|
TDV-2200
TDV-2200 was a series of terminals produced by Tandberg Data from the early 1980s. Norsk Data sold rebranded versions of the TDV 2200 series under their own designations ND-240/242 (TDV-2215 variants), ND-246/266/267 (TDV-2200/9 variants) and ND-320 (TDV-2200/9S).Norsk Data Service Handbook, Vol.1, 1984. The rebranded TDV-2200/9(S) terminals had keyboards customized for the ND-NOTIS text processing system. For Siemens, Tandberg build the similar MTS 2000 series. Another important customer was Mycron. It optionally used ISO/IEC 646, ISO 646-NO for mapping of the Norwegian characters, which made them a pet hate among UNIX people. (Some users still humorously pronounce the vertical bar as "ø".) Versions with vector graphics were available, as were versions supporting Thai script and other scripts. It won several awards for ergonomic design, and its keyboard was widely considered to be one of the best on the market. Its immediate predecessor was the TDV-2100 series, and its su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ND-NOTIS
ND-NOTIS was a office automation suite by Norsk Data introduced in the early 80s, running on the SINTRAN III platform on both ND-100 and ND-500 architectures. It was also available on Microsoft Windows running in networks of Norsk Data servers. Overview ND-NOTIS was successful, and was the main product line of the company for quite a while, cementing its position in the Norwegian government office automation market. It was also widespread in Germany and in the UK (local municipality, DHSS etc.) The NOTIS family of products was presented to the British Computer Society by Jeremy Salter. Roger Tagg et al. (BCS, End User SG, 1985) and was received with praise as the BCS model for user interface. The same praise was awarded to NOTIS-IR as a model for information storage and retrieval. The European Commission published in 1985 NOTIS-IR as reference model for document and information search and retrieval. ND-NOTIS was unique for its time and had innovative features like multilingua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandberg Data
Tandberg Data GmbH was a company focused on data storage products, especially streamers, headquartered in Dortmund, Germany. They were the only company still selling drives that use the QIC (also known as SLR) and VXA formats, but also produced LTO along with autoloaders, tape libraries, NAS devices, RDX Removable Disk Drives, Media and Virtual Tape Libraries. Tandberg Data used to manufacture computer terminals (e.g., TDV 2200), keyboards, and other hardware. The company was liquidated in January 2025. They had offices in Dortmund, Germany; Tokyo, Japan; Singapore; Guangzhou, China and Westminster, Colorado, U.S. History * Tandberg radio factory was founded in Oslo on 25 January 1933 by Vebjørn Tandberg. * In 1970, Tandberg produces its first data tape drives. * In December 1978, Tandbergs Radiofabrikk goes bankrupt. * In January 1979, Siemens and the state of Norway establish Tandberg Data, rescuing the data storage and computer terminal divisions from the ashes. Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norsk Data
Norsk Data was a minicomputer manufacturer located in Oslo, Norway. Existing from 1967 to 1998, it had its most active period from the early 1970s to the late 1980s. At the company's peak in 1987, it was the second largest company in Norway and employed over 4,500 people. Throughout its history Norsk Data produced a long string of extremely innovative systems, with a disproportionately large number of world firsts. Some examples of this are the NORD-1, the first minicomputer to have memory paging as a standard option, and the first machine to have floating-point instructions standard, the NORD-5, the world's first 32-bit minicomputer (beating the VAX, often claimed the first, by 6 years). Historical overview The origins of Norsk Data go back to the development of digital computers at the Norwegian Defense Research Establishment at Kjeller, Norway, where several early computers had been designed, such as the SAM and the SAM 2, also known as the FLINK. The success of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational technology conglomerate. It is focused on industrial automation, building automation, rail transport and health technology. Siemens is the largest engineering company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software. The origins of the conglomerate can be traced back to 1847 to the ''Telegraphen Bau-Anstalt von Siemens & Halske'' established in Berlin by Werner von Siemens and Johann Georg Halske. In 1966, the present-day corporation emerged from the merger of three companies: Siemens & Halske, Siemens-Schuckert, and Siemens-Reiniger-Werke. Today headquartered in Munich and Berlin, Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 320,000 people worldwide and reported a global revenue of around €78 billion in 2023. The company is a component of the DAX and Euro Stoxx 50 stock market indices. As of December 2023, Siemens is the second largest German company by market ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
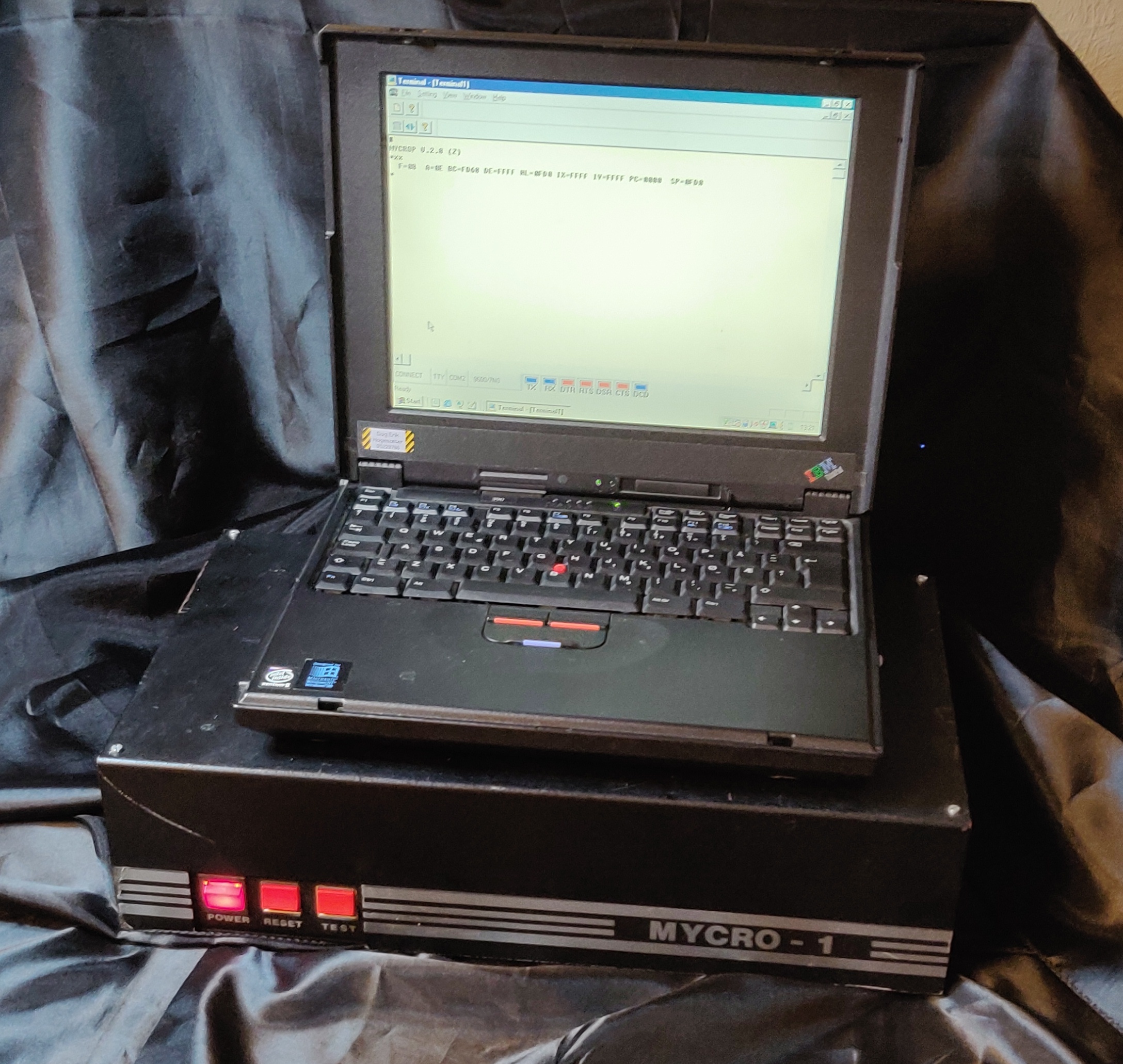
Mycron
Mycron was a pioneer manufacturer of microcomputers, located in Oslo, Norway. Originally named Norsk Data Industri, the company was founded in 1975 by Lars Monrad Krohn, who was also one of the founding fathers of Norsk Data. Among the employees are Arne Maus (1986–89) and Gisle Hannemyr. The company was renamed MySoft in 1999. Computers manufactured by Mycron MYCRO-1 was an Intel 8080 machine, running the ''MYCROP''operating system. Afterwards the Mycron 3 was developed, running CP/M. The Mycron 1000 featured a Zilog Z80 processor and ran MP/M. In 1981, the Mycron 2000 was released, based on an Intel 8086 CPU, running CP/M-86 and MP/M-86 operating systems An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for .... References External linksComputer-Archiv – Mycron [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 646
ISO/IEC 646 ''Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange'', is an International Organization for Standardization, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the Ecma International, ECMA standard ECMA-6 and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. The first version of ECMA-6 had been published in 1965, based on work the ECMA's Technical Committee TC1 had carried out since December 1960. The first edition of ISO/IEC 646 was published in 1973, and the most recent, third, edition in 1991. ISO/IEC 646 specifies a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived. It allocates a set of 82 unique graphic characters to 7-bit code points, known as the ''invariant'' (INV) or ''basic character set'', including letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet, Numerical digit, digits, and some common English language, English pun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Bar
The vertical bar, , is a glyph with various uses in mathematics, computing, and typography. It has many names, often related to particular meanings: Sheffer stroke (in logic), pipe, bar, or (literally, the word "or"), vbar, and others. Usage Mathematics The vertical bar is used as a mathematical symbol in numerous ways. If used as a pair of brackets, it suggests the notion of the word "size". These are: * absolute value: , x, , read "the ''absolute value'' of ''x''" * cardinality: , S, , read "the ''cardinality'' of the set ''S''" or "the ''length'' of a string ''S''" * determinant: , A, , read "the ''determinant'' of the matrix ''A''". When the matrix entries are written out, the determinant is denoted by surrounding the matrix entries by vertical bars instead of the usual brackets or parentheses of the matrix, as in \begin a & b \\ c & d\end. * order: , G, , read "the ''order'' of the group ''G''", or , g, , "the ''order'' of the element g \in G" Likewise, the vertical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Character-oriented Terminal
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical computer hardware, hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. Most early computers only had a front panel to input or display bits and had to be connected to a terminal to print or input text through a keyboard. Teleprinters were used as early-day hard-copy terminals and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. The computer would typically transmit a line of data which would be printed on paper, and accept a line of data from a keyboard over a Serial communication, serial or other interface. Starting in the mid-1970s with microcomputers such as the Sphere 1, Sol-20, and Apple I, display circuitry and keyboards began to be integrated into personal computer, personal and workstation computer systems, with the computer handling character generation and outputting to a Cathode-ray_tube, CRT display such as a computer monitor or, sometimes, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |