|
Surplus Product
Surplus product (german: Mehrprodukt, links=no) is an economic concept explicitly theorised by Karl Marx in his critique of political economy. Roughly speaking, it is the extra goods produced above the amount needed for a community of workers to survive at its current standard of living. Marx first began to work out his idea of surplus product in his 1844 notes on James Mill's ''Elements of political economy''. Notions of "surplus produce" have been used in economic thought and commerce for a long time (notably by the Physiocrats), but in ''Das Kapital'', '' Theories of Surplus Value'' and the '' Grundrisse'' Marx gave the concept a central place in his interpretation of economic history. Nowadays the concept is mainly used in Marxian economics, political anthropology, cultural anthropology, and economic anthropology. The frequent translation of the German "" as "surplus" makes the term "surplus product" somewhat inaccurate, because it suggests to English speakers that the prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 pamphlet ''The Communist Manifesto'' and the four-volume (1867–1883). Marx's political and philosophical thought had enormous influence on subsequent intellectual, economic, and political history. His name has been used as an adjective, a noun, and a school of social theory. Born in Trier, Germany, Marx studied law and philosophy at the universities of Bonn and Berlin. He married German theatre critic and political activist Jenny von Westphalen in 1843. Due to his political publications, Marx became stateless and lived in exile with his wife and children in London for decades, where he continued to develop his thought in collaboration with German philosopher Friedrich Engels and publish his writings, researching in the British Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruling Class
In sociology, the ruling class of a society is the social class who set and decide the political and economic agenda of society. In Marxist philosophy, the ruling class are the capitalist social class who own the means of production and by extension determine and establish the dominant ideology (culture, mores, norms, traditions) of society by way of cultural hegemony. In the 21st century, the worldwide political economy established by globalization has created a transnational capitalist class that is not native to any one country. Background In previous modes of production, such as feudalism (inheritable property and rights), the feudal lords of the manor were the ruling class; in an economy based upon chattel slavery, the slave owners were the ruling class. The political economy of the feudal system gave socio-economic and legal power to the feudal lord over the life, labour, and property of the vassal, including military service. The political economy of a slave state gav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
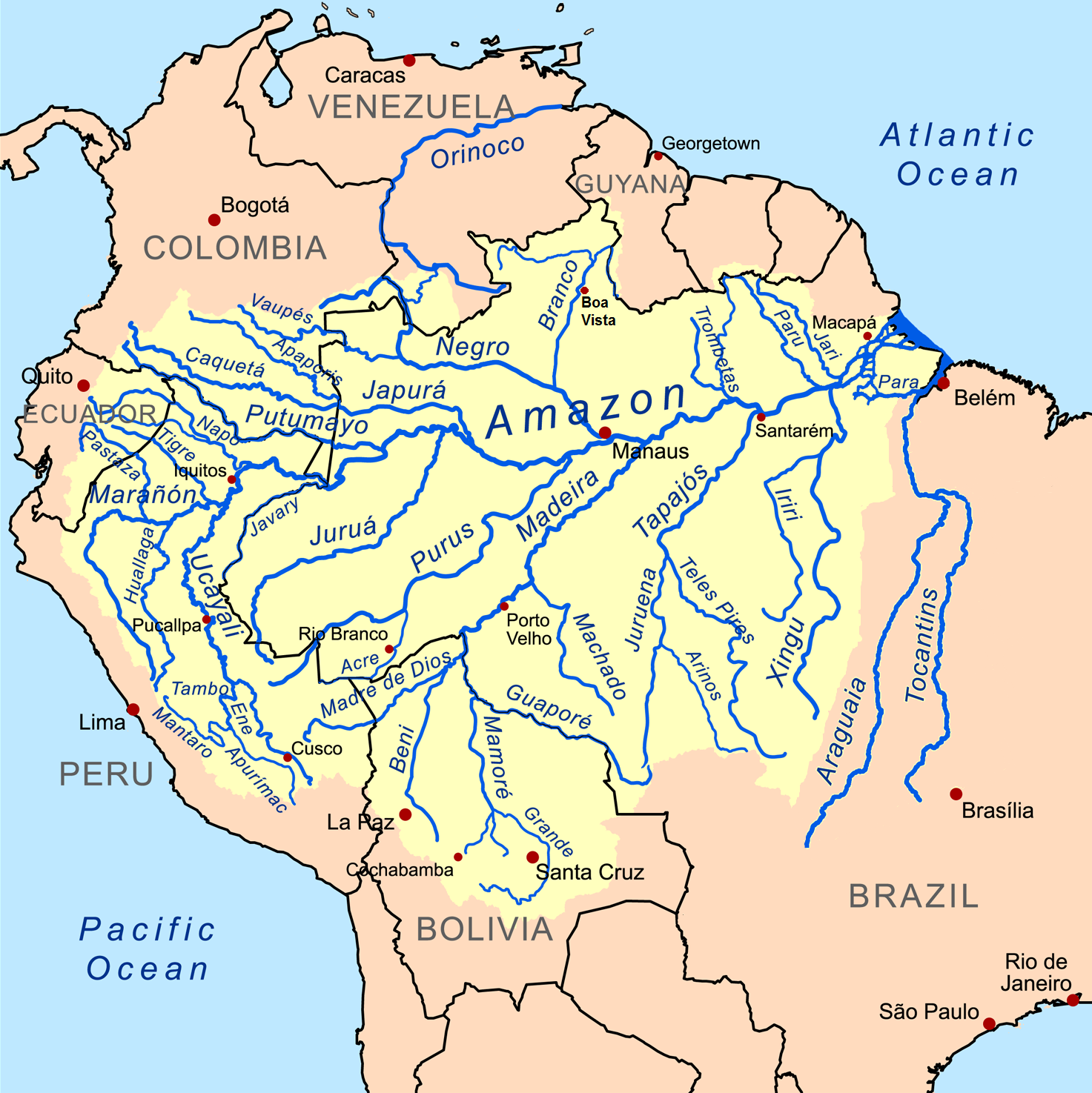
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuikuro
The Kuikuro are an indigenous people from the Mato Grosso region of Brazil. Their language, Kuikuro, is a part of the Cariban language family. The Kuikuro have many similarities with other Xingu tribes. They have a population of 592 in 2010, up from 450 in 2002. The Kuikuro are likely the descendants of the people who built the settlements known to archaeologists as Kuhikugu, located at the headwaters of the Xingu River.Heckenberger, Michael. ''The Ecology of Power: Culture, Place, and Personhood in the Southern Amazon, A.D. 1000-2000.'' New York: Routledge, 2005. The settlements were probably inhabited from around 1,500 years ago to about 400 years ago; after this point the population may have been reduced by diseases introduced by Europeans or, indirectly, by other native tribes who had traded with Europeans. Grann, David. ''The Lost City of Z: A Tale of Deadly Obsession in the Amazon.'' New York: Doubleday Publishing, 2009. Stories of Kuhikugu may have inspired the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Sahlins
Marshall David Sahlins ( ; December 27, 1930April 5, 2021) was an American cultural anthropologist best known for his ethnographic work in the Pacific and for his contributions to anthropological theory. He was the Charles F. Grey Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus of Anthropology and of Social Sciences at the University of Chicago.Moore, Jerry D. 2009. "Marshall Sahlins: Culture Matters" in ''Visions of Culture: an Introduction to Anthropological Theories and Theorists'', Walnut Creek, California: Altamira, pp. 365-385. Biography Marshall Sahlins was born in Chicago, the son of Bertha (Skud) and Paul A. Sahlins. His parents were Russian Jewish immigrants. His father was a doctor while his mother was a homemaker. He grew up in a secular, non-practicing family. His family claims to be descended from Baal Shem Tov, a mystical rabbi considered to be the founder of Hasidic Judaism. Sahlins' mother admired Emma Goldman and was a political activist as a child in Russia. Sahlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Childe
Vere Gordon Childe (14 April 189219 October 1957) was an Australian archaeologist who specialised in the study of European prehistory. He spent most of his life in the United Kingdom, working as an academic for the University of Edinburgh and then the Institute of Archaeology, London. He wrote twenty-six books during his career. Initially an early proponent of culture-historical archaeology, he later became the first exponent of Marxist archaeology in the Western world. Born in Sydney to a middle-class English migrant family, Childe studied classics at the University of Sydney before moving to England to study classical archaeology at the University of Oxford. There, he embraced the socialist movement and campaigned against the First World War, viewing it as a conflict waged by competing imperialists to the detriment of Europe's working class. Returning to Australia in 1917, he was prevented from working in academia because of his socialist activism. Instead, he worked for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Hudson (economist)
Michael Hudson (born March 14, 1939) is an American economist, Professor of Economics at the University of Missouri–Kansas City and a researcher at the Levy Economics Institute at Bard College, former Wall Street analyst, political consultant, commentator and journalist. He is a contributor to ''The Hudson Report'', a weekly economic and financial news podcast produced by Left Out. Hudson graduated from the University of Chicago (BA, 1959) and New York University (MA, 1965, PhD, 1968) and worked as a balance of payments economist in Chase Manhattan Bank (1964–1968). He was assistant professor of economics at the New School for Social Research (1969–1972) and worked for various governmental and non-governmental organizations as an economic consultant (1980s–1990s). Hudson has devoted his career to the study of debt, both domestic debt (loans, mortgages, interest payments), and external debt. In his works, he consistently advocates the idea that loans and exponentially g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral
A moral (from Latin ''morālis'') is a message that is conveyed or a lesson to be learned from a story or event. The moral may be left to the hearer, reader, or viewer to determine for themselves, or may be explicitly encapsulated in a maxim. A moral is a lesson in a story or in real life. Finding morals As an example of an explicit maxim, at the end of Aesop's fable of the Tortoise and the Hare, in which the plodding and determined tortoise won a race against the much-faster yet extremely arrogant hare, the stated moral is "slow and steady wins the race". However, other morals can often be taken from the story itself; for instance, that arrogance or overconfidence in one's abilities may lead to failure or the loss of an event, race, or contest. The use of stock characters is a means of conveying the moral of the story by eliminating complexity of personality and depicting the issues arising in the interplay between the characters, enabling the writer to generate a clear mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power (sociology)
In social science and politics, power is the social production of an effect that determines the capacities, actions, beliefs, or conduct of actors. Power does not exclusively refer to the threat or use of force ( coercion) by one actor against another, but may also be exerted through diffuse means (such as institutions). Power may also take structural forms, as it orders actors in relation to one another (such as distinguishing between a master and a slave), and discursive forms, as categories and language may lend legitimacy to some behaviors and groups over others. The term ''authority'' is often used for power that is perceived as legitimate or socially approved by the social structure. Power can be seen as evil or unjust; however, power can also be seen as good and as something inherited or given for exercising humanistic objectives that will help, move, and empower others as well. Scholars have distinguished between soft power and hard power. Theories Five b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surplus Labour
Surplus labour (German: ''Mehrarbeit'') is a concept used by Karl Marx in his critique of political economy. It means labour performed in excess of the labour necessary to produce the means of livelihood of the worker ("necessary labour"). The "surplus" in this context means the ''additional'' labour a worker has to do in their job, beyond earning their keep. According to Marxian economics, surplus labour is usually uncompensated (unpaid) labour. Origin Marx explains the origin of surplus labour in the following terms: The historical emergence of surplus labour is, according to Marx, also closely associated with the growth of trade (the economic exchange of goods and services) and with the emergence of a society divided into social classes. As soon as a permanent surplus product can be produced, the moral-political question arises as to how it should be distributed, and for whose benefit surplus-labour should be performed. The strong defeat the weak, and it becomes possible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |