|
TERRA (biology)
TERRA in biology is an abbreviation for "TElomeric Repeat-containing RNA". TERRA is RNA that is transcribed from telomeres — the repeating 6-nucleotide sequences that cap the ends of chromosomes. TERRA functions with shelterin to inhibit telomere lengthening by enzyme telomerase. However, other studies have shown that under certain conditions TERRA can recruit telomerase to telomeres. TERRAs are essential for telomere length and maintenance. At least four factors contribute to telomere maintenance: telomerase, shelterin, TERRA and the CST Complex. TERRA can also regulate telomere length by increasing euchromatin formation. On the other hand, nonsense-mediated decay factor enrichment at telomeres may exist to prevent TERRA inhibition of telomerase. TERRA levels vary during the cell cycle, decreasing during S phase, and increasing in the transition from G2 phase to G1 phase The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that take ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The EMBO Journal
''The EMBO Journal'' is a semi-monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal focusing on full-length papers describing original research of general interest in molecular biology and related areas. The editor-in-chief is Facundo D. Batista ( Harvard Medical School). History The journal was established in 1982 and was published by Nature Publishing Group on behalf of the European Molecular Biology Organization until the launch of EMBO Press in 2013. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 9.4. See also *'' EMBO Reports'' *'' Molecular Systems Biology'' References External links * * (1986–2003 issues from microfilm) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
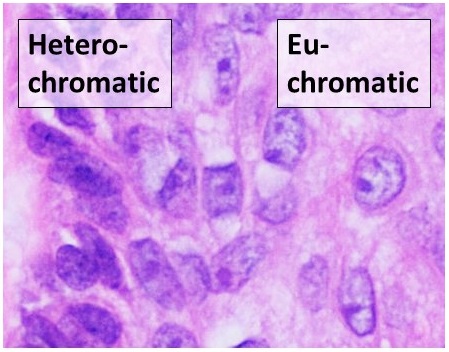
Euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin (DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and less accessible for transcription. 92% of the human genome is euchromatic. In eukaryotes, euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes, euchromatin is the ''only'' form of chromatin present; this indicates that the heterochromatin structure evolved later along with the nucleus, possibly as a mechanism to handle increasing genome size. Structure Euchromatin is composed of repeating subunits known as nucleosomes, reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads on a string, that are approximately 11 nm in diameter. At the core of these nucleosomes are a set of four histone protein pairs: H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Each core histone protein possesses a 'tail' structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G1 Phase
The G1 phase, gap 1 phase, or growth 1 phase, is the first of four phases of the cell cycle that takes place in eukaryotic cell division. In this part of interphase, the cell synthesizes Messenger RNA, mRNA and proteins in preparation for subsequent steps leading to mitosis. G1 phase ends when the cell moves into the S phase of interphase. Around 30 to 40 percent of cell cycle time is spent in the G1 phase. Overview G1 phase together with the S phase and G2 phase, G2 phase comprise the long growth period of the cell cycle cell division called interphase that takes place before cell division in mitosis (M phase). During G1 phase, the cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and protein that are required for DNA synthesis. Once the required proteins and growth are complete, the cell enters the next phase of the cell cycle, S phase. The duration of each phase, including the G1 phase, is different in many different types of cells. In human somatic cells, the G1 stage of the cell c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G2 Phase
G2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. It follows the successful completion of S phase, during which the cell’s DNA is replicated. G2 phase ends with the onset of prophase, the first phase of mitosis in which the cell’s chromatin condenses into chromosomes. G2 phase is a period of rapid cell growth and protein synthesis during which the cell prepares itself for mitosis. Curiously, G2 phase is not a necessary part of the cell cycle, as some cell types (particularly young ''Xenopus'' embryos and some cancers)) proceed directly from DNA replication to mitosis. Though much is known about the genetic network which regulates G2 phase and subsequent entry into mitosis, there is still much to be discovered concerning its significance and regulation, particularly in regards to cancer. One hypothesis is that the growth in G2 phase is regulated as a method of cell size control. Fission yeast (''Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Phase
S phase (Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S-phase are tightly regulated and widely conserved. Regulation Entry into S-phase is controlled by the G1 restriction point (R), which commits cells to the remainder of the cell-cycle if there is adequate nutrients and growth signaling. This transition is essentially irreversible; after passing the restriction point, the cell will progress through S-phase even if environmental conditions become unfavorable. Accordingly, entry into S-phase is controlled by molecular pathways that facilitate a rapid, unidirectional shift in cell state. In yeast, for instance, cell growth induces accumulation of Cln3 cyclin, which complexes with the cyclin dependent kinase CDK2. The Cln3-CDK2 complex promotes transcription of S-phase genes by inactivating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells, the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase, and the M phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the M phase, the replicated Chromosome, chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
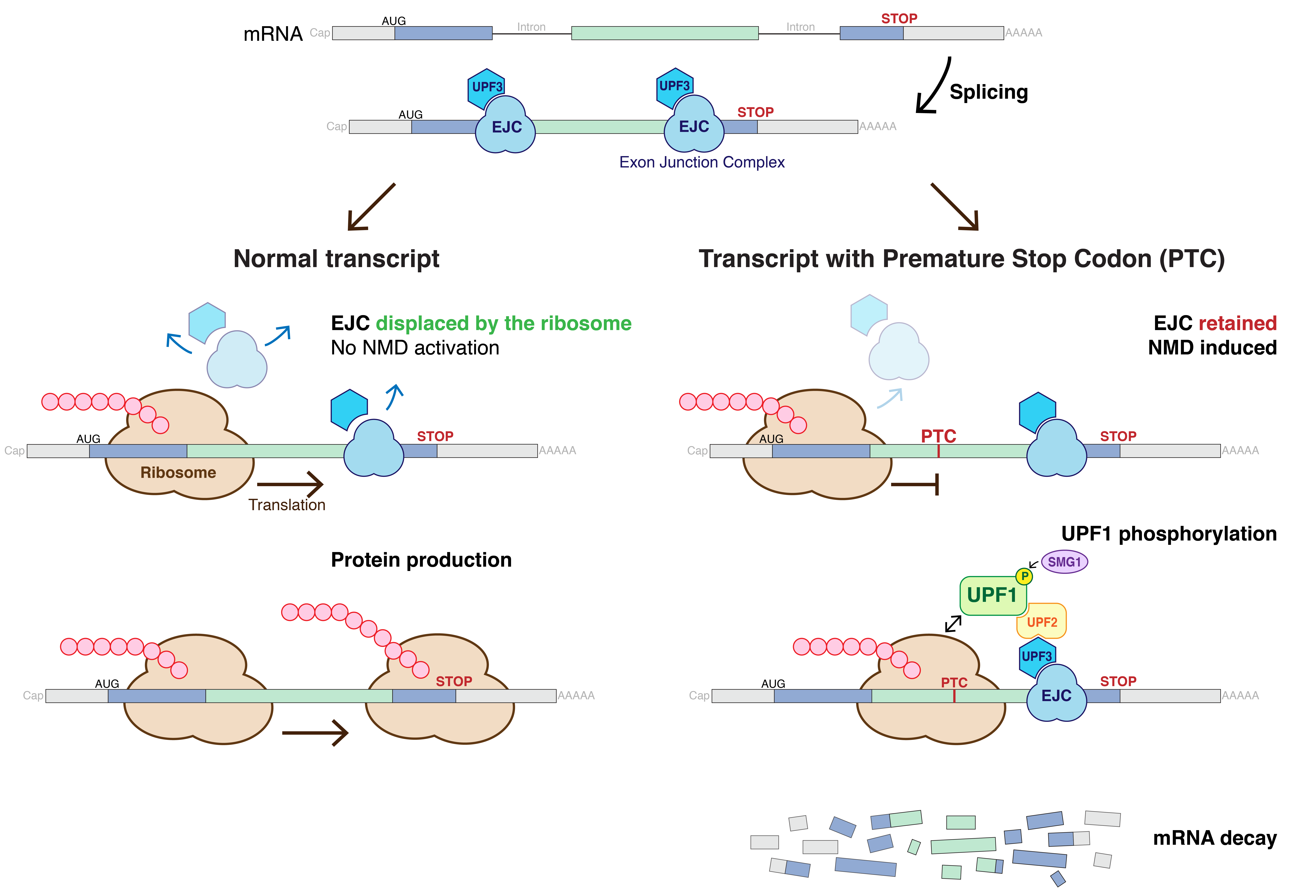
Nonsense-mediated Decay
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins. NMD was first described in human cells and in yeast almost simultaneously in 1979. This suggested broad phylogenetic conservation and an important biological role of this intriguing mechanism. NMD was discovered when it was realized that cells often contain unexpectedly low concentrations of mRNAs that are transcribed from alleles carrying nonsense mutations. Nonsense mutations code for a premature stop codon which causes the protein to be shortened. The truncated protein may or may not be functional, depending on the severity of what is not translated. In human genetics, NMD has the possibility to not only limit t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Biological Sciences
The ''International Journal of Biological Sciences'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal published by Ivyspring International Publisher. It publishes original articles, reviews, and short research communications in all areas of biological sciences. The editor-in-chief is Chuxia Deng (National Institutes of Health). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in MEDLINE/PubMed, Science Citation Index Expanded, Current Contents/Life Sciences, Current Contents/Clinical Medicine, Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, The Zoological Record, EMBASE, Chemical Abstracts, CAB International, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 9.2. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Cell
''Molecular Cell'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that covers research on cell biology at the molecular level, with an emphasis on new mechanistic insights. It was established in 1997 and is published two times per month. The journal is published by Cell Press and is a companion to ''Cell''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed, for example, in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports ''Journal Citation Reports'' (''JCR'') is an annual publication by Clarivate. It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science Core Collection. It provides information about academic journals in the natur ...'', the journal had an impact factor of 14.5 in 2023. References External links * Academic journals established in 1997 Molecular and cellular biology journals Biweekly journals English-language journals Cell Press academic journals {{Molec-cell-biology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |