|
Tomatidine
Tomatidine is a natural compound found in leaves of tomatoes and green tomatoes. Chemically, it is the aglycone of tomatine. It has been shown to have potential health benefits in animal models. For instance, tomatidine inhibited skeletal muscle atrophy in a mouse model of skeletal unloading-induced atrophy and to prevent or reverse sarcopenia (loss of muscle mass and strength due to biological aging) by inhibiting the activation of genes by ATF4. Dietary supplementation with ~0.04% tomatidine for 10 weeks reduced plasma cholesterol and atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice without evidence of toxicity. Research It is investigated as compound to increase longevity and it increased lifespan and healthspan of ''C. elegans''. It is also investigated in osteoporosis. See also * Ursolic acid Ursolic acid (sometimes referred to as urson, prunol, malol, or 3β-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid), is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomatine
Tomatine (sometimes called tomatin or lycopersicin) is a glycoalkaloid, found in the stems and leaves of tomato plants, and in the fruits at much lower concentrations. Chemically pure tomatine is a white crystalline solid at standard temperature and pressure. Tomatine is sometimes confused with the glycoalkaloid solanine. History Tomatoes were brought to Europe in the early 1500s. The English botanist John Gerard was one of the first cultivators of the tomato plant. In his publication '' Grete Herball'', he considered tomatoes poisonous due to their levels of what would later be called tomatine, plus high acid content. Consequently, tomatoes were generally not eaten in Britain until the mid-18th century. In 1837, the first medicinal tomato pills were advertised in the United States because of their positive effects upon the biliary organs. The product “Phelp’s Compound Tomato Pills” was extracted from the tomato plant, and contained tomatine. The pills were made by the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aglycone
An aglycone (aglycon or genin) is the chemical compound remaining after the glycosyl group on a glycoside is replaced by a hydrogen atom. For example, the aglycone of a cardiac glycoside would be a steroid A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ... molecule. Detection A way to identify aglycone is proposed to extract it from Agave spp. by using H-NMR and Heteronuclear multiple bond correlation (HMBC) experiments. The HMBC experiment can be combined with other techniques such as mass spectrometry to further examine the structure and the function of aglycone. Samples of glycones and glycosides from limonoids can be simultaneously quantified through a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method, where a binary solvent system and a diode array detector separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperidines
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). It is a colorless liquid with an odor described as objectionable, typical of amines. The name comes from the genus name ''Piper (genus), Piper'', which is the Latin word for Black pepper, pepper. Although piperidine is a common organic compound, it is best known as a representative structure element within many pharmaceuticals and alkaloids, such as natural-occurring Solenopsin, solenopsins. Production Piperidine was first reported in 1850 by the Scottish chemist Thomas Anderson (chemist), Thomas Anderson and again, independently, in 1852 by the French chemist Auguste André Thomas Cahours, Auguste Cahours, who named it. Both of them obtained piperidine by reacting piperine with nitric acid. Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compounds With 5 Rings
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursolic Acid
Ursolic acid (sometimes referred to as urson, prunol, malol, or 3β-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid), is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme. It is an isomer of Betulinic & Oleanic acid. Natural occurrence Ursolic acid is present in many plants, such as '' Mirabilis jalapa'', as well as in many fruits and herbs used in daily life (e.g. apples, basil and holy basil, bilberries, cranberries, elder flower, peppermint, rosemary, lavender, oregano, thyme, hawthorn, and prunes). Apple peels contain large quantities of ursolic acid and related compounds. Potential biochemical effects A number of potential biochemical effects of ursolic acid have been investigated, but there has been no clinical study demonstrating benefits to human health. ''In vitro'', ursolic acid inhibits the proliferation of various cancer cell types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FASEB Journal
''The FASEB Journal'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal related to experimental biology. The journal was established in 1987 and has been published since 2020 by Wiley on behalf of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. It is published monthly and contains special collections throughout the year. The journal publishes research in the biological and biomedical sciences as well as interdisciplinary research cutting across multiple fields and areas. The FASEB Journal offers both a subscription model and open access. Ranking According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 4.4."The FASEB Journal." 2023 Journal Citation Reports. Web of Science (Science ed.). Clarivate. 2024. Past FJ Editors-In Chief Thoru Pederson, PhD (2016-2022) Gerald Weissmann Gerald Weissmann (August 7, 1930 – July 10, 2019) was an Austrian-born American physician/scientist, editor, and essayist. He was Professor Emeritus and Research Professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the Old age, elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the Vertebral column, spine, the bones of the forearm, the wrist, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, some people may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal peak bone mass, maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after menopause in women due to lower levels of estrogen, and after andropause in older men due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor 3.8. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
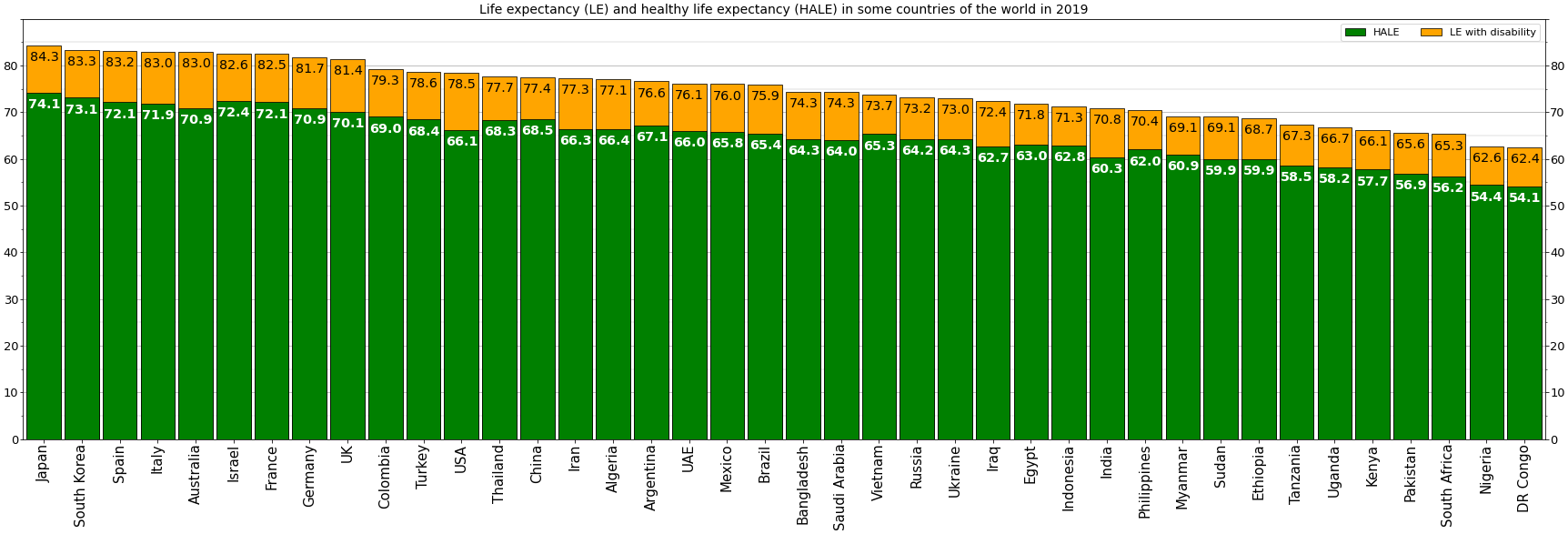
Healthspan
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where ''e''x denotes the average life remaining at age ''x''). This can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. Human remains from the early Bronze Age indicate an LEB of 24. In 2019, world LEB was 73.3. A combination of high infant mortality and deaths in young adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ApoE
Apolipoprotein E (Apo-E) is a protein involved in the metabolism of fats in the body of mammals. A subtype is implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular diseases. It is encoded in humans by the gene ''APOE''. Apo-E belongs to a family of fat-binding proteins called apolipoproteins. In the circulation, it is present as part of several classes of lipoprotein particles, including chylomicron remnants, VLDL, Intermediate-density lipoprotein, IDL, and some High-density lipoprotein, HDL. Apo-E interacts significantly with the LDL receptor, low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), which is essential for the normal processing (catabolism) of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. In peripheral tissues, Apo-E is primarily produced by the liver and macrophages, and mediates cholesterol metabolism. In the central nervous system, Apo-E is mainly produced by astrocytes and transports cholesterol to neurons via Apo-E receptors, which are members of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |