|
T. Rice Holmes
Thomas Rice Edward Holmes, FBA (24 May 1855 – 4 August 1933), who usually published his works under the names T. Rice Holmes or T.R.E. Holmes, was a scholar best known for his extensive and "fundamental" work on Julius Caesar and his Gallic War commentaries. Holmes was born at Moycashel (today Castletown-Geoghegan), Ireland. He was the fifth son of Robert Holmes, a landed proprietor and a descendant of John Arbuthnot, a friend of Alexander Pope and Jonathan Swift. Holmes was educated at Merchant Taylors' School and Christ Church, Oxford. He was assistant master at Lincoln Grammar School (1878–80), Blackheath Proprietary School (1880–85), and St. Paul's School (beginning in 1886). In 1888, he married Isabel Isaacs, the daughter of Lionel Isaacs of Mandeville, Jamaica. They lived at 11 Douro Place, Kensington. In addition to his books, Holmes published a number of articles in the ''English Historical Review'', ''Classical Quarterly'', and other journals. He died at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The British Academy
Fellowship of the British Academy (post-nominal letters FBA) is an award granted by the British Academy to leading academics for their distinction in the humanities and social sciences. The categories are: # Fellows – scholars resident in the United Kingdom # Corresponding Fellows – scholars resident overseas # Honorary Fellows – an Honorary title (academic), honorary academic title (whereby the post-nominal letters "Hon FBA" are used) # Deceased Fellows – Past Fellows of the British Academy The award of fellowship is based on published work and fellows may use the post-nominal letters ''FBA''. Examples of Fellows are Edward Rand; Mary Beard (classicist), Mary Beard; Roy Porter; Nicholas Stern, Baron Stern of Brentford; Michael Lobban; M. R. James; Friedrich Hayek; John Maynard Keynes; Lionel Robbins; and Rowan Williams. See also * List of fellows of the British Academy References Fellows of learned societies of the United Kingdom, British Academy Fello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Quarterly
The Classical Association (CA) is an educational organisation which aims to promote and widen access to the study of classical subjects in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1903, the Classical Association supports and advances classical learning in schools, colleges, universities and local areas, and it has a wide membership. The Classical Association is a member of the Council for Subject Associations and is a registered charity. Foundation The Association was founded on 19 December 1903 at a public meeting held at University College London, and its objects are defined in its constitution as: # The advancement of education by the promotion, development and maintenance of classical studies # To increase public awareness of the contribution and importance of classics to education and public life. It was founded with the name "The Classical Association of England and Wales" but the name was soon changed to "The Classical Association". The incumbent Chair of the Classical Associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historians Of Ancient Rome
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human species; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity Among historians Ancient historians In the 19th century, scholars used to study ancient Greek and Roman historians to see how generally reliable they were. In recent decades, however, scholars have focused more on the constructions, genres, and meanings that ancient historians sought to convey to their audiences. History is always written with contemporary concerns and ancient hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Classical Scholars
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 Deaths
Events January * January 11 – Australian aviator Sir Charles Kingsford Smith makes the first commercial flight between Australia and New Zealand. * January 17 – The United States Congress votes in favour of Philippines independence, against the wishes of U.S. President Herbert Hoover. * January 28 – "Pakistan Declaration": Choudhry Rahmat Ali publishes (in Cambridge, UK) a pamphlet entitled ''Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?'', in which he calls for the creation of a Muslim state in northwest India that he calls "Pakistan, Pakstan"; this influences the Pakistan Movement. * January 30 ** Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler is appointed Chancellor of Germany (German Reich), Chancellor of Germany by President of Germany Paul von Hindenburg. ** Édouard Daladier forms a government in France in succession to Joseph Paul-Boncour. He is succeeded on October 26 by Albert Sarraut and on November 26 by Camille Chautemps. February * February 1 – Adolf Hitle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1855 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Ottawa, Ontario, is incorporated as a city.' * January 5 – Ramón Castilla begins his third term as President of Peru. * January 23 ** The first bridge over the Mississippi River opens in modern-day Minneapolis, a predecessor of the Father Louis Hennepin Bridge. ** The 8.2–8.3 Wairarapa earthquake claims between five and nine lives near the Cook Strait area of New Zealand. * January 26 – The Point No Point Treaty is signed in the Washington Territory. * January 27 – The Panama Railway becomes the first railroad to connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. * January 29 – Lord Aberdeen resigns as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, over the management of the Crimean War. * February 5 – Lord Palmerston becomes Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. * February 11 – Kassa Hailu is crowned Tewodros II, Emperor of Ethiopia. * February 12 – Michigan State University (the "pioneer" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; ; – 46 BC) was a Gauls, Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman Republic, Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After surrendering to Caesar and spending almost six years in prison, he was executed in Rome. Vercingetorix was the son of Celtillus the Arvernian, leader of the Gallic tribes. Vercingetorix came to power after his formal designation as chieftain of the Arverni at the oppidum Gergovia in 52 BC. He immediately established an alliance with other Gallic tribes, took command, combined all forces and led them in the Celts' most significant revolt against Roman power. He won the Battle of Gergovia against Julius Caesar in which several thousand Romans and their allies were killed and the Roman legions withdrew. Caesar had been able to exploit Gaulish internal divisions to easily subjugate the country, since Vercingetorix's attempt to unite the Gauls against Roman in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Jullian
Camille Jullian (15 March 1859 – 12 December 1933) was a French historian, philologist, archaeologist and historian of literature. A Professor of ancient history and classics at the University of Bordeaux from 1891, Jullian was awarded a chair at the Collège de France in 1905, where he taught national antiquities until 1930. He was made Grand Officier de la Légion d'Honneur in 1926, and was elected to the Académie française in 1924. Jullian is the author of a monumental ''Histoire de la Gaule'', published in eight volumes between 1907 and 1928, which has influenced Celtic studies throughout the 20th century. Biography Camille Louis Jullian was born on 15 March 1859 in Marseille, the son of Camille Jullian, a merchant and banker, and Marie Rouvière. Jullian came from a Protestant family of farmers originally from Calvisson, Gard. He attended the lycée of Marseille between 1864 and 1877, then the École Normale Supérieure, where he earned an agrégation in history and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typically activated by a mouse (computing), mouse click, keypress set, or screen touch. Apart from text, the term "hypertext" is also sometimes used to describe tables, images, and other presentational content formats with integrated hyperlinks. Hypertext is one of the key underlying concepts of the World Wide Web, where Web pages are often written in the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). As implemented on the Web, hypertext enables the easy-to-use publication of information over the Internet. Etymology The English prefix "hyper-" comes from the Greek language, Greek prefix "ὑπερ-" and means "over" or "beyond"; it has a common origin with the prefix "super-" which comes from Latin. It signifies the overcoming of the previous linear cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LacusCurtius
LacusCurtius is the ancient Graeco-Roman part of a large history website, hosted as of March 2025 on a server at the University of Chicago. Starting in 1995, as of January 2004 it gave "access to more than 594 photos, 559 drawings and engravings, 69 plans, and 59 maps".Others have stated that, "as of October 2024 it had '3916 webpages, 779 photos, 772 drawings & engravings, 120 plans, 139 maps.' The overall site is the creation of William P. Thayer. Overview The main resources to be found on it include: * a number of Latin and Greek texts, usually in English translation, and often in the original language also * '' Smith's Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities'' * '' Platner's Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome'' * several secondary works, mostly on Rome and Roman Britain * a photogazetteer of Roman remains and medieval churches of central Italy including the city of Rome * an often-cited online copy of Richard Hinckley Allen's '' Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 Britannica
Events January * January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are added to the Commonwealth of Australia. * January 3 ** 1911 Kebin earthquake: An earthquake of 7.7 moment magnitude strikes near Almaty in Russian Turkestan, killing 450 or more people. ** Siege of Sidney Street in London: Two Latvian anarchists die, after a seven-hour siege against a combined police and military force. Home Secretary Winston Churchill arrives to oversee events. * January 4 – Amundsen and Scott expeditions: Robert Falcon Scott's British ''Terra Nova'' Expedition to the South Pole arrives in the Antarctic and establishes a base camp at Cape Evans on Ross Island. * January 5 – Egypt's Zamalek SC is founded as a general sports and Association football club by Belgian lawyer George Merzbach as Qasr El Nile Club. * January 14 – Amundsen and Scott expeditions: Roald Amundsen's Norwegian S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
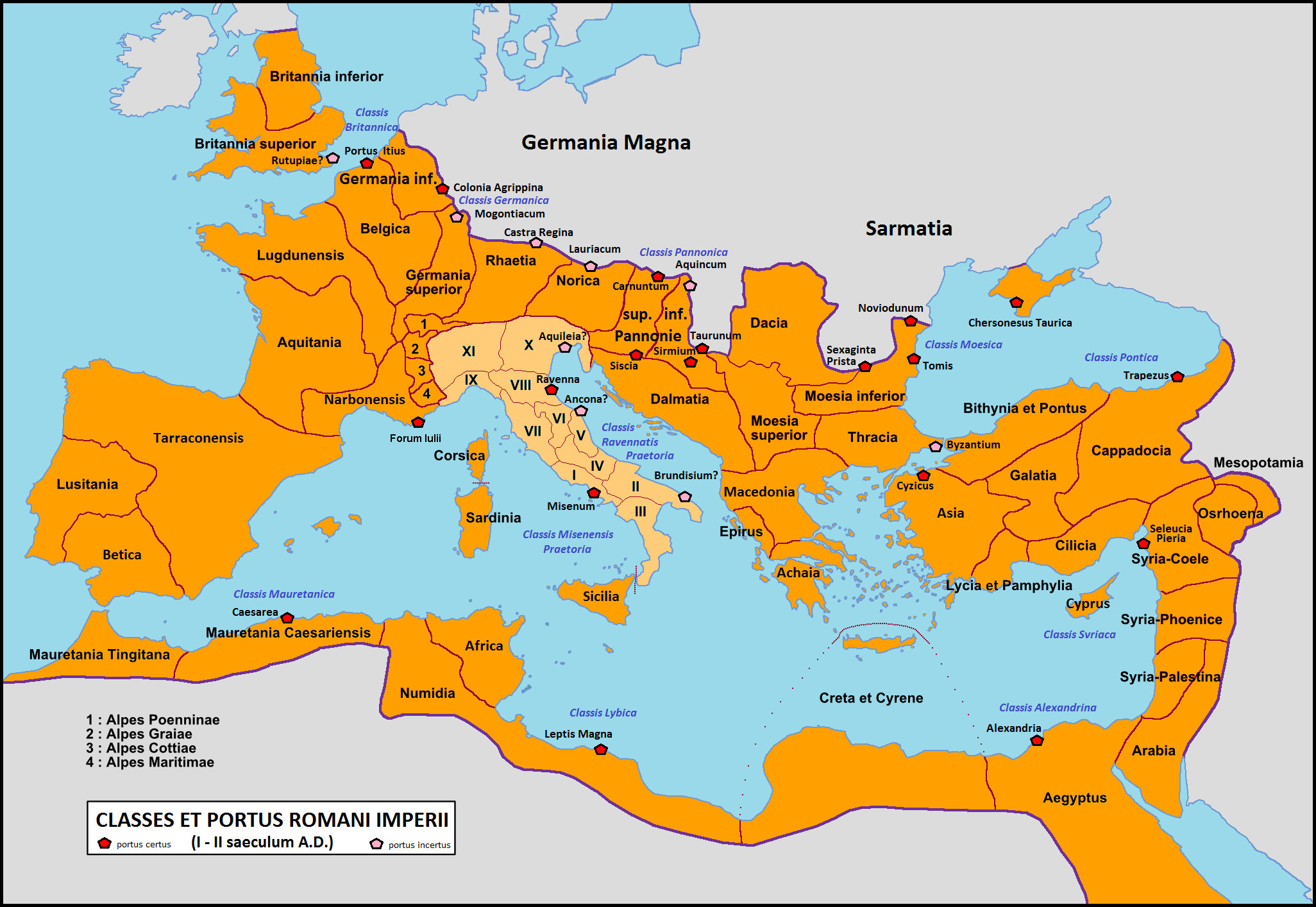
Portus Itius
Itius Portus or Portus Itius was the ancient Roman name for a sea port on the English Channel in what is now Nord-Pas-de-Calais, France, though its precise location is unknown. The main candidates have been Saint-Omer (''Sithiu''), Wissant and Boulogne (more usually called Gesoriacum and later Bononia), but a silted-up lagoon on the Flanders shore behind Calais now seems a most likely speculated area. Caesar Julius Caesar described calling ships ''ad portum Itium'' (used twice) to embark troops for his invasions of Britain in 54 BC. The location of the port was near the uplands round Cap Gris Nez (''Promunturium Itium''), but the exact site has been violently disputed ever since the Renaissance. Many critics have assumed that Caesar used the same port for his first expedition, but the name does not appear at all in that connection. This fact, coupled with other considerations, might make it probable that the two expeditions started from different places. However, Strabo (Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |