|
Titanium Adhesive Bonding
Titanium adhesive bonding is an engineering process used in the aerospace industry, medical-device manufacture and elsewhere. Titanium alloy is often used in medical and military applications because of its strength, weight, and corrosion resistance characteristics. In implantable medical devices, titanium is used because of its Titanium biocompatibility, biocompatibility and its passive, stable oxide layer. Also, titanium allergies are rare and in those cases mitigations like Parylene coating are used. In the aerospace industry titanium is often bonded to save cost, touch times, and the need for mechanical fasteners. In the past, Russian submarines' hulls were completely made of titanium because the non-magnetic nature of the material went undetected by the defense technology at that time. Bonding adhesive to titanium requires preparing the surface beforehand, and there is not a single solution for all applications. For example, etchant and chemical methods are not biocompati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Alloy
Titanium alloys are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical elements. Such alloys have very high tensile strength and toughness (even at extreme temperatures). They are light in weight, have extraordinary corrosion resistance and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, the high cost of Titanium#Production, processing limits their use to military applications, aircraft, spacecraft, bicycles, medical devices, jewelry, highly stressed components such as connecting rods on expensive sports cars and some premium sports equipment and consumer electronics. Although "commercially pure" titanium has acceptable mechanical properties and has been used for orthopedics, orthopedic and dental implants, for most applications titanium is alloyed with small amounts of aluminium and vanadium, typically 6% and 4% respectively, by weight. This mixture has a solid solubility which varies dramatically with temperature, allowing it to undergo precipitation strengtheni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Angle Of Laser Roughened Ti
Contact may refer to: Interaction Physical interaction * Contact (geology), a common geological feature * Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye * Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects * Contact juggling * Contact mechanics, the study of solid objects that deform when touching each other * Contact process (mathematics), a model of an interacting particle system * Electrical contacts * ''Sparśa'', a concept in Buddhism that in Sanskrit/Indian language is translated as "contact", "touching", "sensation", "sense impression", etc. Social interaction * Contact (amateur radio) * Contact (law), a concept related to visitation rights * Contact (social), a person who can offer help in achieving goals * Contact Conference, an annual scientific conference * Extraterrestrial contact, see Search for extraterrestrial intelligence * First contact (anthropology), an initial meeting of two cultures * Language contact, the interaction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can Permeation, permeate solid metals. Once absorbed, hydrogen lowers the Stress (mechanics), stress required for cracks in the metal to initiate and propagate, resulting in embrittlement. Hydrogen embrittlement occurs in steels, as well as in iron, nickel, titanium, cobalt, and their alloys. Copper, aluminium, and stainless steels are less susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. The essential facts about the nature of hydrogen embrittlement have been known since the 19th century. Hydrogen embrittlement is maximised at around room temperature in steels, and most metals are relatively immune to hydrogen embrittlement at temperatures above 150 °C. Hydrogen embrittlement requires the presence of both atomic ("diffusible") hydrogen and a Stress (mechanics), mechanical stress to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
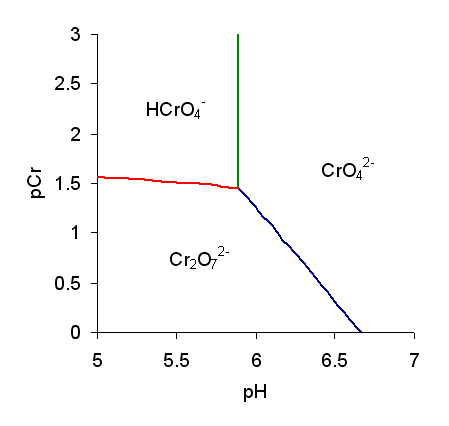
Chromic Acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide. The term "chromic acid" is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (and a valence of VI or 6). It is a strong and corrosive oxidizing agent and a moderate carcinogen. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, , in principle, resembles sulfuric acid, . It would ionize accordingly: : The p''K''a for the equilibrium is not well characterized. Reported values vary between about −0.8 to 1.6. The structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degreaser
Parts cleaning is a step in various industrial processes, either as preparation for surface finishing or to safeguard delicate components. One such process, electroplating, is particularly sensitive to part cleanliness, as even thin layers of oil can hinder coating adhesion. Cleaning methods encompass solvent cleaning, hot alkaline detergent cleaning, electro-cleaning, and acid etch. In industrial settings, the water-break test is a common practice to assess machinery cleanliness. This test involves thoroughly rinsing and vertically holding the surface. Hydrophobic contaminants, like oils, cause water to bead and break, leading to rapid drainage. In contrast, perfectly clean metal surfaces are hydrophilic and retain an unbroken sheet of water without beading or draining off. It is important to note that this test may not detect hydrophilic contaminants, but they can be displaced during the water-based electroplating process. Surfactants like soap can reduce the test's sensitivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Roughening
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |