|
Thomas King Observatory
The Thomas King Observatory stands at the top of the Wellington Botanic Garden, Botanic Garden in Wellington, New Zealand, as part of the Carter Observatory. In the past it has housed research, preservation of heritage, education and promotion of astronomy to the public. Facilities In May 2001 refurbishment began of the 5-inch Grubb telescope housed in the Thomas King Observatory. This telescope was made in 1882 by Grubb in Dublin and over its 120 years it is in remarkably good condition. The Thomas King Observatory, was used until recently for public viewing of the sun during the day. The H-alpha, hydrogen-alpha filter used to view the sun through the Thomas King refractor has moved to one of the telescopes mounted to the side of the Thomas Cooke refractor, in the main observatory building. History In the 1910s, members of the Wellington Philosophical Society formed an Astronomical Section to promote the study of astronomy and to erect an observatory for star-gazing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-alpha
H-alpha (Hα) is a specific deep-red visible spectral line in the Balmer series with a wavelength of 656.28 nm in air and 656.46 nm in vacuum; it occurs when a hydrogen electron falls from its third to second lowest energy level. H-alpha light is the brightest hydrogen line in the visible spectral range. It is important to astronomers as it is emitted by many emission nebulae and can be used to observe features in the Sun's atmosphere, including solar prominences and the chromosphere. Balmer series According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons exist in quantized energy levels surrounding the atom's nucleus. These energy levels are described by the principal quantum number ''n'' = 1, 2, 3, ... . Electrons may only exist in these states, and may only transit between these states. The set of transitions from ''n'' ≥ 3 to ''n'' = 2 is called the Balmer series and its members are named sequentially by Greek letters: *''n'' = 3 to ''n'' = 2 is called Balmer-alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatories In New Zealand
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonians, Greeks, Indians, Egyptians, Chinese, Maya, and many ancient indigenous peoples of the Americas. In the past, astronomy included disciplines as diverse as astrometry, celestial navigation, observational astronomy, and the making of calendars. Nowadays, professi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
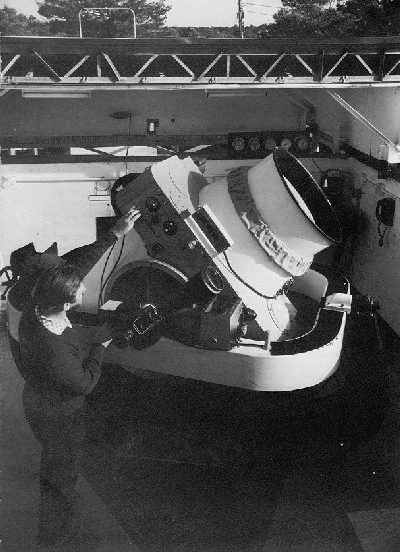
Boller And Chivens
Boller and Chivens was an American manufacturer of high-quality telescopes and spectrographs headquartered in South Pasadena, California. History Founded about 1946 by Harry Berthold Boller (1915-1997) and Clyde Cuthbertson Chivens (1915-2008). the company was acquired in 1965 by Perkin-Elmer. In the 1950s, Boller and Chivens collaborated with Perkin-Elmer to develop and manufacture the large-aperture Baker-Nunn satellite tracking camera for the United States Vanguard space satellite program. In culture A 41-cm (16-inch) Boller and Chivens Cassegrain reflector originally housed at the Harvard-Smithsonian Oak Ridge Observatory in Massachusetts is available for public use at the National Air and Space Museum's Public Observatory Project on the National Mall The National Mall is a landscaped park near the downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums of the Smithsonian Institution, art galleries, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gifford Observatory
The Gifford Observatory is an astronomical observation facility located in the suburb of Mount Victoria, Wellington, New Zealand. Operated by the Gifford Observatory Trust with the intent of making it available for use to Wellington school children, it is primarily used by secondary school students, and members of the Wellington Astronomical Society. History of the observatory The observatory was first established in 1912 by the efforts of Charles Gifford, a science teacher. The observatory was moved to the current site in 1926, on land that is now occupied in trust by Wellington College and Wellington East Girls' College. The observatory fell into disrepair in the late 1970s due to a momentary lack of time and enthusiasm from staff and students at the school. A trust was established in 1998 by a small group of interested teachers and amateur astronomers from the Wellington Astronomical Society, with the goal of restoring the observatory to a working state. On March 25, 2002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cooke (machinist)
Thomas Cooke (8 March 1807 – 19 October 1868) was a British scientific instrument maker based in York. He founded T. Cooke & Sons, the scientific instrument company. Life Thomas Cooke was born in Allerthorpe, near Pocklington, East Riding of Yorkshire, the son of James Cook (a shoemaker). His formal education consisted of two years at an elementary school (possibly the school of John Whitaker, also of Allerthorpe), but he continued learning after this and he taught himself navigation and astronomy with the intention of becoming a sailor. His mother dissuaded him from that career and he became a teacher. He made such a success of being an impromptu teacher to the farmers’ sons of the Pocklington district, that only a year later he was able to open a village school at Bielby. He continued to teach others by day and learn himself by night, and soon moved his school from Bielby to Skirpenbeck. At Skirpenbeck he met his future wife, who was one of his pupils, and five years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas King (astronomer)
Thomas King (1858 – 16 March 1916) was a New Zealand astronomer. Early life King was born in Glasgow, Scotland and came to Auckland with his parents as an infant. He was educated at Auckland Grammar School. He later received private tuition in Wellington. Carter Observatory Thomas King took over the charge of the Carter Observatory in 1887 from the Reverend Arthur Stock, vicar of St Peters (former astronomer in charge of the Wellington time-ball station on Lambton House Quay). King has an astronomical observatory facility named after him at Carter Observatory Space Place at Carter Observatory (or simply Space Place) is an observatory in Wellington, New Zealand, located at the top of the Wellington Botanic Garden. The site was originally home to the Wellington City Observatory (nicknamed "The Tin Sh ... in Wellington, New Zealand. Thomas King Observatory The Thomas King Observatory ( mi, Ataira Te Ao Nui) in Wellington, near the Carter Observatory, is now i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heritage New Zealand
Heritage New Zealand Pouhere Taonga (initially the National Historic Places Trust and then, from 1963 to 2014, the New Zealand Historic Places Trust) ( mi, Pouhere Taonga) is a Crown entity with a membership of around 20,000 people that advocates for the protection of ancestral sites and heritage buildings in New Zealand. It was set up through the Historic Places Act 1954 with a mission to "...promote the identification, protection, preservation and conservation of the historical and cultural heritage of New Zealand" and is an autonomous Crown entity. Its current enabling legislation is the Heritage New Zealand Pouhere Taonga Act 2014. History Charles Bathurst, 1st Viscount Bledisloe gifted the site where the Treaty of Waitangi was signed to the nation in 1932. The subsequent administration through the Waitangi Trust is sometimes seen as the beginning of formal heritage protection in New Zealand. Public discussion about heritage protection occurred in 1940 in conjunction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominion Observatory, Wellington
The Dominion Observatory is a historic observatory in the Botanic Gardens in Wellington, New Zealand. It was the second observatory in Wellington. It was built in 1907 and originally named the Hector Observatory after James Hector until 1925. It was built to replace the Colonial Observatory which was located in the Bolton Street Cemetery. The observatory was primarily used to maintain New Zealand Mean Time for the Time Service based on astronomical observations. It was designed by architect John Campbell in the Edwardian Baroque style. The observatory was vacant in 1993, and in 2003 it was refurbished by the Department of Conservation An environmental ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for the environment and/or natural resources. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of the Environment, ... to be used by private businesses. References External links Dominion Observatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, Maya, and many anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carter Observatory
Space Place at Carter Observatory (or simply Space Place) is an observatory in Wellington, New Zealand, located at the top of the Wellington Botanic Garden. The site was originally home to the Wellington City Observatory (nicknamed "The Tin Shed"), established in 1924. This was demolished and replaced by the Carter Observatory, which officially opened on 20 December 1941. Since renamed the Space Place, it is now managed by Museums Wellington, which is part of Experience Wellington, and is a public museum and planetarium with a focus on space and New Zealand astronomy. The Observatory houses a digital planetarium as well as an historic 9-inch Cooke refractor telescope, through which evening visitors can observe a variety of Solar System and deep-sky objects. History The original name, Carter Observatory, commemorates Charles Carter, who gifted his estate to what later became the Royal Society of New Zealand for the purposes of establishing an astronomical observatory in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


