|
Thermal Emittance
Thermal emittance or thermal emissivity (\varepsilon) is the ratio of the radiant emittance of heat of a specific object or surface to that of a standard black body. Emissivity and emittivity are both dimensionless quantities given in the range of 0 to 1, representing the comparative/relative emittance with respect to a blackbody operating in similar conditions, but emissivity refers to a material property (of a homogeneous material), while emittivity refers to specific samples or objects. For building products, thermal emittance measurements are taken for wavelengths in the infrared. Determining the thermal emittance and solar reflectance of building materials, especially roofing materials, can be very useful for reducing heating and cooling energy costs in buildings. Combined index Solar Reflectance Index (SRI) is often used to determine the overall ability to reflect solar heat and release thermal heat. A roofing surface with high solar reflectance and high thermal emittance wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiant Emittance
Radiant may refer to: Computers, software, and video games * GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games * Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for ''The Elder Scrolls'' games * Radiant, the team that opposes ''Dire'' on ''Dota 2'' Music * ''Radiant'' (Atlantic Starr album), 1981 * ''Radiant'' (Iris album), 2014 Ships * HMS ''Radiant'' (1916), a destroyer of the British Royal Navy launched in 1916 and sold in 1920 * USS ''Radiant'', the name of more than one United States Navy ship * ''Radiant'' (yacht), a 2009 Lürssen built yacht Others * Radiant heat, or thermal radiation, electromagnetic radiation emitted from the surface of an object which is due to the object's temperature * Radiant heating, a technology for heating indoor and outdoor areas * Radiant (Kitchen manufacturer), an Australian manufacturer of products for kitchens and laundries * Radiant (meteor shower), the apparent origin point of meteors in a meteor shower * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, atomic, or molecular particles, or small surface irregularities, as distinct from the macroscopic modes of energy transfer, which are thermodynamic work and transfer of matter. For a closed system (transfer of matter excluded), the heat involved in a process is the difference in internal energy between the final and initial states of a system, after subtracting the work done in the process. For a closed system, this is the formulation of the first law of thermodynamics. Calorimetry is measurement of quantity of energy transferred as heat by its effect on the states of interacting bodies, for example, by the amount of ice melted or by change in temperature of a body. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement for he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium with its environment is called ''black-body radiation''. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. In contrast, a white body is one with a "rough surface that reflects all incident rays completely and uniformly in all directions." A black body in thermal equilibrium (that is, at a constant temperature) emits electromagnetic black-body radiation. The radiation is emitted according to Planck's law, meaning that it has a spectrum that is determined by the temperature alone (see figure at right), not by the body's shape or composition. An ideal black body in thermal equilibrium has two main properties: #It is an ideal emitter: at every frequency, it emits as much or more thermal radiative energy as any other body at the same temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Quantities
Dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one, are quantities implicitly defined in a manner that prevents their aggregation into units of measurement. ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. Typically expressed as ratios that align with another system, these quantities do not necessitate explicitly defined units. For instance, alcohol by volume (ABV) represents a volumetric ratio; its value remains independent of the specific units of volume used, such as in milliliters per milliliter (mL/mL). The number one is recognized as a dimensionless base quantity. Radians serve as dimensionless units for angular measurements, derived from the universal ratio of 2π times the radius of a circle being equal to its circumference. Dimensionless quantities play a crucial role serving as parameters in differential equations in various technical disciplines. In calculus, concepts like the unitless ratios in limits or derivatives often involve dimensionless quantities. In differential geometry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emissivity
The emissivity of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation. Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation that most commonly includes both visible radiation (light) and infrared radiation, which is not visible to human eyes. A portion of the thermal radiation from very hot objects (see photograph) is easily visible to the eye. The emissivity of a surface depends on its chemical composition and geometrical structure. Quantitatively, it is the ratio of the thermal radiation from a surface to the radiation from an black body, ideal black surface at the same temperature as given by the Stefan–Boltzmann law. (A comparison with Planck's law is used if one is concerned with particular wavelengths of thermal radiation.) The ratio varies from 0 to 1. The surface of a perfect black body (with an emissivity of 1) emits thermal radiation at the rate of approximately 448 watts per square metre (W/m) at a room temperature of . Objects have emi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Property
A material property is an intensive property of a material, i.e., a physical property or chemical property that does not depend on the amount of the material. These quantitative properties may be used as a metric by which the benefits of one material versus another can be compared, thereby aiding in materials selection. A property having a fixed value for a given material or substance is called material constant or constant of matter. (Material constants should not be confused with physical constants, that have a universal character.) A material property may also be a function of one or more independent variables, such as temperature. Materials properties often vary to some degree according to the direction in the material in which they are measured, a condition referred to as anisotropy. Materials properties that relate to different physical phenomena often behave linearly (or approximately so) in a given operating range . Modeling them as linear functions can significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Reflectance
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roofing Material
Domestic roof construction is the framing (construction), framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different List of roof shapes, shapes, and are covered with a variety of List of commercially available roofing material, materials. Overview Modern timber roofs are mostly framed with pairs of common rafters or prefabricated wooden trusses fastened together with truss connector plates. Timber framed and historic buildings may be framed with principal rafters or timber roof trusses. Roofs are also designated as ''warm'' or ''cold roof'' depending on the way they are designed and built with regard to thermal building insulation and Ventilation (architecture), ventilation. The steepness or roof pitch of a sloped roof is determined primarily by the roof covering material and aesthetic design. Flat roofs actually slope up to approximately ten degrees to shed water. Flat r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Accounting
Energy accounting is a system used to measure, analyze and report the energy consumption of different activities on a regular basis. This is done to improve energy efficiency, and to monitor the environment impact of energy consumption. Energy management Energy accounting is a system used in energy management systems to measure and analyze energy consumption to improve energy efficiency within an organization. Organisations such as Intel corporation use these systems to track energy usage. Various energy transformations are possible. An energy balance can be used to track energy through a system. This becomes a useful tool for determining resource use and environmental impacts. How much energy is needed at each point in a system is measured, as well as the form of that energy. An accounting system keeps track of energy in, energy out, and non-useful energy versus work done, and transformations within a system. Sometimes, non-useful work is what is often responsible for environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
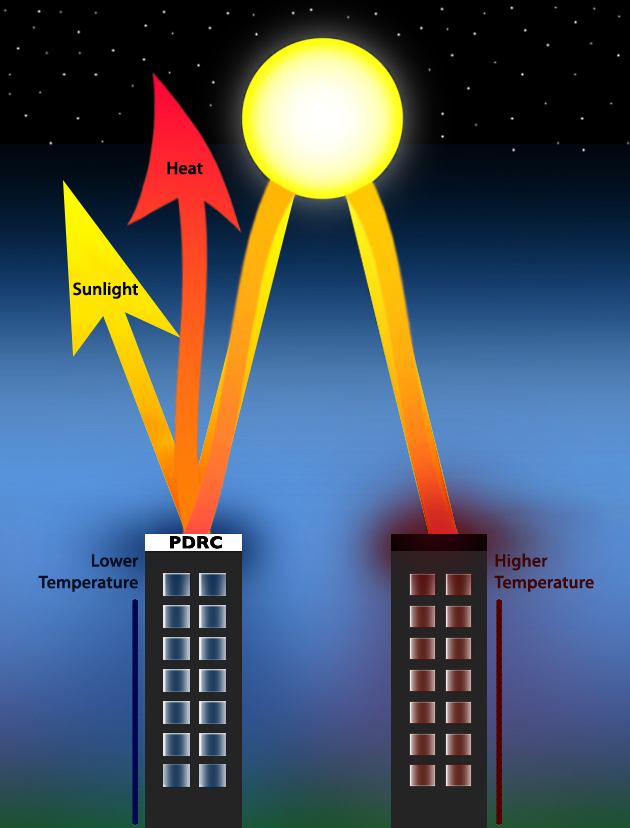
Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling
Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC) (also passive radiative cooling, daytime passive radiative cooling, radiative sky cooling, photonic radiative cooling, and terrestrial radiative cooling) is the use of unpowered, reflective/Emissivity, thermally-emissive surfaces to lower the temperature of a building or other object. It has been proposed as a method of reducing temperature increases caused by greenhouse gases by reducing the energy needed for air conditioning, lowering the Urban heat island, urban heat island effect, and lowering human body temperatures. PDRCs can aid systems that are more efficient at lower temperatures, such as photovoltaic systems, dew collection devices, and thermoelectric generators. Some estimates propose that dedicating 1–2% of the Earth's surface area to PDRC would stabilize surface temperatures. Regional variations provide different cooling potentials with Desert climate, desert and temperate climates benefiting more than tropical climates, att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |