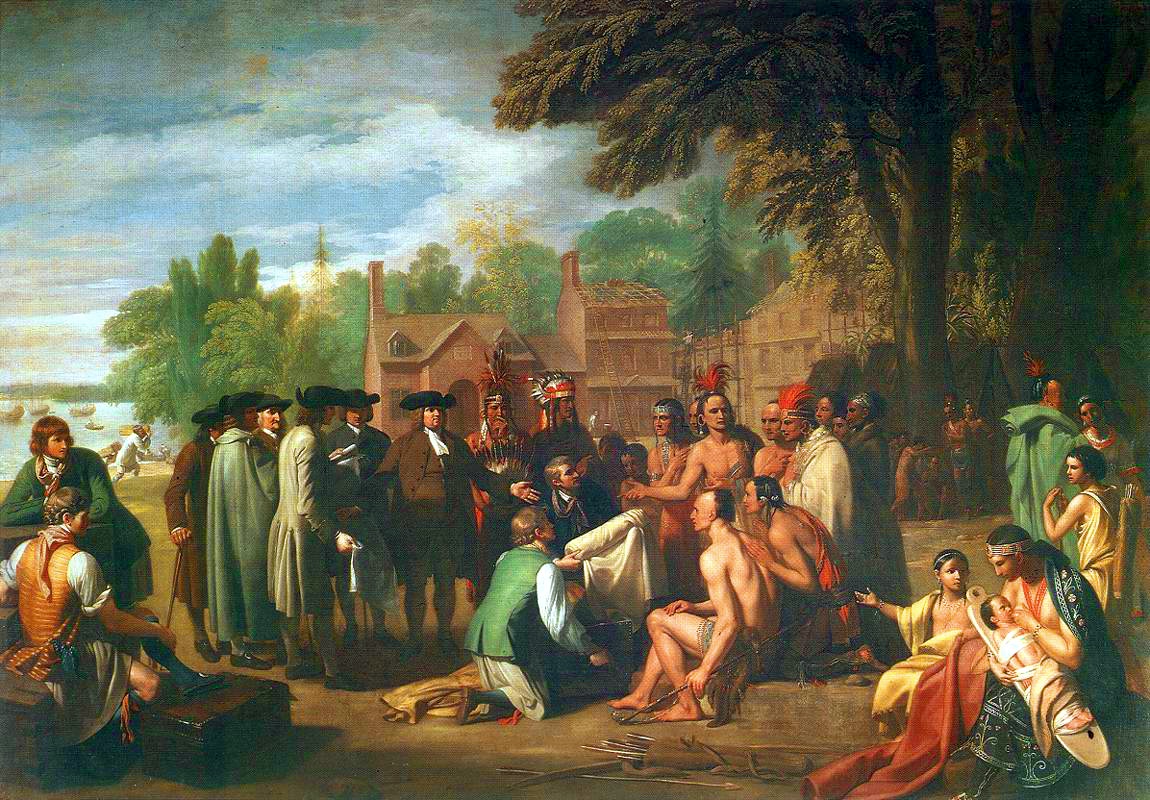|
Tamanend
Tamanend ("the Affable"; ), historically also known as Taminent, Tammany, Saint Tammany or King Tammany, was the Chief of Chiefs and Chief of the Turtle Clan of the Lenni-Lenape nation in the Delaware Valley signing the founding peace treaty with William Penn. Also called a "Patron Saint of America", Tamanend represented peace and amity, and became a popular figure in 18th-century America, especially in Philadelphia. A Tammany society founded in Philadelphia holds an annual Tammany festival. Tammany societies (Tammany Hall being the most well-known and influential) were established across the United States after the American Revolutionary War, and Tammany assumed mythic status as an icon for the peaceful politics of negotiation. Life and legend Tamanend reputedly took part in a meeting between the leaders of the Lenni-Lenape nation, and the leaders of the Pennsylvania colony held under a large elm tree at Shakamaxon in the early 1680s. William Penn and Tamanend continued to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tammany Hall LC-USZ62-101734
Tamanend ("the Affable"; ), historically also known as Taminent, Tammany, Saint Tammany or King Tammany, was the Chief of Chiefs and Chief of the Turtle Clan of the Lenni-Lenape nation in the Delaware Valley signing the founding peace treaty with William Penn. Also called a "Patron Saint of America", Tamanend represented peace and amity, and became a popular figure in 18th-century America, especially in Philadelphia. A Tammany society founded in Philadelphia holds an annual Tammany festival. Tammany societies (Tammany Hall being the most well-known and influential) were established across the United States after the American Revolutionary War, and Tammany assumed mythic status as an icon for the peaceful politics of negotiation. Life and legend Tamanend reputedly took part in a meeting between the leaders of the Lenni-Lenape nation, and the leaders of the Pennsylvania colony held under a large elm tree at Shakamaxon in the early 1680s. William Penn and Tamanend continued to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tammany Hall
Tammany Hall, also known as the Society of St. Tammany, the Sons of St. Tammany, or the Columbian Order, was an American political organization founded in 1786 and incorporated on May 12, 1789, as the Tammany Society. It became the main local political machine of the History of the United States Democratic Party, Democratic Party and played a major role in controlling History of New York City, New York City and New York (state), New York state politics. It helped immigrants, most notably Irish Americans in New York City, the Irish, rise in American politics from the 1850s into the 1960s. Tammany usually controlled Democratic nominations and political patronage in Manhattan for over 100 years following the mayoral victory of Fernando Wood in 1854, and used its patronage resources to build a loyal, well-rewarded core of district and precinct leaders; after 1850, the vast majority were Irish Catholics due to mass immigration from Ireland during and after the Great Famine (Ireland), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shackamaxon
The Treaty of Shackamaxon, also called the Great Treaty and Penn's Treaty, was a treaty between William Penn and Tamanend of the Lenape signed in 1682. The treaty created peace between the Quakers and Lenape, with Tamanend saying the two would "live in peace as long as the waters anin the rivers and creeks and as long as the stars and moon ndured" Description William Penn, who had been granted a land charter by King Charles II, arrived in North America in late October 1682. According to historical tradition, he soon made a treaty with the Lenni Lenape under an ancient elm tree. Francis Jennings argues that William Penn very likely signed a treaty, but that his less scrupulous sons, William Jr., John, and Thomas, destroyed the original document. Through such means, according to Jennings, the younger Penns sought to renege on the treaty to which their father had agreed. Curators of the Philadelphia History Museum at Atwater Kent claim that a wampum belt in their possession ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamaqua (Lenape Chief)
Tamaqua or Tamaque, also known as The Beaver and King Beaver ( – 1769 or 1771), was a leading man of the Unalachtigo (Turkey) phratry of the Lenape people. Although the Haudenosaunee in 1752 had appointed Shingas chief of the Lenape at the Treaty of Logstown, after the French and Indian War Tamaqua rose in prominence through his active role as peace negotiator, and was acknowledged by many Lenape as their "king" or chief spokesman. He was among the first to hand over English captives at the end of the French and Indian War and was active in peace negotiations at the conclusion of Pontiac's War. By 1758, he was recognized as one of three principal leaders of the Lenape, being the primary spokesman for the western Lenape in the Ohio Country. He founded the town of Tuscarawas, Ohio, in 1756 and died there in 1769 or 1771. Birth and early life Tamaqua was born and raised in the Tulpehocken Creek Valley, in Berks and Lebanon counties, on the upper Schuylkill River, with his u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenape
The Lenape (, , ; ), also called the Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. The Lenape's historical territory included present-day northeastern Delaware, all of New Jersey, the eastern Pennsylvania regions of the Lehigh Valley and Northeastern Pennsylvania, and New York Bay, western Long Island, and the lower Hudson Valley in New York (state), New York state. Today communities are based in Oklahoma, Wisconsin, and Ontario. During the last decades of the 18th century, European settlers and the effects of the American Revolutionary War displaced most Lenape from their homelands and pushed them north and west. In the 1860s, under the Indian removal policy, the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government relocated most Lenape remaining in the Eastern United States to the Indian Territory and surrounding regions. The la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from Latin, meaning "Penn's Woods", a reference to William Penn's father Admiral Sir William Penn. History European settlement The Province of Pennsylvania was one of two major Restoration colonies in colonial-era British America. A plan for government of the colony of Pennsylvania was heavily influenced by the ideas and utopian aspirations of English political scientist James Harrington. The proprietary colony's charter remained in the Penn family until the Penns were ousted in 1776 during the American Revolutionary War, and the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania was established as one of the original thirteen states. In June 1776, the Lower counties on the Delaware, a separate colony within the Province of Pennsylvania, broke away from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisquetomen
Pisquetomen (died 1762)Colin Gordon Calloway, ''The Indian World of George Washington: The First President, the First Americans, and the Birth of the Nation,'' Oxford University Press, 2018 was a Lenape chief who acted as interpreter and negotiator for the Lenape in dealings with the Province of Pennsylvania, Provincial government of Pennsylvania during the mid-eighteenth century. After being rejected in his bid to succeed his uncle Sassoonan as Lenape chief, Pisquetomen joined Shingas and Captain Jacobs in a series of deadly attacks on Pennsylvania settlements at the beginning of the French and Indian War. He eventually participated in peace negotiations that led to the Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nenatcheehunt
Nenatcheehunt (died 30 April 1762), also spelled Nenacheehunt, or Nenatchehan, and sometimes referred to as Menatochyand, was a Lenape chief known for participating in peace negotiations at the end of the French and Indian War. He is referred to as "Delaware George" by both George Croghan and James Kenny. Confusingly, Christian Frederick Post refers to both Nenatcheehunt and Keekyuscung as "Delaware George." It is not always clear which man is being identified, as they often attended the same meetings and events. Family and early life He has been identified as a brother of Netowatquelemond, but he was more likely an older brother of Pisquetomen, Shingas and Tamaqua. If the latter is true, then Nenatcheehunt was born and raised in the Tulpehocken Creek Valley, in Berks and Lebanon counties, on the upper Schuylkill River, with his uncle Sassoonan (Allumapees) and his brothers. One source reports that Nenatcheehunt had six brothers (Tamaqua, Pisquetoman, Shingas, Buffalo Horn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin West
Benjamin West (October 10, 1738 – March 11, 1820) was a British-American artist who painted famous historical scenes such as ''The Death of Nelson (West painting), The Death of Nelson'', ''The Death of General Wolfe'', the ''Treaty of Paris (painting), Treaty of Paris'', and ''Benjamin Franklin Drawing Electricity from the Sky''. Entirely self-taught, West soon gained valuable patronage and toured Europe, eventually settling in London. He impressed King George III and was largely responsible for the launch of the Royal Academy of Arts, Royal Academy, of which he became the second president (after Sir Joshua Reynolds). He was appointed historical painter to the court and Surveyor of the King's Pictures. West also painted religious subjects, as in his huge work ''The Preservation of St Paul after a Shipwreck at Malta'', at the Chapel of St Peter and St Paul at the Old Royal Naval College in Greenwich, and ''Christ Healing the Sick'', presented to the National Gallery. Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress (1775–1781) was the meetings of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, which established American independence from the British Empire. The Congress constituted a new federation that it first named the United Colonies of North America, and in 1776, renamed the United States, United States of America. The Congress began convening in present-day Independence Hall in Philadelphia, on May 10, 1775, with representatives from 12 of the 13 colonies, following the Battles of Lexington and Concord, the first battles of the Revolutionary War, which were fought on April 19, 1775. The Second Continental Congress succeeded the First Continental Congress, which met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, also in Philadelphia. The Second Congress functioned as the ''de facto'' federation government at the outset of the Revolutionary War by raising militias, direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abigail Adams
Abigail Adams ( ''née'' Smith; – October 28, 1818) was the wife and closest advisor of John Adams, the second president of the United States, and the mother of John Quincy Adams, the sixth president of the United States. She was a founder of the United States, and was both the first second lady and second first lady of the United States, although such titles were not used at the time. She and Barbara Bush are the only two women in American history who were both married to a U.S. president and the mother of a U.S. president. Adams's life is one of the most documented of the first ladies; many of the letters she wrote to her husband John Adams while he was in Philadelphia as a delegate in the Continental Congress prior and during the American Revolution document the closeness and versatility of their relationship. John Adams frequently sought the advice of Abigail on many matters, and their letters are filled with intellectual discussions on government and politics. Her lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War against the British Empire. He is commonly known as the Father of the Nation for his role in bringing about American independence. Born in the Colony of Virginia, Washington became the commander of the Virginia Regiment during the French and Indian War (1754–1763). He was later elected to the Virginia House of Burgesses, and opposed the perceived oppression of the American colonists by the British Crown. When the American Revolutionary War against the British began in 1775, Washington was appointed Commanding General of the United States Army, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army. He directed a poorly organized and equipped force against disciplined British troops. Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |