|
Teng (state)
Teng (; 1046–414 BC) was a minor Chinese Ancient Chinese states, vassal state that existed during the Spring and Autumn period and the Warring States period, and was located in the south of modern-day Shandong province. Its territory is now the county-level city of Tengzhou. Teng's ruling family was the Ji (Zhou dynasty ancestral surname), Ji family, with the founder, Shu Xiu of Cuo (錯叔繡), being the 14th brother of King Wu of Zhou. It was conquered and annexed by the Yue (state), Yue state during the reign of Goujian Teng was a vassal of the Lu (state), Lu state, and is famed as the birthplace of the Chinese philosopher Mozi and architect Lu Ban. The name of the state survives in both the city of Tengzhou and the Chinese clan name of Teng (surname), Teng (). It was conquered by King Zhugou (朱勾) of the Yue state. Then its nobility re-established the country. Finally it was annihilated by Yan, King of Song, King Kang of Song in 297 BC. References History of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=西周, p=Xīzhōu; 771 BC) was a period of Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended in 771 BC when Quanrong pastoralists sacked the Zhou capital at Haojing and killed King You of Zhou. The "Western" label for the period refers to the location of the Zhou royal capitals, which were clustered in the Wei River valley near present-day Xi'an. The early Zhou state was ascendant for about 75 years; thereafter, it gradually lost power. The former lands of the Shang were divided into Ancient Chinese states, hereditary fiefs that became increasingly independent of the Zhou king over time. The Zhou court was driven out of the Wei River valley in 771 BC: this marked the beginning of the Eastern Zhou period, wherein political power was wielded in actuality by the king's nominal vassals. Sources The Western Zhou are known from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wu Of Zhou
King Wu of Zhou (; died ), personal name Ji Fa, was the founding king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty. The chronology of his reign is disputed but is generally thought to have begun around 1046 BCE and ended with his death three years later. King Wu was the second son of Ji Chang (posthumously King Wen) and Tai Si. In most accounts, his older brother Bo Yikao was said to have predeceased his father, typically at the hands of King Zhou of Shang, the last king of the Shang dynasty; in the '' Book of Rites'', however, it is assumed that his inheritance represented an older tradition among the Zhou of passing over the eldest son. (Fa's grandfather Jili had likewise inherited Zhou despite two older brothers.) Upon his succession, Fa worked with his father-in-law Jiang Ziya to accomplish an unfinished task: overthrowing the Shang dynasty. During the ninth year of his reign, Fa marched down the Yellow River to the Mengjin ford and met with more than 800 dukes. He constructed an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
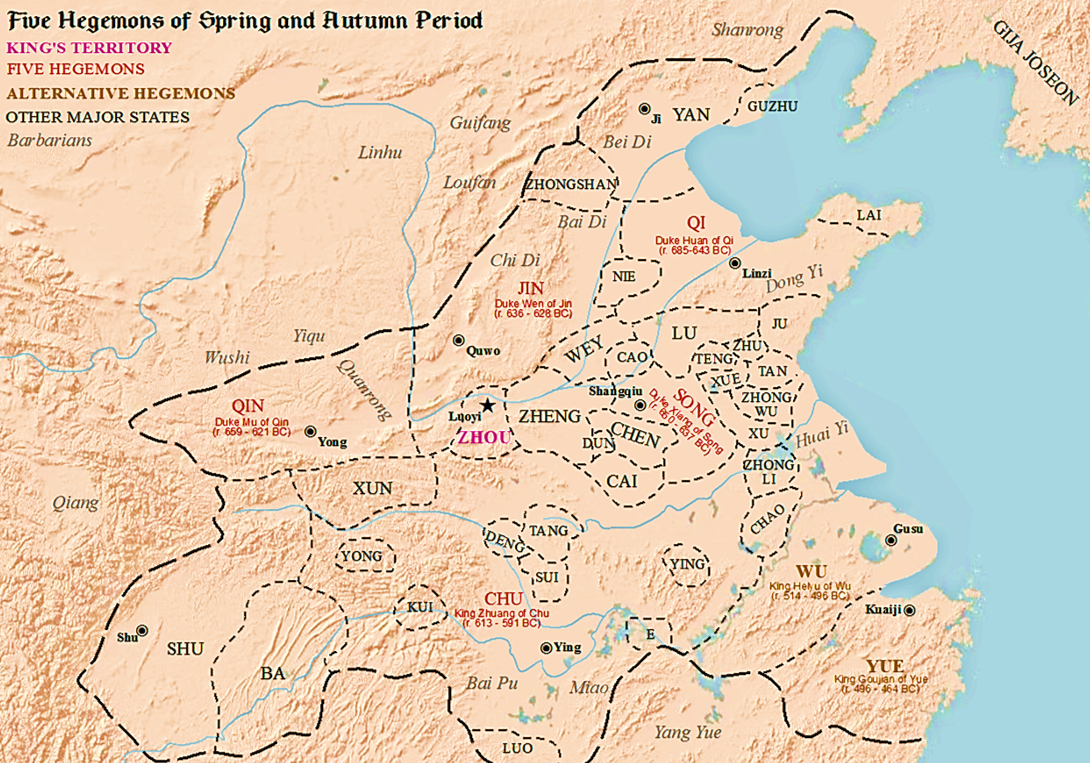
States Of The Spring And Autumn Period
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * '' State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Shandong
Shandong is a coastal province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu was the birthplace of Confucius, and later became the center of Confucianism. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern north–south and east–west trading routes has helped establish it as an economic center. After a period of political instability and economic hardship beginning in the late 19th century, Shandong has experienced rapid growth in recent decades. Home to over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yan, King Of Song
Yan, King of Song (, died 286 BC), also known as King Kang of Song (宋康王) or King Xian of Song (宋獻王), was the last ruler of Song. He ruled the state between 328 BC until his death in 286 BC. Yan was a descendant of Duke Dai, the 11th ruler of Song. He was also a younger brother of Lord Ticheng. Just like his elder brother, Yan was a usurper too. In 328 BC, he killed Lord Ticheng and seized the throne. Yan was ambitious ruler, during his reign, Song had succeeded in beating troops from Chu, Wei and Qi and annexing Teng. According to ''Mencius'', though Song was a small state, he was setting about to practise the " true royal government" (王政).''Mencius'', Teng Wen Gong II: "Sung is a small State. Its ruler is now setting about to practise the true royal government (宋,小國也。今將行王政,齊楚惡而伐之)" However, in ''Records of the Grand Historian'' and many other history books, he was described as a tyrant and oppressor. In 318 BC, Yan d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teng (surname)
Teng () is a Chinese surname derived from State of Teng (Imperial clan descendants) in the Western Zhou dynasty.The Oxford Dictionary of Family Names in Britain and Ireland It is the 73rd name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem.K. S. Tom. 989(1989). Echoes from Old China: Life, Legends and Lore of the Middle Kingdom. University of Hawaii Press. . It is T'eng in Wade–Giles, ''Tàhng'' in Cantonese and is usually Romanized as "Tang" in Hong Kong. It is ''Têng'' in Hokkien and Teochew. It is "ddàng"in Wenzhou. "Teng" can also be used as an alternate spelling of the Chinese surname Deng (鄧/邓, ''Dèng'') used especially in Taiwan based on the Wade-Giles transliteration of Mandarin Chinese. This spelling is used in many English language sources on China written before the widespread adoption of the pinyin transliteration system in the 1980s. For example, Deng Xiaoping Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu Ban
Lu Ban (–444BC). was a Chinese architect or master carpenter, structural engineer, and inventor, during the Zhou Dynasty. He is revered as the Chinese Deity (Patron) of builders and contractors. Life Lu Ban was born in the state of Lu; a few sources claim he was born further to the west, in Dunhuang, to a family of carpenters or artisans during the Spring and Autumn period of the Zhou dynasty. His original name was He was also referred to as or Pan. He was supposed to have been an indifferent pupil until his love of learning was kindled by the scholar Zi Xia. He later learned woodworking from Bao Laodong. The great demand for his work supposedly compelled him to invent or improve several carpenter's tools—the saw, the square, the planer, the drill, the shovel, and an ink marking tool—to complete his many projects more quickly. His wife was also credited with inventing the umbrella in order to permit him to work in inclement weather. Inventions According to tradition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozi
Mozi, personal name Mo Di, was a Chinese philosopher, logician, and founder of the Mohist school of thought, making him one of the most important figures of the Warring States period (221 BCE). Alongside Confucianism, Mohism became the most prominent, organized schools of the Hundred Schools of Thought throughout the period. The Mozi (book), ''Mozi'' is an anthology of writings traditionally attributed to Mozi and to his followers. Born in what is now Tengzhou, Shandong, Mozi and his followers argued strongly against both Confucianism and Taoism, with a philosophy emphasizing universal love, social order, the will of Tian, Heaven, sharing, and honoring the worthy. Mohism was actively developed and practiced across Warring States–era China, but fell out of favor following the establishment of the Qin dynasty in 221 BCE. While tradition assumes the destruction of many Mohist texts in 213 BCE as part of Emperor Qin Shi Huang's burning of books and burying of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu (state)
Lu (; 249 BC) was a vassal Ancient Chinese states, state during the Zhou dynasty of History of China#Ancient China, ancient China located around modern Shandong. Founded in the 11th century BC, its rulers were from a cadet branch of the Jī, House of Ji () that ruled the Zhou dynasty. The first duke was Boqin, a son of the Duke of Zhou, who was brother of King Wu of Zhou and regent to King Cheng of Zhou. Lu was the home state of Confucius as well as Mozi, and, as such, has an outsized cultural influence among the states of the Eastern Zhou and in history. The ''Annals of Spring and Autumn'', for instance, was written with the Lu rulers' years as their basis. Another great work of Chinese history, the ''Zuo Zhuan'' or ''Commentary of Zuo'', was traditionally considered to have been written in Lu by Zuo Qiuming. Geography The state's capital was in Qufu and its territory mainly covered the central and southwest regions of what is now Shandong Province. It was borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goujian
Goujian (; r. 496–465 BC) was a king of the Yue state. He succeeded his father, Yunchang (允常), to the Yue throne. Goujian's reign coincided with arguably the last major conflict of the Spring and Autumn period: the struggle between Wu and Yue states, wherein he eventually led his state to victory, annexing Wu. As such, Goujian is sometimes considered the last of the Five Hegemons of the Spring and Autumn period. War between Wu and Yue The war between Wu and Yue comprised several separate phases. It began when a Yue princess, who was married to one of the princes of the neighboring state of Wu, left her husband and fled back to the State of Yue. This became the spark for the war to come. Also, as Yunchang developed Yue's strength, he came into conflict with King Helü of Wu, causing a feud between the two states. Upon the death of Yunchang and the accession of Goujian, Helü seized the opportunity and launched an attack on Yue. At the Battle of Zuili (), however, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Xiu Of Cuo
Shu may refer to: China * Sichuan, China, officially abbreviated as Shu (蜀) * Shu (kingdom) (conquered by Qin in 316 BC), an ancient kingdom in modern Sichuan * Shu Han (221–263) during the Three Kingdoms period * Cheng-Han (成汉/成漢), also named Later Shu (后蜀/後蜀), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Western Shu (405–413), also known as Qiao Shu, a state founded by Qiao Zong during the Eastern Jin dynasty * Former Shu (907–925) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Later Shu (934–965) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shū'' 書) People * Shu, the guitarist in the Japanese rock band, BACK-ON * Shu (surname), Chinese surname 舒 * Frank Shu (1943–2023), Chinese-American professor of astronomy * Quan-Sheng Shu, American physicist *, Japanese footballer * Will Shu (born 1979), American businessman, the co-founder and CEO of Deliveroo Fictional characters * Shu, in the Xbox 360 game ''Blue Dragon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject to the Zhou exercised increasing political autonomy. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 481 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, local polities negotiated their own alliances, waged wars against one another, up to defying the king's court in Luoyang, Luoyi. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, is generally considered to mark the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. The periodization dates to the late Western Han (). Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng (state), Zeng and Shen (state), Shen— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |