|
Tawasa
Tawasa is an extinct Native American language. Ostensibly the language of the Tawasa people of what is now Alabama, it is known exclusively through a word list attributed to a Tawasa named Lamhatty, collected in 1707. John Swanton studied the Lamhatty word list and identified the language as a Timucuan dialect, suggesting it was intermediary between Timucua and Muskogean. This opinion has been the subject of significant scholarly debate, with some such as Julian Granberry considering it a dialect of Timucua, others arguing it was a distinct language in the Timucua family, and yet others such as John Hann doubting that Lamhatty was a Tawasa at all. The language shows significant Alabama influence, including the Muskogean same-subject suffix ''-t''. Evidence In 1707 an Indian named Lamhatty arrived in the British colony of Virginia, eventually arriving at the estate of Colonel John Walker. Taking an interest in him, Walker introduced him to colonial historian Robert Beverley. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tawasa People
The Tawasa Indian Tribe, also known as the ''Alibamu Indian Tribe'', was located near the Alabama River, in Autauga County, Alabama. The population of the tribe was known to be around 330 members, all living in or near what were known as the Tawasa and Autauga Towns. The tribe existed around the late 1600s, early 1700s, however somewhat disappeared in the early 1700s, due to violence and flee. The tribe was split, with around 60 members joining the Alabama tribe, at Fort Toulouse. Some time later, the tribe at Fort Toulouse migrated south joining various tribes in Florida. For the remaining count, there is little evidence to show where they all went, however there is evidence to show that some ended up in Oklahoma, along with some Creeks who migrated there. History In the early 1500s, the nomadic Tawasa tribe was found by Hernando De Soto, near central Alabama. Almost two centuries later, the Tawasa were ambushed by other tribes, who enslaved and relocated some of them. As for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timucua Language
Timucua is a language isolate formerly spoken in northern and central Florida and southern Georgia by the Timucua peoples. Timucua was the primary language used in the area at the time of Spanish colonization in Florida. Differences among the nine or ten Timucua dialects were slight, and appeared to serve mostly to delineate band or tribal boundaries. Some linguists suggest that the Tawasa of what is now northern Alabama may have spoken Timucua, but this is disputed. Most of what is known of the language comes from the works of Francisco Pareja, a Franciscan missionary who came to St. Augustine in 1595. During his 31 years living with the Timucua, he developed a writing system for the language. From 1612 to 1628, he published several Spanish–Timucua catechisms, as well as a grammar of the Timucua language. Including his seven surviving works, only ten primary sources of information about the Timucua language survive, including two catechisms written in Timucua and Spanish b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscarora People
The Tuscarora (in Tuscarora language, Tuscarora ''Skarù:ręˀ'') are an indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands in Canada and the United States. They are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian Native Americans in the United States, Native American and First Nations in Canada, First Nations people. The Tuscarora Nation, a federally recognized tribe, is based in New York (state), New York, and the Tuscarora First Nation is one of the Six Nations of the Grand River in Ontario. Prior to European contact, the Tuscarora lived in the Carolinas along the Roanoke River, Roanoke, Neuse River, Neuse, Tar River, Tar, and Pamlico River, Pamlico Rivers.F.W. Hodge, "Tuscarora" ''Handbook of American Indians'', Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1906, at AccessGenealogy, accessed 28 Oct. 2009 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American History Of Florida
Native may refer to: People * '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood * '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes * List of Australian plants termed "native", whose common name is of the form "native . . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Languages Of North America
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its last member. A taxon may become functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce and recover. As a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of The North American Southeast
Indigenous may refer to: *Indigenous peoples *Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention *Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band *Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse * ''Indigenous'' (film), Australian, 2016 See also *Indigenous Australians *Indigenous language *Indigenous peoples in Canada *Indigenous religion *Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women are instances of violence against Indigenous women in Canada and the United States, notably those in the First Nations in Canada and Native American communities, but also amongst other Indigenous peoples s ... * Native (other) * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
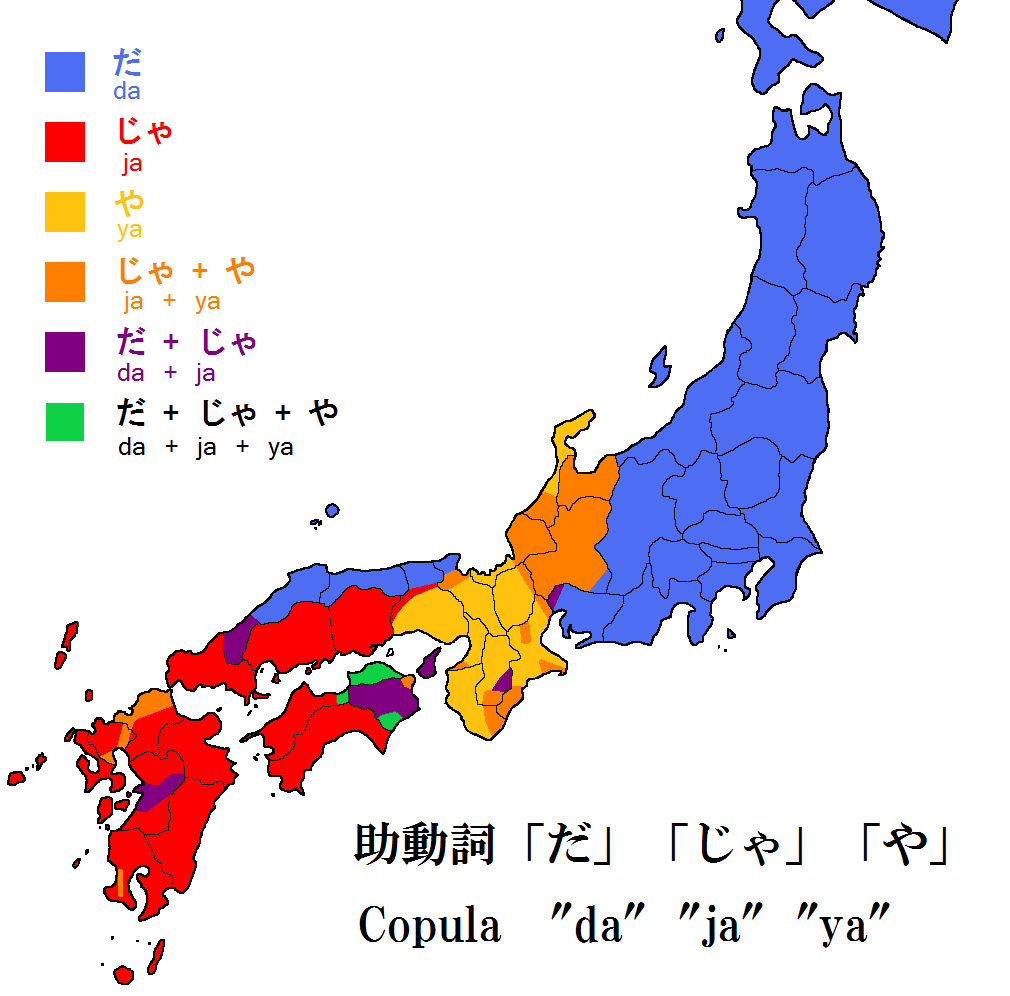
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (; : copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being cooperative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula (in English, the verb "to be"), although some (such as Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shawnee
The Shawnee ( ) are a Native American people of the Northeastern Woodlands. Their language, Shawnee, is an Algonquian language. Their precontact homeland was likely centered in southern Ohio. In the 17th century, they dispersed through Ohio, Illinois, Maryland, Delaware, and Pennsylvania. In the early 18th century, they mostly concentrated in eastern Pennsylvania but dispersed again later that century across Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois, with a small group joining Muscogee people in Alabama. In the 19th century, the U.S. federal government forcibly removed them under the 1830 Indian Removal Act to areas west of the Mississippi River; these lands would eventually become the states of Missouri, Kansas, and Texas. Finally, they were removed to Indian Territory, which became the state of Oklahoma in the early 20th century. Today, Shawnee people are enrolled in three federally recognized tribes, the Absentee-Shawnee Tribe of Indians of Okl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Beverley, Jr
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 30th largest by area, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 24th-most populous of the List of states and territories of the United States, 50 U.S. states. Alabama is nicknamed the ''Northern flicker, Yellowhammer State'', after the List of U.S. state birds, state bird. Alabama is also known as the "Heart of Dixie" and the "Cotton State". The state has diverse geography, with the north dominated by the mountainous Tennessee Valley and the south by Mobile Bay, a historically significant port. Alabama's capital is Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery, and its largest city by population and area is Huntsville, Ala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The state's List of capitals in the United States, capital is Richmond, Virginia, Richmond and its most populous city is Virginia Beach, Virginia, Virginia Beach. Its most populous subdivision is Fairfax County, Virginia, Fairfax County, part of Northern Virginia, where slightly over a third of Virginia's population of more than 8.8million live. Eastern Virginia is part of the Atlantic Plain, and the Middle Peninsula forms the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay. Central Virginia lies predominantly in the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont, the foothill region of the Blue Ridge Mountains, which cross the western and southwestern parts of the state. The fertile Shenandoah Valley fosters the state's mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |