|
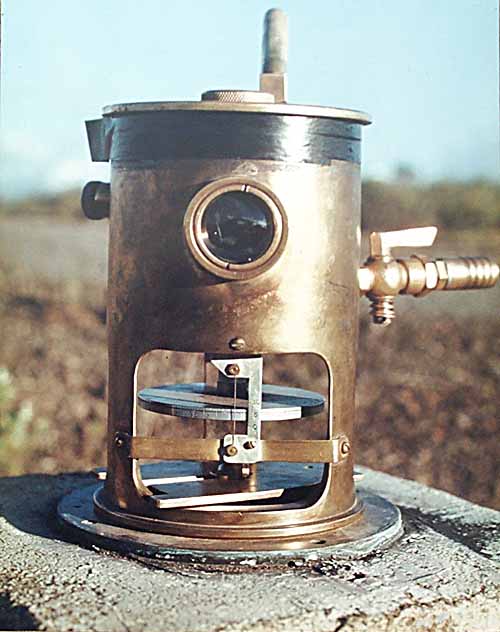
Tiltmeter
A tiltmeter is a sensitive inclinometer designed to measure very small changes from the vertical level, either on the ground or in structures. Tiltmeters are used extensively for monitoring volcanoes, the response of dams to filling, the small movements of potential landslides, the orientation and volume of hydraulic fractures, and the response of structures to various influences such as loading and foundation settlement. Tiltmeters may be purely mechanical or incorporate vibrating-wire or electrolytic sensors for electronic measurement. A sensitive instrument can detect changes of as little as one arc second. Tiltmeters have a long history, somewhat parallel to the history of the seismometer. The very first tiltmeter was a long-length stationary pendulum. These were used in the very first large concrete dams, and are still in use today, augmented with newer technology such as laser reflectors. Although they had been used for other applications such as volcano monitoring, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiltmeter On Mauna Loa
A tiltmeter is a sensitive inclinometer designed to measure very small changes from the vertical level, either on the ground or in structures. Tiltmeters are used extensively for monitoring volcanoes, the response of dams to filling, the small movements of potential landslides, the orientation and volume of hydraulic fractures, and the response of structures to various influences such as loading and foundation settlement. Tiltmeters may be purely mechanical or incorporate vibrating-wire or electrolytic sensors for electronic measurement. A sensitive instrument can detect changes of as little as one arc second. Tiltmeters have a long history, somewhat parallel to the history of the seismometer. The very first tiltmeter was a long-length stationary pendulum. These were used in the very first large concrete dams, and are still in use today, augmented with newer technology such as laser reflectors. Although they had been used for other applications such as volcano monitoring, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclinometer
An inclinometer or clinometer is an instrument used for measuring angles of slope, elevation, or depression of an object with respect to gravity's direction. It is also known as a ''tilt indicator'', ''tilt sensor'', ''tilt meter'', ''slope alert'', ''slope gauge'', ''gradient meter'', ''gradiometer'', ''level gauge'', ''level meter'', ''declinometer'', and ''pitch & roll indicator''. Clinometers measure both inclines and declines using three different units of measure: degrees, percentage points, and topos. The astrolabe is an example of an inclinometer that was used for celestial navigation and location of astronomical objects from ancient times to the Renaissance. A ''tilt sensor'' can measure the tilting in often two axes of a reference plane in two axes. In contrast, a full motion would use at least three axes and often additional sensors. One way to measure tilt angle with reference to the earth's ground plane, is to use an accelerometer. Typical applications can be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dam Safety System
Dam safety systems are used to monitor the state of dams, including external physical threats to the dams, and issuing emergency warnings at various degrees of automation. This includes the use of differential GPS and SAR remote sensing to monitor the risks imposed by landslides and subsidence. For large dams, seismographs are used to detect reservoir-induced seismicity that could threaten the stability of the dam. The output of these systems can provide warning to the local population ahead of a potential collapse. Particular applications Ukraine The monitoring and warning system safeguarding the Kiev Reservoir dam is complicated enough to include protection from a space object impact. Italy The dam monitoring system of Enel green Power in the Riolunato Dam controls all of the dam's important parameters. Optical and physical alignment systems are installed to control any movement of the land under and around the dam. The dam monitoring system checks the level of the water b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
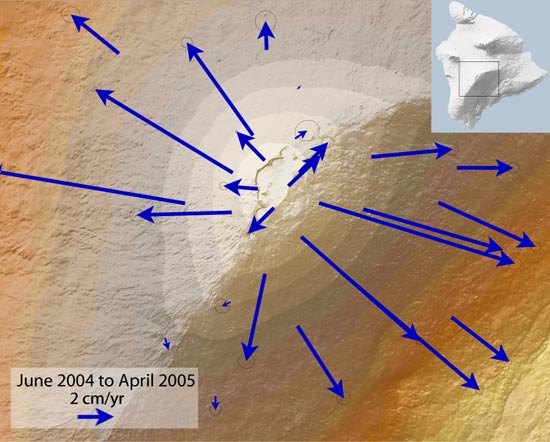
Deformation (volcanology)
In volcanology, deformation is any change in the shape of a volcano or the land surrounding it. This can be in the form of inflation, which is a response to pressurization, or deflation, which is a response to depressurization. Inflation is represented by swelling of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma accumulation, exsolution of volatiles, geothermal processes, heating, and tectonic compression. Deflation is represented by shrinking of the ground surface, a volcanic edifice, or a subsurface magma body. It can be caused by magma withdrawal (related to intrusion or eruption), volatile escape, thermal contraction, phase changes during crystallization, and tectonic extension. Deformation is a key indicator of pre-eruptive unrest at many active volcanoes. The term bradyseism is used in the volcanological literature to mean the vertical ground movements associated with the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area west of Naples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word '' vulcan''. Vulcan was the ancient Roman god of fire. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, especially active ones, to observe volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as ash or pumice), rock and lava samples. One major focus of enquiry is the prediction of eruptions; there is currently no accurate way to do this, but predicting eruptions, like predicting earthquakes, could save many lives. Modern volcanology Volcanologist examining tephra horizons in south-central Iceland. In 1841, the first volcanological observatory, the Vesuvius Observatory, was founded in the Kingdom of the Two Sicil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground noises and shaking such as caused by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a seismogram. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the Earth's internal structure. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential GPS
Differential Global Positioning Systems (DGPSs) supplement and enhance the positional data available from global navigation satellite systems (GNSSs). A DGPS for GPS can increase accuracy by about a thousandfold, from approximately to . DGPSs consist of networks of fixed position, ground-based reference stations. Each reference station calculates the difference between its highly accurate known position and its less accurate satellite-derived position. The stations broadcast this data locally—typically using ground-based transmitters of shorter range. Non-fixed (mobile) receivers use it to correct their position by the same amount, thereby improving their accuracy. The United States Coast Guard (USCG) and the Canadian Coast Guard (CCG) each run DGPSs in the United States and Canada on longwave radio frequencies between and near major waterways and harbors. The USCG's DGPS was named NDGPS (Nationwide DGPS) and was jointly administered by the Coast Guard and the U.S. Departme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology Instruments
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilt Test (geotechnical Engineering)
In geomechanics, a tilt test is a simple test to estimate the shear strength parameters of a discontinuity. Two pieces of rock containing a discontinuity are held in hand or mounted in test equipment with the discontinuity horizontal. The sample is slowly tilted until the top block moves. The angle with the horizontal at onset of movement is called the ''tilt-angle''. The size of the specimen is limited to 10–20 cm for hand-held tests, while machine-operated tilt test equipment may handle up to meter-sized samples. In the field, the angle can be determined most easily with an inclinometer as present in most geological or structural compasses. Tilt-angle The ''tilt-angle'' equals the material friction of the discontinuity wall plus the roughness i-angle (''tilt-angle'' = ''φwall material'' + ''i'') if no real cohesion is present (i.e. no cementing or gluing material between the two blocks), no infill material is present, the asperities do not break, and the walls of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Mechanics
Rock mechanics is a theoretical and applied science of the mechanical behavior of rock and rock masses; compared to geology, it is that branch of mechanics concerned with the response of rock and rock masses to the force fields of their physical environment. 

[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_IF_24935.jpg)