|
Tezcatlipoca
Tezcatlipoca ( ) or Tezcatl Ipoca was a central deity in Aztec religion. He is associated with a variety of concepts, including the night sky, hurricanes, obsidian, and conflict. He was considered one of the four sons of Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl, the primordial dual deity. His main festival was Toxcatl, which, like most religious festivals of Aztec culture, involved human sacrifice. Tezcatlipoca's nagual, his animal counterpart, was the jaguar. In the form of a jaguar he became the deity Tepeyollotl ("Mountainheart"). In one of the two main Aztec calendars (the Tonalpohualli), Tezcatlipoca ruled the trecena ''1 Ocelotl'' ("1 Jaguar"); he was also patron of the days with the name ''Acatl'' ("reed"). A strong connection with the calendar as a whole is suggested by his depiction in texts such as the Codex Borgia and Codex Fejéváry-Mayer, where Tezcatlipoca is surrounded by day signs, implying a sort of mastery over them. A talisman related to Tezcatlipoca was a disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tezcatlipocas
In Aztec mythology, Creator-Brothers gods are the only four Tezcatlipocas, the children of the creator couple Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl "Lord and Lady of Duality", "Lord and Lady of the Near and the Nigh", "Father and Mother of the Gods", "Father and Mother of us all", who received the gift of the ability to create other living beings without childbearing. They reside atop a mythical thirteenth heaven Ilhuicatl- Omeyocan "the place of duality". Each of the four sons takes a turn as Sun, these suns are the sun of earth, the sun of air, the sun of fire, the sun of water ( Tlaloc, rain god replaces Xipe-Totec). Each world is destroyed. The present era, the Fifth Sun is ushered in when a lowly god, Nanahuatzin sacrifices himself in fire and becomes Tonatiuh, the Fifth Sun. In his new position of power, he refuses to go into motion until the gods make sacrifice to him. In an elaborate ceremony, Quetzalcoatl cuts the hearts out of each of the gods and offers it to Tonatiuh (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
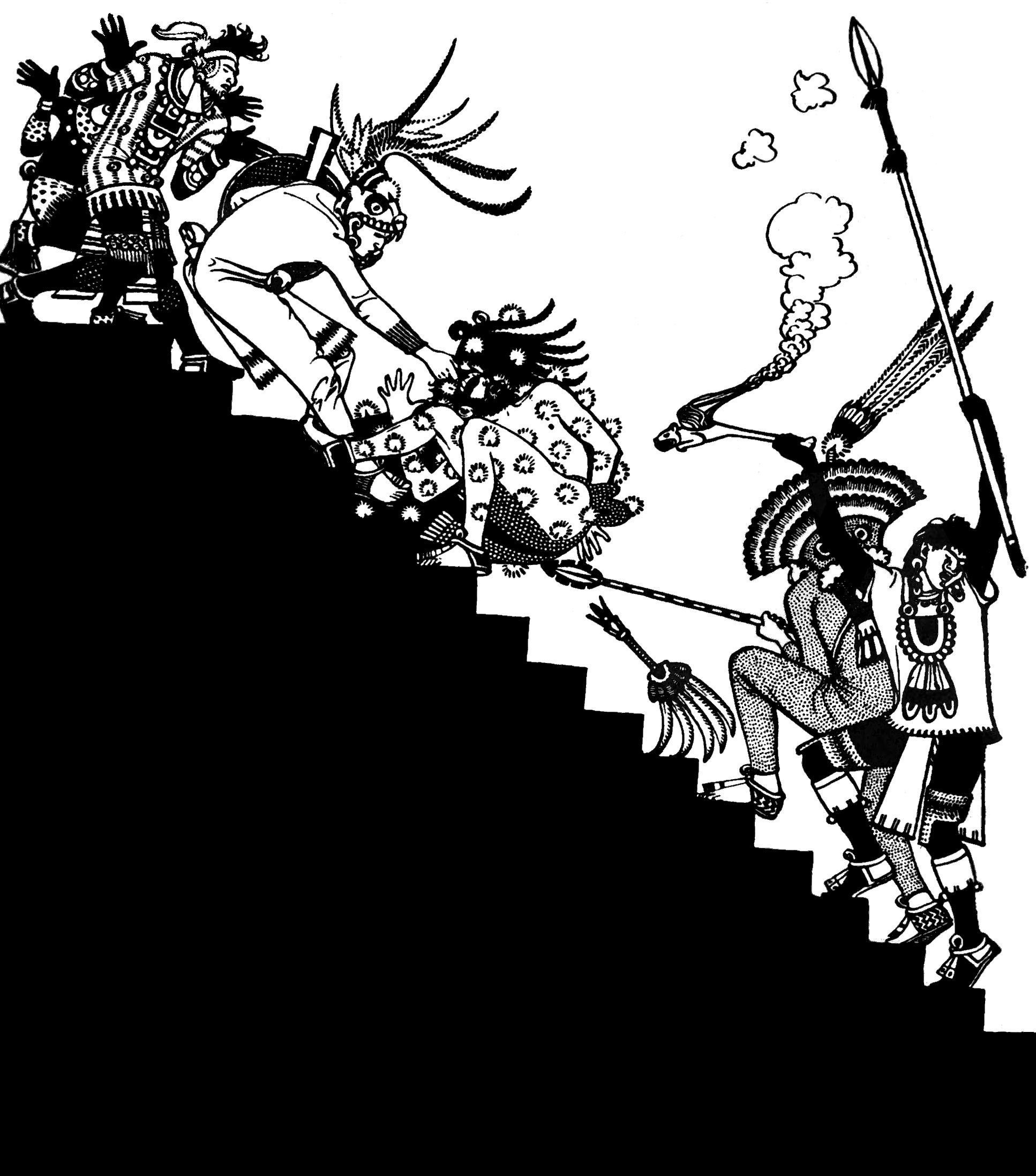
Human Sacrifice In Aztec Culture
Human sacrifice was a common practice in many parts of Mesoamerica. The rite was not new to the Aztecs when they arrived at the Valley of Mexico, nor was it something unique to pre-Columbian Mexico. Other Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Purépecha culture, Purépechas and Toltecs, and the Maya peoples, Maya performed sacrifices as well, and from archaeological evidence, it probably existed since the time of the Olmecs (1200–400 BC), and perhaps even throughout the early farming cultures of the region. However, the extent of human sacrifice is unknown among several Mesoamerican civilizations. What distinguished Aztec practice from Human sacrifice in Maya culture, Maya human sacrifice was the way in which it was embedded in everyday life. In 1519, explorers such as Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. Bernal Díaz del Castillo, who participated in the Cortés expediti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Religion
The Aztec religion is a polytheistic and monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of '' teotl'' was construed as the supreme god Ometeotl, as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies. The most important deities were worshiped by priests in Tenochtitlan, particularly Tlaloc and the god of the Mexica, Huitzilopochtli, whose shrines were located on Templo Mayor. Their priests would receive special dispensation from the empire. When other states were conquered the empire would often incorporate practices from its new territories into the mainstream religion. In common with many other indigenous Mesoamerican civilizations, the Aztecs put great ritual emphasis on calendrics, and scheduled festivals, government ceremonies, and even war around key tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xipe-Totec
In Aztec mythology, Xipe Totec (; ) or XipetotecRobelo 1905, p. 768. ("Our Lord the Flayed One") was a life-death-rebirth deity, god of agriculture, vegetation, the east, spring, goldsmiths, silversmiths, liberation, deadly warfare, the seasons, and the earth. The female equivalent of Xipe Totec was the goddess Xilonen- Chicomecoatl. Xipe Totec connected agricultural renewal with warfare. He flayed himself to give food to humanity, symbolic of the way maize seeds lose their outer layer before germination and of snakes shedding their skin. He is often depicted as being red beneath the flayed skin he wears, likely referencing his own flayed nature. Xipe Totec was believed by the Aztecs to be the god that invented war. His insignia included the pointed cap and rattle staff, which was the war attire for the Mexica emperor. He had a temple called Yopico within the Great Temple of Tenochtitlan.Miller & Taube 1993, 2003, p.188. Xipe Totec is associated with pimples, inflammation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco (altepetl), Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Borgia
The Codex Borgia ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Borg.mess.1), also known as ''Codex Borgianus'', ''Manuscrit de Veletri'' and ''Codex Yohualli Ehecatl'', is a pre-Columbian Middle American pictorial manuscript from Central Mexico featuring calendrical and ritual content, dating from the 16th century. It is named after the 18th century Italian cardinal, Stefano Borgia, who owned it before it was acquired by the Vatican Library after the cardinal's death in 1804. The Codex Borgia is a member of, and gives its name to, the Borgia Group of manuscripts. It is considered to be among the most important sources for the study of Central Mexican gods, ritual, divination, calendar, religion and iconography. It is one of only a handful of pre-Columbian Mexican codices that were not destroyed during the conquest in the 16th century; it was perhaps written near Cholula, Tlaxcala, Huejotzingo or the Mixtec region of Puebla. Its ethnic affiliation is unclear, and could either have been produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirteen Heavens
The Nahua people such as the Aztecs, Chichimecs and the Toltecs believed that the heavens were constructed and separated into 13 levels, usually called Topan or simply each one Ilhuicatl iohhui, Ilhuicatl iohtlatoquiliz. Each level had from one to many Lords (gods) living in and ruling them. Aztec mythology In Aztec mythology, the Thirteen Heavens were formed out of Cipactli's head when the gods made creation out of its body, whereas Tlaltícpac, the earth, was made from its center and the nine levels of the underworld ( Mictlan) from its tail. The most important of these heavens was Omeyocan (Place of Two), where Ometeotl - the dual Lord/Lady, creator of the Dual-Genesis who, as male, takes the name Ometecuhtli (Two Lord), and as female is named Omecihuatl (Two Lady) —resided. File:Codex Borgia page 51.jpg, Tlahuiztlampa, East hemisphere with its respective trees, temples, patron deities and divinatory signs. File:Codex Borgia page 52.jpg, Mictlampa, North hemisp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Calendar
The Aztec or Mexica calendar is the calendar, calendrical system used by the Aztecs as well as other Pre-Columbian era, Pre-Columbian indigenous peoples of Mexico, peoples of central Mexico. It is one of the Mesoamerican calendars, sharing the basic structure of calendars from throughout the region. The Aztec sun stone, often erroneously called the calendar stone, is on display at the National Museum of Anthropology (Mexico), National Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City. The actual Aztec calendar consists of a 365-day calendar cycle called (year count), and a 260-day ritual cycle called (day count). These two cycles together form a 52-year "century", sometimes called the "Calendar Round, calendar round". The is considered to be the agricultural calendar, since it is based on the sun, and the is considered to be the sacred calendar. Tōnalpōhualli The ("day count") consists of a cycle of 260 days, each day signified by a combination of a number from 1 to 13, and one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagual
In Mesoamerican and Toltec spiritual traditions, a Nagual (from the Nahuatl word nāhualli) refers to a human being who can access spiritual power through transformation or deep connection with their tonal counterpart. This ability is not merely about shapeshifting but also about guiding spiritual development and fostering personal transformation by bridging the physical and metaphysical realms. Nagualism involves the belief that each person possesses a dual aspect: the tonal, representing their everyday awareness and ego, and the nagual, representing their deeper, limitless self. The Nagual serves as a guide, helping individuals access hidden potential and spiritual insight by harmonizing these two aspects. In Mesoamerican folk religion, a nagual (pronounced a'wal or nahual (both from the Nahuatl word ''nāhualli'' ) is a human being who has the power to shapeshift into their tonal animal counterpart. Nagualism is tied to the belief one can access power and spiritual insigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōmeteōtl
() ("Two-God") is a name used to refer to the pair of Aztec deities and , also known as and . translates as "two" or "dual" in Nahuatl and translates as "Divinity". Ometeotl was one as the first divinity, and Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl when the being became two to be able to reproduce all creation. Definition Multiple Nahuatl sources, notably the '' Florentine Codex'', name the highest level of heaven or "place of duality" ( specifically terms it "in in " or "the place of duality, above the nine-tiered heavens)." In the , Franciscan priest translated a Nahuatl source reporting that in this layer of heaven there existed "a god named , which means two-gods, and one of them was a goddess." The '' History of the Mexicans as Told by Their Paintings'' () names the inhabitants of the uppermost heaven and (Lord and Lady of Abundance). concurs that these are epithets of "in in ", giving as another name of "in " ("the mansion of the Lord of Abundance"). There is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicomecōātl
In Aztec mythology, Chicōmecōātl "Seven Serpent", was the Aztec goddess of agriculture during the Middle Culture period. She is sometimes called "goddess of nourishment", a goddess of plenty and the female aspect of maize. More generally, Chicōmecōātl can be described as a deity of food, drink, and human livelihood. She is regarded as the female counterpart of the maize god ''Centeōtl'', their symbol being an ear of corn. She is occasionally called ''Xīlōnen'', (meaning doll made of corn), who was married also to ''Tezcatlipoca''. Significance of Name Chicomecōātl's name, "Seven Serpent", is thought to be a reference to the duality of the deity. While she symbolizes the gathering of maize and agricultural prosperity, she also is thought to be harmful to the Aztecs, as she was thought to be of blame during years of poor harvest. Appearance & Depiction Her appearance is mostly represented with red ochre on the face, paper headdress on top, water-flowers patterned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium. It is commonly found within the margins of rhyolite, rhyolitic lava flows known as obsidian flows. These flows have a high content of silicon dioxide, silica, giving them a high viscosity. The high viscosity inhibits the atomic diffusion, diffusion of atoms through the lava, which inhibits the first step (nucleation) in the formation of mineral crystals. Together with rapid cooling, this results in a natural glass forming from the lava. Obsidian is hard, Brittleness, brittle, and amorphous; it therefore Fracture (mineralogy)#Conchoidal fracture, fractures with sharp edges. In the past, it was used to manufacture cutting and piercing tools, and it has been used experimentally as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |