|
Teige-an-Duna MacCarthy
Teige-an-Duna MacCarthy () (1584 – 24 May 1649), Lord of Glean-na-Chroim, was the last hereditary Prince of the Dunmanway branch of the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty of Carbery (barony), Carbery "who exercised the rights of his position." He was Prince from 1618 to 1648, dying the following year on 24 May 1649. He was also known as Teige the Hospicious for his great hospitality, while his epithet ''an Duna'' means "of the Fortress". During the so-called Irish Rebellion of 1641, Insurrection of 1641, Teige-an-Duna was second in command of the MacCarthy Reagh forces. For this his family were dispossessed by the Cromwellians. He was the son of Eleanor, daughter of Rory MacSheehy, and Teige-an-Fhorsa MacCarthy ("Teige of the Forces"), Lord of Glean-na-Chroim. Marriages and issue Teige-an-Duna first married a daughter of Brian mac Owen Mac Sweeny of Cloghda, by whom he had 1) Teige-an-Fhorsa II MacCarthy, and 2) Dermod MacCarthy Glas, ancestor of ''MacCarthy Glas''. He married secondly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
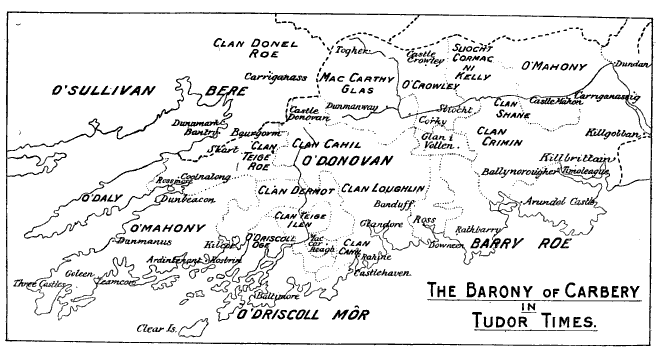
Barony Of Carbery
Carbery, or the Barony of Carbery, was once the largest barony in Ireland, and essentially a small, semi-independent kingdom on the southwestern coast of Munster, in what is now County Cork, from its founding in the 1230s by Donal Gott MacCarthy to its gradual decline in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. His descendants, the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty, were its ruling family. The kingdom officially ended in 1606 when Donal of the Pipes, 17th Prince of Carbery chose to surrender his territories to the Crown of England; but his descendants maintained their position in Carbery until the Cromwellian confiscations, following their participation in the Irish Rebellion of 1641 after which some emigrated to the Chesapeake Colonies. Its modern descendants in name are the baronies of Carbery West and Carbery East, but Carbery once included territories from several of the surrounding baronies as well. To the north/northwest it shared a long and shifting border with the Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Donovan (scholar)
John O'Donovan (; 25 July 1806 – 10 December 1861), from Atateemore, in the parish of Kilcolumb, County Kilkenny, and educated at Hunt's Academy, Waterford, was an Irish scholar of the Irish language. Life He was the fourth son of Edmond O'Donovan and Eleanor Hoberlin of Rochestown. His early career may have been inspired by his uncle Patrick O'Donovan. He worked for antiquarian James Hardiman researching state papers and traditional sources at the Public Records Office. Hardiman had secured O'Donovan a place in Maynooth College which he turned down. He also taught Irish to Thomas Larcom for a short period in 1828 and worked for Myles John O'Reilly, a collector of Irish manuscripts. Following the death of Edward O'Reilly in August 1830, he was recruited to the Topographical Department of the first Ordnance Survey of Ireland under George Petrie in October 1830. Apart from a brief period in 1833, he worked steadily for the Survey on place-name researches until 1842, unea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1649 Deaths
Events January–March * January 4 – In England, the Rump Parliament passes an ordinance to set up a High Court of Justice, to try Charles I for high treason. * January 17 – The Second Ormonde Peace concludes an alliance between the Cavaliers, Irish Royalists and the Irish Confederates during the War of the Three Kingdoms. Later in the year the alliance is decisively defeated during the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. * January 20 – Charles I of England goes on trial, for treason and other "high crimes". * January 27 – King Charles I of England, Scotland and Ireland is found guilty of high treason in a public session. * January 29 – Serfdom in Russia begins legally as the Sobornoye Ulozheniye (, "Code of Law") is signed by members of the Zemsky Sobor, the parliament of the estates of the realm in the Tsardom of Russia. Slaves and free peasants are consolidated by law into the new hereditary class of "serfs", and the Russian nobility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1584 Births
Events January–March * January 11 – Sir Walter Mildmay is given a royal licence to found Emmanuel College, Cambridge in England. * January 16 – Roman Catholic priest George Haydock, imprisoned in the Tower of London since 1582, states during an interrogation that he claimed that Queen Elizabeth, leader of the Church of England, was a heretic. Convicted of treason, he is executed on February 12. * February 2 – (6th waning moon of the Magha, BE 2126) In what is now Thailand, Prince Naresuan, the Uparaja of the Ayutthaya Kingdom and the son of King Mahathammarachathirat carries out the orders of Burma's King Nanda Bayin, and leads an army to suppress a rebellion by the Viceroy of the Ava Kingdom, Thado Minsaw. Arriving in April, Naresuan learns that King Nanda has ordered Naresuan to be assassinated, and begins his own rebellion against Burma, the Burmese–Siamese War.''Hmannan Yazawin'' (Ministry of Information of Myanmar, 2003) * February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Dunmanway
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Soldiers In The Irish Confederate Wars
Irish commonly refers to: * Someone or something of, from, or related to: ** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ***Éire, Irish language name for the island and the sovereign state *** Erse (other), Scots language name for the Irish language or Irish people ** Republic of Ireland, a sovereign state ** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland * Irish language, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family spoken in Ireland * Irish English, set of dialects of the English language native to Ireland * Irish people, people of Irish ethnicity Irish may also refer to: Places * Irish Creek (Kansas), a stream in Kansas * Irish Creek (South Dakota), a stream in South Dakota * Irish Lake, Watonwan County, Minnesota * Irish Sea, the body of water which separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain People * Irish (surname), a list of people * William Irish, pse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Lords
''Hemilepidotus'', the Irish lords, is a genus of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Agonidae, the poachers and sea ravens. These fishes are found in northern Pacific, northern Atlantic and Arctic oceans. Species There are currently six recognized species in this genus: * '' Hemilepidotus gilberti'' D. S. Jordan & Starks, 1904 (Gilbert's Irish lord) * ''Hemilepidotus hemilepidotus'' ( Tilesius, 1811) (Red Irish lord) * '' Hemilepidotus jordani'' T. H. Bean, 1881 (Yellow Irish lord) * '' Hemilepidotus papilio'' (T. H. Bean, 1880) (Butterfly sculpin) * '' Hemilepidotus spinosus'' Ayres, 1854 (Brown Irish lord) * '' Hemilepidotus zapus'' C. H. Gilbert & Burke Burke (; ) is a Normans in Ireland, Norman-Irish surname, deriving from the ancient Anglo-Norman and Hiberno-Norman noble dynasty, the House of Burgh. In Ireland, the descendants of William de Burgh (''circa'' 1160–1206) had the surname'' de B ..., 1912 (Longfin Irish lord) References Agonidae Marine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of Glean-na-Chroim
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are entitled to courtesy titles. The collective "Lords" can refer to a group or body of peers. Etymology According to the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'', the etymology of the word can be traced back to the Old English word ''hlāford'' which originated from ''hlāfweard'' meaning "loaf-ward" or "bread-keeper", reflecting the Germanic tribal custom of a chieftain providing food for his followers. The appellation "lord" is primarily applied to men, while for women the appellation "lady" is used. This is no longer universal: the Lord of Mann, a title previously held by the Queen of the United Kingdom, and female Lords Mayor are examples of women who are styled as "Lord". Historical usage Feudalism Under the feudal system, "lord" had a wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Hart
John O'Hart (; 1824–1902) was an Irish historian and genealogist. He is noted for his work on ancient Irish lineage. He was born in Crossmolina, County Mayo, Ireland. A committed Roman Catholic and Irish nationalist, O'Hart had originally planned to become a priest but instead spent two years as a police officer. He was an Associate in Arts at the Queen's University, Belfast. He worked at the Commissioners of National Education during the years of the Great Famine. He worked as a genealogist and took an interest in Irish history. He died in 1902 in Clontarf near Dublin, at the age of 78. O'Hart's 800-page, ''The Irish and Anglo-Irish landed gentry'' (Dublin 1884), was reprinted in 1969, with an introduction by Edward MacLysaght, the first Chief Herald of Ireland. Another work, ''Irish pedigrees; or, The origin and stem of the Irish nation'', first published in 1876, has come out in several subsequent editions. To complete his genealogies he used the writings of Cú Choig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the natural sciences, arts, literature, and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier List of Irish learned societies, learned society and one of its leading cultural institution, cultural and academic institutions. The academy was established in 1785 and granted a royal charter by King George III in 1786. the RIA has 600 members, with regular members being Irish residents elected in recognition of their academic achievements, and honorary members similarly qualified but usually based abroad; a small number of members are also elected in recognition of non-academic contributions to the Irish society. All members are entitled to use the honorific title MRIA with their names. Until the late 19th century the Royal Irish Academy was the owner of the main national collection of Irish antiquities. It presented its collection of archaeological artefacts and similar items, which included such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' () or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' () are chronicles of Middle Ages, medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Genesis flood narrative, Deluge, dated as 2,242 Anno Mundi, years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th-century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal (town), Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donal Of The Pipes, 13th Prince Of Carbery
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers. A short form of Donald is Don, and pet forms of Donald include Donnie and Donny. The feminine given name Donella is derived from Donald. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name '' Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many ancient and medieval Gaelic kings and noblemen: * Dyfnwal Moelmud (Dunvallo Molmutius), legendary king of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |