|
Tetrathiafulvene
Tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . It is the parent of many tetrathiafulvenes. Studies on these heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics, although no practical applications of TTF emerged. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene () by replacement of four CH groups with sulfur atoms. Over 10,000 scientific publications discuss TTF and its derivatives. Preparation The high level of interest in TTFs spawned many syntheses of TTF and its analogues. Most preparations entail the coupling of cyclic building blocks such as 1,3-dithiole-2-thion or the related 1,3-dithiole-2-ones. For TTF itself, the synthesis begins with the cyclic trithiocarbonate ( 1,3-dithiole-2-thione), which is ''S''-methylated and then reduced to give (1,3-dithiole-2-yl methyl thioether), which is treated as follows: Protonolysis of a thioether: : Followed by deprotonation of the dithiolium cation with triethylamine: : Redox proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TCNQ
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an orange crystalline solid. This cyanocarbon, a relative of para-quinone, is an electron acceptor that is used to prepare charge transfer salts, which are of interest in molecular electronics. Preparation and structure TCNQ is prepared by the condensation of 1,4-cyclohexanedione with malononitrile, followed by dehydrogenation of the resulting diene with bromine: : : The molecule is planar, with D2h symmetry. Reactions Like tetracyanoethylene (TCNE), TCNQ is easily reduced to give a blue-coloured radical anion. The reduction potential is about −0.3 V relative to the ferrocene/ ferrocenium couple. This property is exploited in the development of charge-transfer salts. TCNQ also forms complexes with electron-rich metal complexes. Charge transfer salts TCNQ achieved great attention because it forms charge-transfer salts with high electrical conductivity. These discoveries were influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye ( , ; symbol: D) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation. The dipole itself is a vector whose direction coincides with the position vector of the positive charge with respect to the negative charge: : p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb-centimetres.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. : 1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
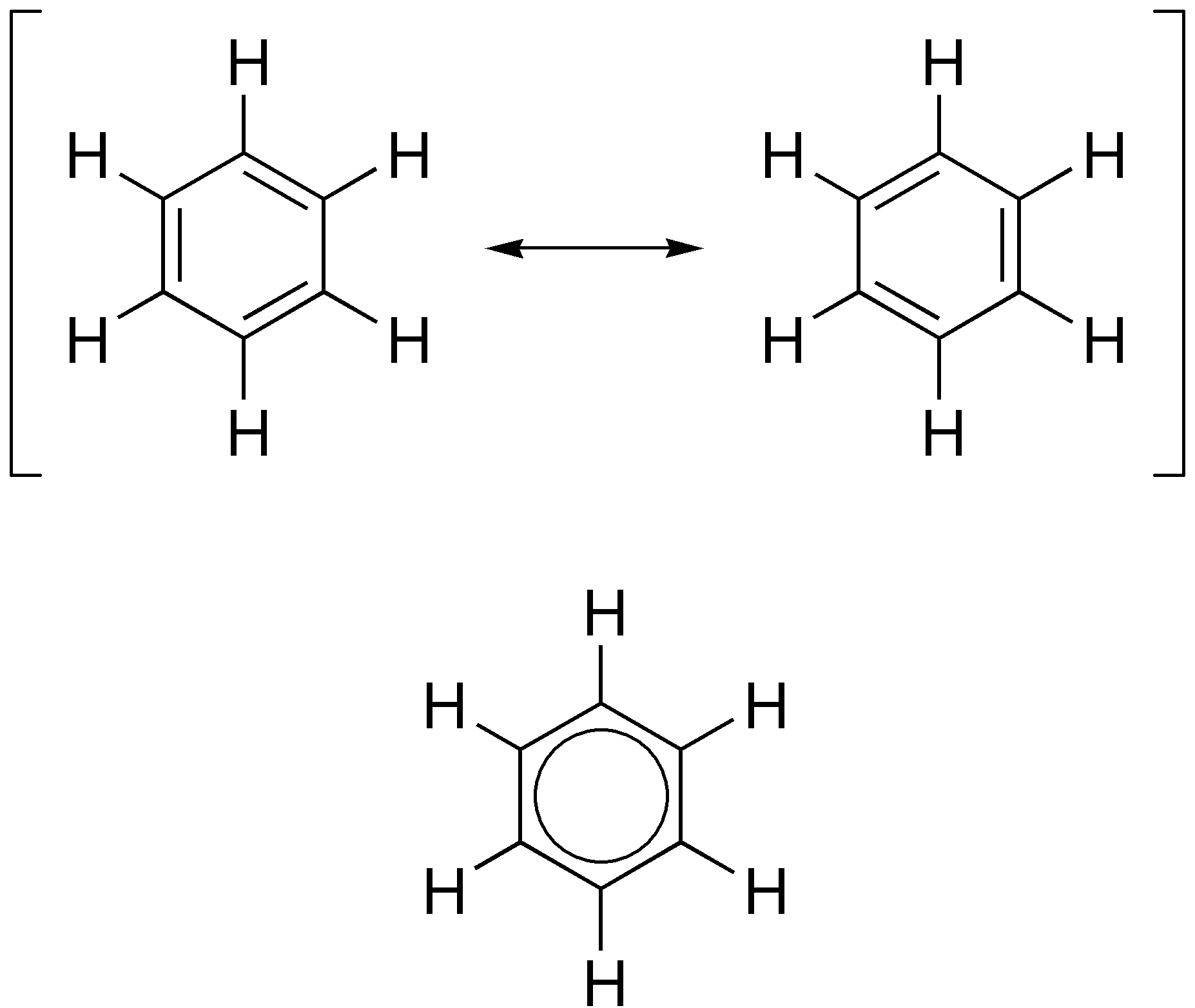
Aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfaction, olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of Resonance (chemistry), resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-covalent bond, bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Friedrich August Kekulé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Hybridisation
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds, the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver(I) Chloride
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Silver, AgChlorine, Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its Photosensitivity, sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts to silver (and chlorine), which is signaled by grey to black or purplish coloration in some samples. AgCl occurs naturally as the mineral chlorargyrite. It is produced by a salt metathesis reaction, metathesis reaction for use in photography and in pH meters as silver chloride electrode, electrodes. Preparation Silver chloride is unusual in that, unlike most chloride salts, it has very low solubility. It is easily synthesized by Salt metathesis reaction, metathesis: combining an aqueous solution of silver nitrate (which is soluble) with a soluble chloride salt, such as sodium chloride (which is used industrially as a method of producing AgCl), or cobalt(II) chloride. The silver chloride that forms will pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt (unit)
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, s, and A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac = \text\text^2\text^. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, s, and A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac = \text\text^2\text^. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronically conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in Electroless nickel-phosphorus plating, electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic chemical species, species in a Solution (chemistry), solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical Voltage, potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the aforementioned electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Cation
Radical cations are denoted M^. Salts of these species have been isolated in the cases of dibenzocyclooctatetraene, various tertiary amines, and some polymethylated derivatives of azulene. Radical cations, like radical anions, have one unpaired electron, i.e. they are paramagnetic. Mass spectrometry Radical cations appear prominently in mass spectrometry. When a gas-phase molecule is subjected to electron ionization one electron is abstracted by an electron in the electron beam to create a radical cation M+.. This species represents the molecular ion or parent ion. A typical mass spectrum shows multiple signals because the molecular ion fragments into a complex mixture of ions and uncharged radical species. For example, the methanol radical cation fragments into a methenium cation and a hydroxyl radical. In naphthalene the unfragmented radical cation is by far the most prominent peak in the mass spectrum. Secondary species are generated from proton gain (M+1) and proton loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulombic
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that calculates the amount of force between two electrically charged particles at rest. This electric force is conventionally called the ''electrostatic force'' or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism and maybe even its starting point, as it allowed meaningful discussions of the amount of electric charge in a particle. The law states that the magnitude, or absolute value, of the attractive or repulsive electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb discovered that bodies with like electrical charges repel: Coulomb also showed that oppositely charged bodies attract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |