|
Superficial Inguinal Ring
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. There is one inguinal canal on each side of the midline. Structure The inguinal canals are situated just above the medial half of the inguinal ligament. In both sexes the canals transmit the ilioinguinal nerves. The canals are approximately 3.75 to 4 cm long. , angled anteroinferiorly and medially. In males, its diameter is normally 2 cm (±1 cm in standard deviation) at the deep inguinal ring.The diameter has been estimated to be ±2.2cm ±1.08cm in Africans, and 2.1 cm ±0.41cm in Europeans. A first-order approximation is to visualize each canal as a cylinder. Walls To help define the boundaries, these canals are often further approximated as boxes with six sides. Not including the two rings, the remaining four sides are usually ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
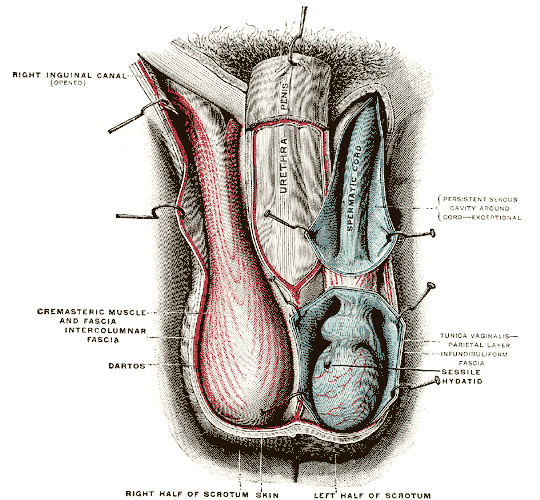
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
The anterior superior iliac spine ( abbreviated: ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle. The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle. Structure The anterior superior iliac spine refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. This is a key surface landmark, and easily palpated. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, the sartorius muscle, and the tensor fasciae latae muscle. A variety of structures lie close to the anterior superior iliac spine, including the subcostal nerve, the femoral artery (which passes between it and the pubic symphysis), and the iliohypogastric nerve. Clinical significance The anterior superior iliac sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labioscrotal Swellings
The labioscrotal swellings (genital swellings or labioscrotal folds) are paired structures in the human embryo that represent the final stage of development of the caudal end of the external genitals before sexual differentiation. In both males and females, the two swellings merge: * In the ''female'', they become the posterior labial commissure. The sides of the genital tubercle grow backward as the genital swellings, which ultimately form the labia majora; the tubercle itself becomes the mons pubis. In contrast, the labia minora are formed by the urogenital folds. * In the ''male'', they become the scrotum The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum co .... References External links "Development of Male External Genitalia", at mcgill.caDiagram at mhhe.com* * {{Authority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Abdominal Wall
In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls. There is a common set of layers covering and forming all the walls: the deepest being the visceral peritoneum, which covers many of the abdominal organs (most of the large and small intestines, for example), and the parietal peritoneum- which covers the visceral peritoneum below it, the extraperitoneal fat, the transversalis fascia, the internal and external oblique and transversus abdominis aponeurosis, and a layer of fascia, which has different names according to what it covers (e.g., transversalis, psoas fascia). In medical vernacular, the term 'abdominal wall' most commonly refers to the layers composing the anterior abdominal wall which, in addition to the layers mentioned above, includes the three layers of muscle: the transversus abdominis (transverse abdominal muscle), the internal (obliquus internus) and the external ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Crest
Medial to the pubic tubercle is the pubic crest, which extends from this process to the medial end of the pubic bone. It gives attachment to the conjoint tendon, the rectus abdominis, the abdominal external oblique muscle, and the pyramidalis muscle. The point of junction of the crest with the medial border of the bone is called the ''angle'' to it, as well as to the symphysis, the superior crus The superficial inguinal ring is bounded below by the crest of the pubis; on either side by the margins of the opening in the aponeurosis, which are called the crura of the ring; and above, by a series of curved intercrural fibers. * The infer ... of the subcutaneous inguinal ring is attached. References External links * Bones of the pelvis Pubis (bone) {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aponeurosis Of The Abdominal External Oblique Muscle
The aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle is a thin but strong membranous structure, the fibers of which are directed downward and medially. It is joined with that of the opposite muscle along the middle line, and covers the whole of the front of the abdomen; above, it is covered by and gives origin to the lower fibers of the pectoralis major; below, its fibers are closely aggregated together, and extend obliquely across from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle and the pectineal line to form the inguinal ligament. In the middle line, it interlaces with the aponeurosis of the opposite muscle, forming the linea alba, which extends from the xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis. That portion of the aponeurosis which extends between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle is a thick band, folded inward, and continuous below with the fascia lata; it is called the inguinal ligament. The portion which is reflected from the inguinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Ligament Of Uterus
The round ligament of the uterus is a ligament that connects the uterus to the labia majora. Structure The round ligament of the uterus originates at the uterine horns, in the parametrium. The round ligament exits the pelvis via the deep inguinal ring. It passes through the inguinal canal, and continues on to the labia majora. At the labia majora, its fibers spread and mix with the tissue of the mons pubis. Development The round ligament develops from the gubernaculum which attaches the gonad to the labioscrotal swellings in the embryo. Blood supply The round ligament is supplied by the artery of the round ligament of uterus, also known as ''Sampson's artery''. Function The function of the round ligament is maintenance of the anteversion of the uterus (a position where the fundus of the uterus is turned forward at the junction of cervix and vagina) during pregnancy. Normally, the cardinal ligament is what supports the uterine angle (angle of anteversion). When the uteru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitofemoral Nerve
The genitofemoral nerve refers to a nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. The femoral branch is different from the femoral nerve, which also arises from the lumbar plexus. Anatomy The genitofemoral nerve originates from the upper L1-2 segments of the lumbar plexus. It passes downwards, pierces the psoas major and emerges from its anterior surface. The nerve divides into two branches, the genital branch and the lumboinguinal nerve also known as the femoral branch, both of which then continue downwards and medially to the inguinal and femoral canal respectively. Genital Branch The genital branch continues downward on the surface of the psoas major muscle and then enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring. In men, the genital branch supplies the cremaster and scrotal skin. In women, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body cavity enclosed by the abdominal muscles, at front and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infundibuliform Fascia
The internal spermatic fascia (infundibuliform fascia, or Le deuxième fascia de Webster) is a thin layer, which loosely invests the spermatic cord. Structure The internal spermatic fascia is derived from the transversalis fascia. It is acquired by the spermatic cord at the deep inguinal ring. It has very little lymphatic drainage. It is mainly supplied by sensory afferents and the sympathetic nervous system. Additional images File:Gray1144.png, The scrotum. File:Mesorchium.svg, Schematic drawing of a cross-section through the vaginal process. References External links * - "The inguinal canal and derivation of the layers of the spermatic cord The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...." * * () Scrotum {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |