|
SrbA SRNA
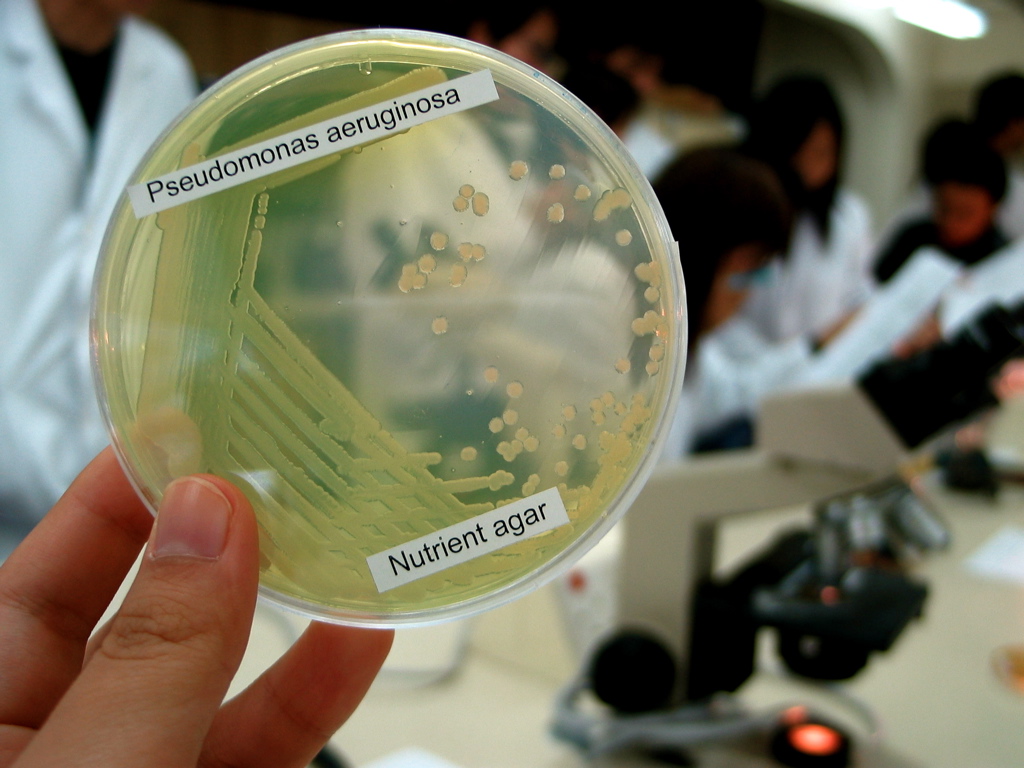
SrbA ( sRNA regulator of biofilms A) is a small regulatory non-coding RNA identified in pathogenic ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'.'' It is important for biofilm formation and pathogenicity. Bacterial strain with deleted SrbA had reduced biofilm mass. As the ability to form biofilms can contribute to the ability a pathogen to thrive within the host, the ''C. elegans'' hosts infected with the srbA deleted strain displayed significantly lower mortality rate than the wild-type strain. However, the deletion of srbA had no effect on growth or antibiotic resistance in ''P. aeruginosa''. See also * NrsZ small RNA * ''Pseudomonas'' sRNA * AsponA antisense RNA AsponA is a small asRNA transcribed antisense to the penicillin-binding protein 1A gene called ''ponA.'' It was identified by RNAseq and the expression was validated by 5' and 3' RACE experiments in '' Pseudomanas aeruginosa''. ''AsponA'' express ... References Non-coding RNA {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small RNA
Small RNA (sRNA) are polymeric RNA molecules that are less than 200 nucleotides in length, and are usually non-coding. RNA silencing is often a function of these molecules, with the most common and well-studied example being RNA interference (RNAi), in which endogenously expressed microRNA (miRNA) or exogenously derived small interfering RNA (siRNA) induces the degradation of complementary messenger RNA. Other classes of small RNA have been identified, including piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) and its subspecies repeat associated small interfering RNA (rasiRNA). Small RNA "is unable to induce RNAi alone, and to accomplish the task it must form the core of the RNA–protein complex termed the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), specifically with Argonaute protein". Small RNA have been detected or sequenced using a range of techniques, including directly by MicroRNA sequencing on several sequencing platforms, or indirectly through genome sequencing and analysis. Identification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not Translation (genetics), translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important list of RNAs, types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, Extracellular RNA, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long noncoding RNA, long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent Transcriptomics, transcriptomic and Bioinformatics, bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function. There is no consensus in the literature on how much of non-coding transcription is functional. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional (sometimes r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
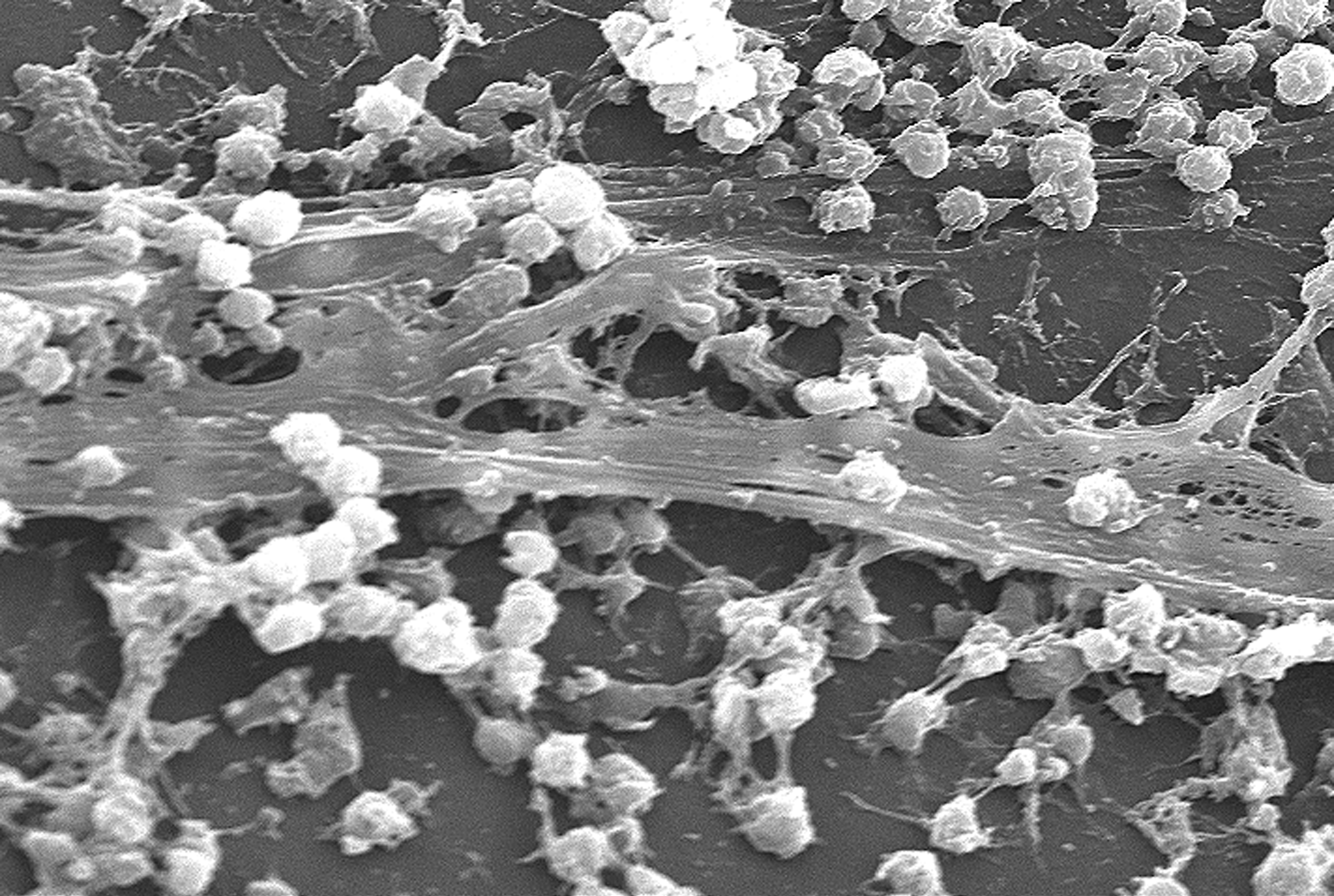
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it '' Rhabditides elegans.'' Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular and developmental biology of ''C. elegans'', which has since been extensively used as a model organism. It was the first mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NrsZ Small RNA
NrsZ (nitrogen regulated small RNA) is a bacterial small RNA found in the opportunistic pathogen ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' PAO1. Its transcription is induced during nitrogen limitation by the NtrB/C two-component system (an important regulator of nitrogen assimilation and swarming motility) together with the alternative sigma factor RpoN ( a global regulator involved in nitrogen metabolism). NrsZ by activating ''rhlA (''a gene essential for rhamnolipids synthesis) positively regulates the production of rhamnolipid Rhamnolipids are a class of glycolipid produced by ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', amongst other organisms, frequently cited as bacterial surfactants. They have a glycosyl head group, in this case a rhamnose moiety, and a 3-(hydroxyalkanoyloxy)alkanoic ... surfactants needed for swarming motility. See also * ''Pseudomonas'' sRNA * SrbA sRNA * AsponA antisense RNA References Non-coding RNA {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas SRNA
''Pseudomonas'' sRNA are non-coding RNAs (ncRNA) that were predicted by the bioinformatics, bioinformatic program SRNApredict2. This program identifies putative sRNAs by searching for co-localization of genetic features commonly associated with sRNA-encoding genes and the gene expression, expression of the predicted sRNAs was subsequently confirmed by Northern blot analysis. These sRNAs have been shown to be conservation (genetics), conserved across several ''pseudomonas'' species but their function is yet to be determined. Using Tet-Trap genetic approach RNA thermometer, RNAT genes post-transcriptionally regulated by temperature upshift were identified: ''ptxS'' (implicated in virulence) and PA5194. See also *Bacillus subtilis BSR sRNAs, ''Bacillus subtilis'' sRNA *C. elegans small RNAs, ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' sRNA *Mycobacterium tuberculosis sRNA, ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' sRNA *Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron sRNA, ''Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron'' sRNA *NrsZ small RNA *Aspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AsponA Antisense RNA
AsponA is a small asRNA transcribed antisense to the penicillin-binding protein 1A gene called ''ponA.'' It was identified by RNAseq and the expression was validated by 5' and 3' RACE experiments in '' Pseudomanas aeruginosa''. ''AsponA'' expression was up or down regulated under different antibiotic stress. Owing to its location it may be able to prevent the transcription or translation of the opposite gene. Study by Wurtzel ''et al.'' and Ferrara ''et al.'' also detected its expression. See also * NrsZ small RNA NrsZ (nitrogen regulated small RNA) is a bacterial small RNA found in the opportunistic pathogen ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' PAO1. Its transcription is induced during nitrogen limitation by the NtrB/C two-component system (an important regulator of ... * SrbA sRNA * ''Pseudomonas'' sRNA References {{Reflist Non-coding RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |