|
Sunadavinodini
Sunadavinodini is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāgam (or ''owdava'' rāgam, meaning pentatonic scale). It is a '' janya'' rāgam (derived scale), as it does not have all the seven '' swaras'' (musical notes). This raga was discovered by Mysore Vasudevachar. Structure and Lakshana ''Sunadavinodini'' is a symmetric rāgam that does not contain ''rishabham'' and ''panchamam''. It is a pentatonic scale (''audava-audava'' ragam''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications in Carnatic music classification – ''audava'' meaning 'of 5'). Its ' structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * : * : (notes used in this scale are ''antara gandharam, prati madhyamam, chathusruthi dhaivatham, kakali nishadham'') ''Sunadavinodini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunadavinodini Scale
Sunadavinodini is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāgam (or ''owdava'' rāgam, meaning pentatonic scale). It is a ''janya'' rāgam (derived scale), as it does not have all the seven ''swaras'' (musical notes). This raga was discovered by Mysore Vasudevachar. Structure and Lakshana ''Sunadavinodini'' is a symmetric rāgam that does not contain ''rishabham'' and ''panchamam''. It is a pentatonic scale (''audava-audava'' ragam''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications in Carnatic music classification – ''audava'' meaning 'of 5'). Its ' structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * : * : (notes used in this scale are ''antara gandharam, prati madhyamam, chathusruthi dhaivatham, kakali nishadham'') ''Sunadavinodini' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graha Bhedam
''Graha Bhedam'' in Carnatic music is the process (or result of the process) of shifting the Tonic note (''śruti'') to another note in the rāgam and arriving at a different rāgam. Its equivalent in Hindustani classical music is called a ''murchhana''. Expressed in Western music theory terms, this is the process of arriving at a different scale by shifting to another mode in the key. ''Graha'' literally means ''position'' and ''Bhedam'' means ''change''. Since the position of the ''śruti'' is changed (pitch of the base note or drone), it is also sometimes called ''Swara Bhedam'' or ''Śruti Bhedam'' though ''Śruti Bhedam'' and ''Graha Bhedam'' have some technical differences. Definition Modal shift of the Tonic note to higher notes of a rāgam, while retaining the note's positions ( swara sthānas – sthāna means position/ pitch), results in different rāgams. This is called ''Graha Bhedam''. Practical demo A simple practical demonstration of ''Graha Bhedam'' can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore Vasudevacharya
Mysore Vasudevacharya (28 May 1865 – 17 May 1961) was an Indian musician and composer of Carnatic music compositions who belonged to the direct line of Thyagaraja's disciples. Vasudevachar's compositions (numbering over 200) were mostly in Telugu and Sanskrit. Some of his most popular kritis include '' Broche varevaru ra'' in Khamas raga, ''Devadideva'' in Sunadavinodini, ''Mamavatu Sri Saraswati'' in Hindolam, ''Shankari Ninne'' in Pantuvarali, ''Bhajare Re Manasa'' in Abheri and ''Ra Ra Rajeevalochana Rama'' in Mohanam. He was a recipient of the civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan. He is credited with two writings in Kannada, one of them an autobiography called ''Nenapugalu'' (memories) and ''Na Kanda Kalavidaru'' (the musicians I have met) in which he wrote the biographies of many well known musicians. Mysore Vasudevachar also taught in Rukmini Devi's Kalakshetra, (founded in 1936). He was already quite old by then, but thanks to Rukmini Devi he agreed to shift to Kalakshe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamsanandi
Hamsanandi (pronounced hamsānandi) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is a hexatonic scale (''shadava'' rāgam, which means "of 6"). It is a derived scale (''janya'' rāgam), as it does not have all the seven ''swaras'' (musical notes). ''Hamsanandi'' is a ''janya'' rāgam of '' Gamanashrama'', the 53rd '' Melakarta'' rāgam. It has only the invariant ''panchamam'' missing from its parent scale, ''Gamanashrama'', like ''Shree ranjani''. Sohni raga in Hindustani classical music that belongs to the Marwa thaat resembles Hamsanandi.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras Structure and Lakshana ''Hamsanandi'' is a symmetric scale that does not contain ''panchamam''. It is called a ''shadava-shadava'' rāgam,''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications in Carnatic music classification (as it has 6 notes in both ascending and descending scales). Its ''ārohaṇa-av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revati (ragam)
Revati is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāgam (or ''owdava'' rāgam, meaning pentatonic scale). It is a ''janya'' rāgam (derived scale), as it does not have all the seven ''swaras'' (musical notes). In Hindustani music a raga that closely resembles ''Revati'' is ''Bairagi Bhairav''.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras It is said to evoke ''Karuṇa'' rasa (pathos). This scale has also been used in chanting Vedas. Structure and Lakshana ''Revati'' is a symmetric rāgam that does not contain ''gāndhāram'' or ''dhaivatam''. It is a pentatonic scale (''audava-audava'' ragam''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications in Carnatic music classification – ''audava'' meaning 'of 5'). Its ' structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * : * : (notes used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivaranjani
Shivaranjani or Sivaranjani is a musical scale used in Indian classical music. There are two scales, one in Hindustani music and one in Carnatic music. The Hindustani rāga is a pentatonic scale, as is the Carnatic scale categorized as Audava-Audava (''audava'' meaning 'of 5') resulting in 5 notes in the Arohanam and 5 in the Avarohanam. Hindustani scale The Hindustani rāga ''Shivaranjani'' belongs to the '' Kaafi thaat'' in terms of classification of the scale.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras Its structure is as follows: * : * : The ''komal''(soft) ''gandhar''(g) in place of ''shuddh gandhar'' (G) is the difference between this rāga and the global musical scale of '' Bhoop''. Borrowed into Carnatic music In Karnatic Music, this is a ''janya'' rāga (derived scale) from 22nd mela-kartha raga Kharaharapriya. It is a ''audava-audava'' rāgam in Carnatic music classification (i.e., a ragam that has five notes in both its arohan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
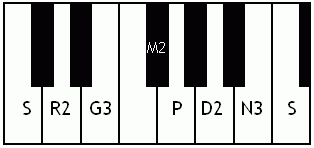
Kalyani (raga)
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the beginning of concerts because it is considered auspicious. Structure and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rāga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each ''rāga'' is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience. Each ''rāga'' provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the ''rāga'' in keeping with rules specific to the ''rāga''. ''Rāga''s range from small ''rāga''s like Bahar and Shahana that are not much more than songs to big ''rāga''s like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances can last over an hour. ''Rāga''s may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilaiyaraaja
Ilaiyaraaja (born R. Gnanathesikan, 3 June 1943) is an Indian musician, composer, arranger, conductor, orchestrator, instrumentalist, lyricist and singer, popular for his works in Indian Cinema, prominently in Tamil films. Reputed to be one of the most prolific Indian composers, in a career spanning over forty-five years, he has composed over 7,000 songs and provided film scores for over 1,000 films, apart from performing in over 20,000 concerts. Ilaiyaraaja received several awards for his works throughout his career. In 2012, for his creative and experimental works in the field of music, he received the Sangeet Natak Akademi Award, the highest Indian recognition given to people in the field of performing arts. In 2010, he was awarded the Padma Bhushan, the third-highest civilian honour in India; and was conferred the Padma Vibhushan in 2018, the second-highest civilian award by the government of India. He is a nominated Member of Parliament in the Indian upper house, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadhiyai Thedi Vandha Kadal
''Nadhiyai Thedi Vandha Kadal'' () is a 1980 Tamil language film. The directorial debut of B. Lenin, it starred Jayalalithaa in the lead role, opposite actor Sarath Babu. It was the last Tamil film to release with Jayalalithaa in the lead role. The film is based on the novel written by Maharishi. Plot Cast * Jayalalithaa * Sarath Babu * Fatafat Jayalaxmi * Srikanth * Master Sekhar * Jamila Production Jayalalithaa agreed to act opposite Sarath Babu at the insistence of her co-star in many films, Rama Prabha, Sarath Babu’s then wife. The other reason for accepting to act in this film was the debutant director B. Lenin, son of A. Bhimsingh, who had directed her in ''Paadhukaappu'' and '' Kanavan Manaivi''. It was not released at every centre in Tamil Nadu, as most film distributors did not buy rights from producers, citing that casting Jayalalithaa, who had a superstar image, with actors who were considered lesser mortals, would not be acceptable to the public. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anonymous Work
Anonymous works are works, such as art or literature, that have an anonymous, undisclosed, or unknown creator or author. In the case of very old works, the author's name may simply be lost over the course of history and time. There are a number of reasons anonymous works arise. Description In the United States, anonymous work is legally defined as "a work on the copies or phonorecords of which no natural person is identified as author." Explanations In the case of very old works, the author's name may simply be lost over the course of history and time. In such cases the author is often referred to as Anonymus, the Latin form of "anonymous". In other cases, the creator's name is intentionally kept secret. The author's reasons may vary from fear of persecution to protection of his or her reputation. Legal reasons may also bar an author from self-identifying. An author may also wish to remain anonymous to avoid becoming famous for their work. See also * Anonymous post * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |