|
TNNT1
Slow skeletal muscle troponin T (sTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNT1'' gene. The TNNT1 gene is located at 19q13.4 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin T (ssTnT). ssTnT is an ~32-kDa protein consisting of 262 amino acids (including the first methionine) with an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.95. It is the tropomyosin binding and thin filament anchoring subunit of the troponin complex in the sarcomeres of slow twitch skeletal muscle fibers. TNNT1 gene is specifically expressed in slow skeletal muscle of vertebrates, with one exception that dry land toad (Bufo) cardiac muscle expresses ssTnT other than cardiac TnT. Evolution Three homologous genes have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three muscle type specific isoforms A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
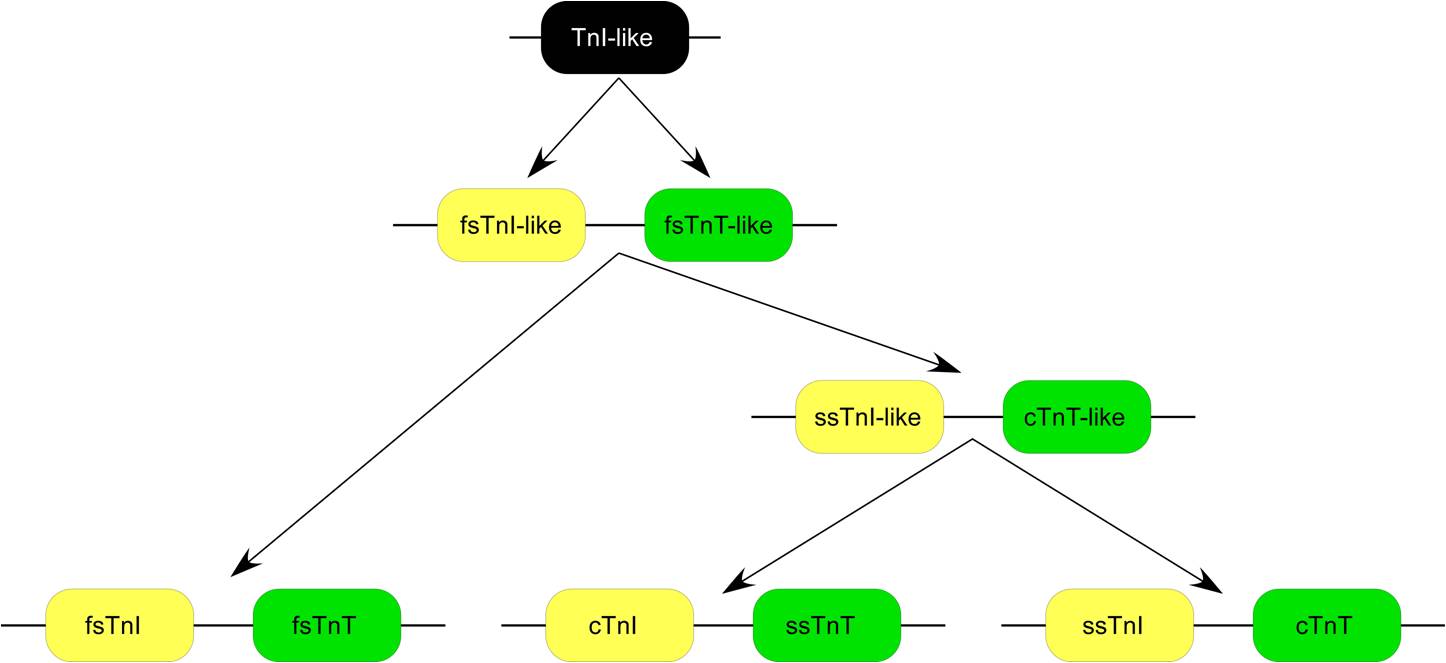
TnT TnI Gene Pairs
Troponin T (shortened TnT or TropT) is a part of the troponin complex, which are proteins integral to the contraction of skeletal and heart muscles. They are expressed in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. Troponin T binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on actin, and together with the rest of the troponin complex, modulates contraction of striated muscle. The cardiac subtype of troponin T is especially useful in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack because it is released into the blood-stream when damage to heart muscle occurs. It was discovered by the German physician Hugo A. Katus at the University of Heidelberg, who also developed the troponin T assay. Subtypes * Slow skeletal troponin T1, TNNT1 (19q13.4, ) * Cardiac troponin T2, TNNT2 (1q32, ) * Fast skeletal troponin T3, TNNT3 (11p15.5, ) Reference values The 99th percentile cutoff for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is 0.01 ng/mL. The reference range for the high sensitivity troponin T is a normal 52 ng/L. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troponin T
Troponin T (shortened TnT or TropT) is a part of the troponin complex, which are proteins integral to the contraction of skeletal and heart muscles. They are expressed in skeletal and cardiac myocytes. Troponin T binds to tropomyosin and helps position it on actin, and together with the rest of the troponin complex, modulates contraction of striated muscle. The cardiac subtype of troponin T is especially useful in the laboratory diagnosis of heart attack because it is released into the blood-stream when damage to heart muscle occurs. It was discovered by the German physician Hugo A. Katus at the University of Heidelberg, who also developed the troponin T assay. Subtypes * Slow skeletal troponin T1, TNNT1 (19q13.4, ) * Cardiac troponin T2, TNNT2 (1q32, ) * Fast skeletal troponin T3, TNNT3 (11p15.5, ) Reference values The 99th percentile cutoff for cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is 0.01 ng/mL. The reference range for the high sensitivity troponin T is a normal 52 ng/L. Backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. Methionine is also involved in angiogenesis and various processes related to DNA transcription, epigenetic expression, and gene regulation. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. It is Genetic code, encoded by the codon AUG. It was named by Satoru Odake in 1925, as an abbreviation of its structural description 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectric Point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electric charge, electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). However, pI is also used. For concision, brevity, this article uses pI. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons#In Physics and biochemistry, protons (H+). Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer (interfacial), double layer. In the common case when the surface charge-determining ions are H+/HO−, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. The pI value can affect the solubility of a molecule at a given pH. Such molecules have minimum solubility in water or salt solutions at the pH that corresponds to their pI and often precipitate out of Solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin
Tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical, coiled coil protein found in many animal and fungal cells. In animals, it is an important component of the muscular system which works in conjunction with troponin to regulate muscle contraction. It is present in smooth and striated muscle tissues, which can be found in various organs and body systems, including the heart, blood vessels, respiratory system, and digestive system. In fungi, tropomyosin is found in cell walls and helps maintain the structural integrity of cells. Tropomyosin is found in other eukaryotes too, but not in plants. Overall, tropomyosin is an important protein that plays a vital role in the proper functioning of many different organisms. Tropomyosin and the actin skeleton All organisms contain organelles that provide physical integrity to their cells. These types of organelles are collectively known as the cytoskeleton, and one of the most ancient systems is based on filamentous polymers of the protein actin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal striated muscle, Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic development, embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long fibrous tail and a globular head that binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to Adenosine triphos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Gene
Homology, homologous, homologation or homological may refer to: Sciences Biology *Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor *Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences *Homologous chromosomes, chromosomes in a biological cell that pair up (synapse) during meiosis *Homologous recombination, genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between molecules of DNA * Homologous desensitization, a receptor decreases its response to a signalling molecule when that agonist is in high concentration *Homology modeling, a method of protein structure prediction Chemistry *Homologous series, a series of organic compounds having different quantities of a repeated unit * Homologous temperature, the temperature of a material as a fraction of its absolute melting point *Homologation reaction, a chemical reaction which produces the next logical member of a homologous series O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoforms.) Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments (exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein. The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions of genes revealed by the human genome project and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |