence on Japanese culture, Chinese influences were in decline and the national culture matured. The Heian period is also considered the peak of the Japanese Emperors of Japan, imperial court, noted for its Japanese art, art, especially Japanese poetry, poetry and Japanese literature, literature. Two syllabaries unique to Japan, katakana and hiragana, emerged during this time. This gave rise to Japan's famous vernacular literature, with many of its texts written by court ladies who were not as educated in Chinese as their male counterparts. Although the Imperial House of Japan had power on the surface, the real power was in the hands of the Fujiwara clan, a powerful Kuge, aristocratic family wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsutsumi Chūnagon Monogatari
is a post late-Heian period Japanese collection of short stories. Authorship With the exception of one story, the authorship is unknown. It is likely each story was written by different authors at various times and later collected together into a single text. ''Ōsaka Koenu Gonchūnagon'' is known to have been composed in 1055 by Lady Koshikibu. This is confirmed in volume 8 of which includes one of the poems from this story. In addition, poems from ''Hanazakura Oru Shōshō'', ''Hodohodo no Kesō'', ''Kaiawase'', and ''Haizumi'' are included in the 1271 '' Fūyō Wakashū'' indicating an upper bound for these stories. Tradition states that Fujiwara no Tameuji (1222–1286) and Fujiwara no Tamesuke (1263–1328) created copies of the manuscripts also indicating completion of the text by the 13th century. Contents The meaning of the title is unknown. There are two main theories: *It is a reflection of the various stories (''monogatari'') bound (''tsutsumi'') together into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murasaki Shikibu
was a Japanese novelist, Japanese poetry#Age of Nyobo or court ladies, poet and lady-in-waiting at the Imperial Court in Kyoto, Imperial court in the Heian period. She was best known as the author of ''The Tale of Genji'', widely considered to be one of the world's first novels, written in Japanese between about 1000 and 1012. Murasaki Shikibu is a descriptive name; her personal name is unknown, but she may have been , who was mentioned in a 1007 court diary as an imperial lady-in-waiting. Heian period, Heian women were traditionally excluded from learning Classical Chinese, Chinese, the written language of government, but Murasaki, raised in her erudite father's household, showed a precocious aptitude for the Chinese classics and managed to acquire fluency. She married in her mid-to-late twenties and gave birth to a daughter, Daini no Sanmi. Her husband died after two years of marriage. It is uncertain when she began to write ''The Tale of Genji'', but it was probably while s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Tale Of Genji
is a classic work of Japanese literature written by the noblewoman, poet, and lady-in-waiting Murasaki Shikibu around the peak of the Heian period, in the early 11th century. It is one of history's first novels, the first by a woman to have won global recognition, and in Japan today has a stature like that of Shakespeare in England. The work is a depiction of the lifestyles of high courtiers during the Heian period. It is written mostly in Japanese phonetic script (''hiragana''), in a vernacular style associated with women's writing of the time (not the same as "vernacular Japanese", which only appeared in late 19th century), not in Chinese characters (''kanji'') used for more prestigious literature, and its archaic language and poetic style require specialised study. The original manuscript no longer exists but there are more than 300 later manuscript copies of varying reliability. It was made in "Folded leaflet#Concertina fold, concertina" or style: several sheets of paper p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. ''Kofun'' is Japanese for the type of tumulus, burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haniwa
The are terracotta clay figures that were made for ritual use and buried with the dead as funerary objects during the Kofun period (3rd to 6th centuries AD) of the history of Japan. ''Haniwa'' were created according to the ''wazumi'' technique, in which mounds of coiled clay were built up to shape the figure, layer by layer. ''Haniwa'' can also refer to offering cylinders, not the clay sculptures on top of them as well as the "wooden haniwa" found in Kofun tumulus, tumuli. Terracotta ''Haniwa'' were made with water-based clay and dried into a coarse and absorbent material that stood the test of time. Their name means "circle of clay", referring to how they were arranged in a circle above the tomb. The protruding parts of the figures were made separately and then attached, while a few things were carved into them. They were smoothed out by a wooden paddle. Terraces were arranged to place them with a cylindrical base into the ground, where the earth would hold them in place. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
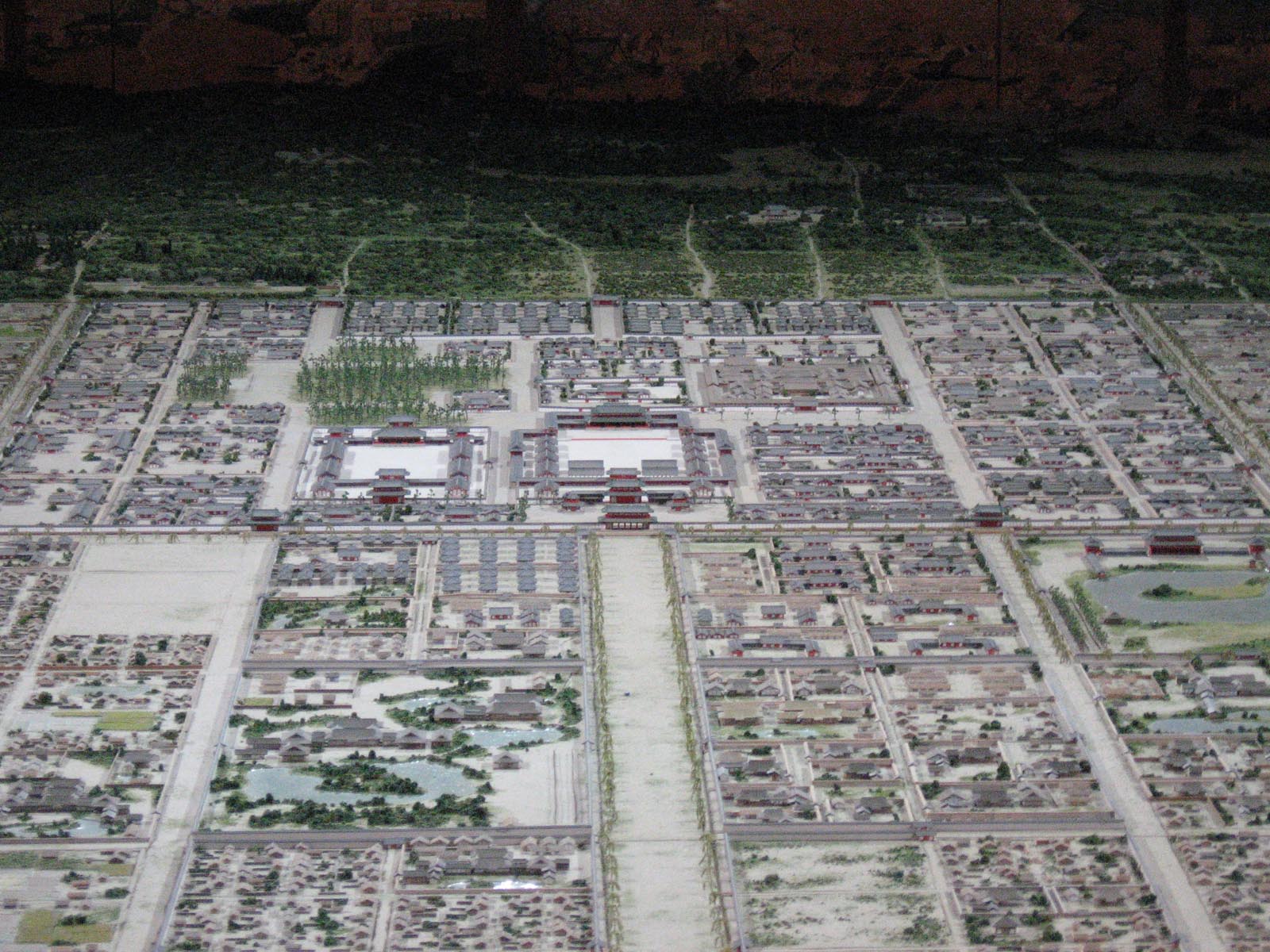
Heian-kyō
Heian-kyō was one of several former names for the city now known as Kyoto. It was the official capital of Japan for over one thousand years, from 794 to 1868 with an interruption in 1180. Emperor Kanmu established it as the capital in 794, moving the Imperial Court there from nearby Nagaoka-kyō at the recommendation of his advisor Wake no Kiyomaro and marking the beginning of the Heian period of Japanese history. According to modern scholarship, the city is thought to have been modelled after the urban planning for the Tang dynasty Chinese capital of Chang'an (modern-day Xi'an). It remained the chief political center until 1185, when the samurai Minamoto clan defeated the Taira clan in the Genpei War, moving administration of national affairs to Kamakura and establishing the Kamakura shogunate. Though political power would be wielded by the samurai class over the course of three different shogunates, Heian-kyō remained the site of the Imperial Court and seat of Imperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
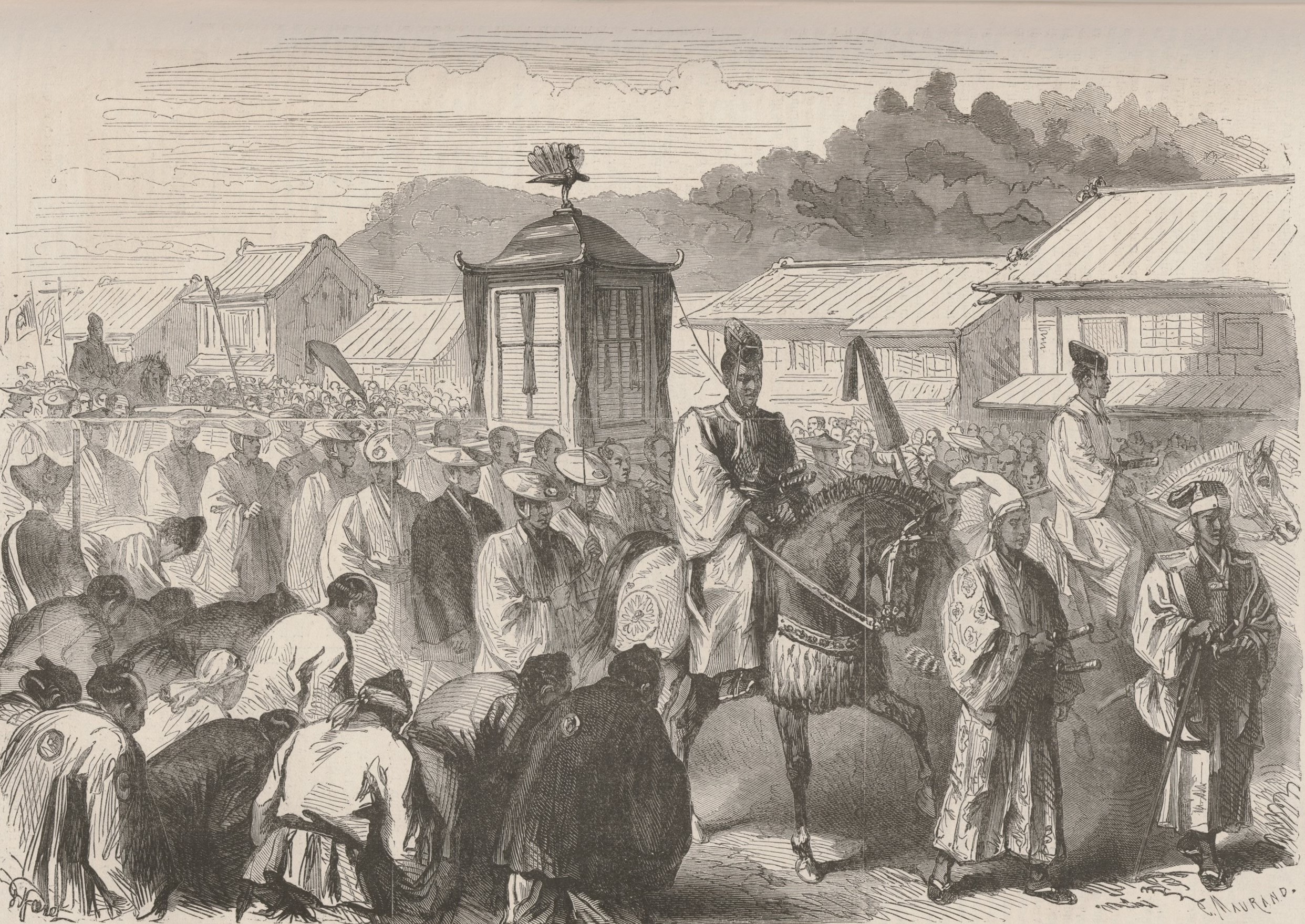
Meiji Period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |