|
Soyuz 7K-ST No. 16L
Soyuz 7K-ST No.16L, sometimes known as Soyuz T-10a or Soyuz T-10-1, was an unsuccessful Soyuz mission intended to visit the Salyut 7 space station, which was occupied by the Soyuz T-9 crew. However, it never finished its launch countdown; the launch vehicle was destroyed on the launch pad by fire on 26 September 1983. The launch escape system of the Soyuz spacecraft fired six seconds before the launch vehicle exploded, saving the crew. As of 2022, it remains the only time a launch escape system has been fired before launch with a crew on board. Crew Mission highlights The crew was sitting on the pad awaiting fueling of the Soyuz-U booster to complete prior to liftoff. Approximately 90 seconds before the intended launch, a bad valve caused nitrogen pressurisation gas to enter the RP-1 turbopump of the Blok B strap-on. The pump began spinning up, but with no propellant in it, the speed of rotation quickly exceeded its design limits which caused it to rupture and all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (russian: Салют-7; en, Salute 7) (a.k.a. DOS-6, short for Durable Orbital Station) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress, and TKS spacecraft. It was part of the Soviet Salyut programme, and launched on 19 April 1982 on a Proton rocket from Site 200/40 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Soviet Union. Salyut 7 was part of the transition from monolithic to modular space stations, acting as a testbed for docking of additional modules and expanded station operations. It was the eighth space station of any kind launched. Salyut 7 was the last of both the second generation of DOS-series space stations and of the monolithic Salyut Program overall, to be replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
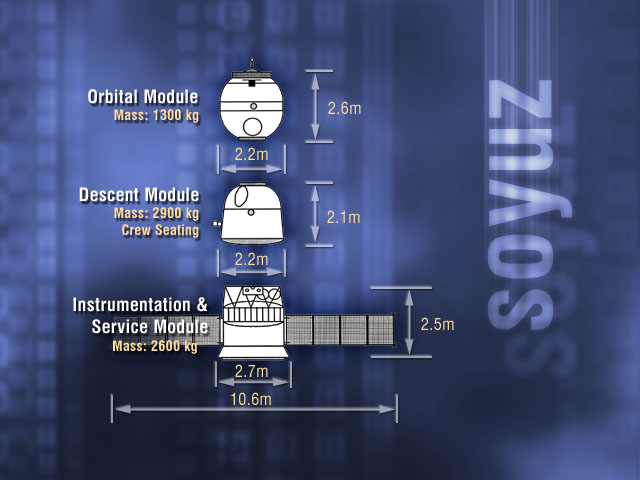
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TASS
The Russian News Agency TASS (russian: Информацио́нное аге́нтство Росси́и ТАСС, translit=Informatsionnoye agentstvo Rossii, or Information agency of Russia), abbreviated TASS (russian: ТАСС, label=none), is a major Russian state-owned news agency founded in 1904. TASS is the largest Russian news agency and one of the largest news agencies worldwide. TASS is registered as a Federal State Unitary Enterprise, owned by the Government of Russia. Headquartered in Moscow, TASS has 70 offices in Russia and in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), as well as 68 bureaus around the world. In Soviet times, it was named the Telegraph Agency of the Soviet Union (russian: Телегра́фное аге́нтство Сове́тского Сою́за, translit=Telegrafnoye agentstvo Sovetskogo Soyuza, label=none) and was the central agency for news collection and distribution for all Soviet newspapers, radio and television stations. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz T-15
Soyuz T-15 (russian: Союз T-15, ''Union T-15'') was a crewed mission to the Mir and Salyut 7 space stations and was part of the Soyuz programme. It marked the final flight of the Soyuz-T spacecraft, the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, which had been in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. This mission marked the first time that a spacecraft visited, and docked with, two space stations in the same mission. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters * Mass: 6850 kg * Perigee: 331 km * Apogee: 366 km * Inclination: 51.6° * Period: 91.5 minutes Mission highlights Soyuz T-15 was both the first expedition to Mir and the last to Salyut 7. Flight to Mir Due to the pressure of launching Mir in time for the 27th Communist Party Congress, mission planners were left without the newer Soyuz-TM spacecraft or any of the planned modules to launch to the station at first. It was decided to launch an older Soyuz-T as Soyuz T-15 on a dual mission to both Mir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
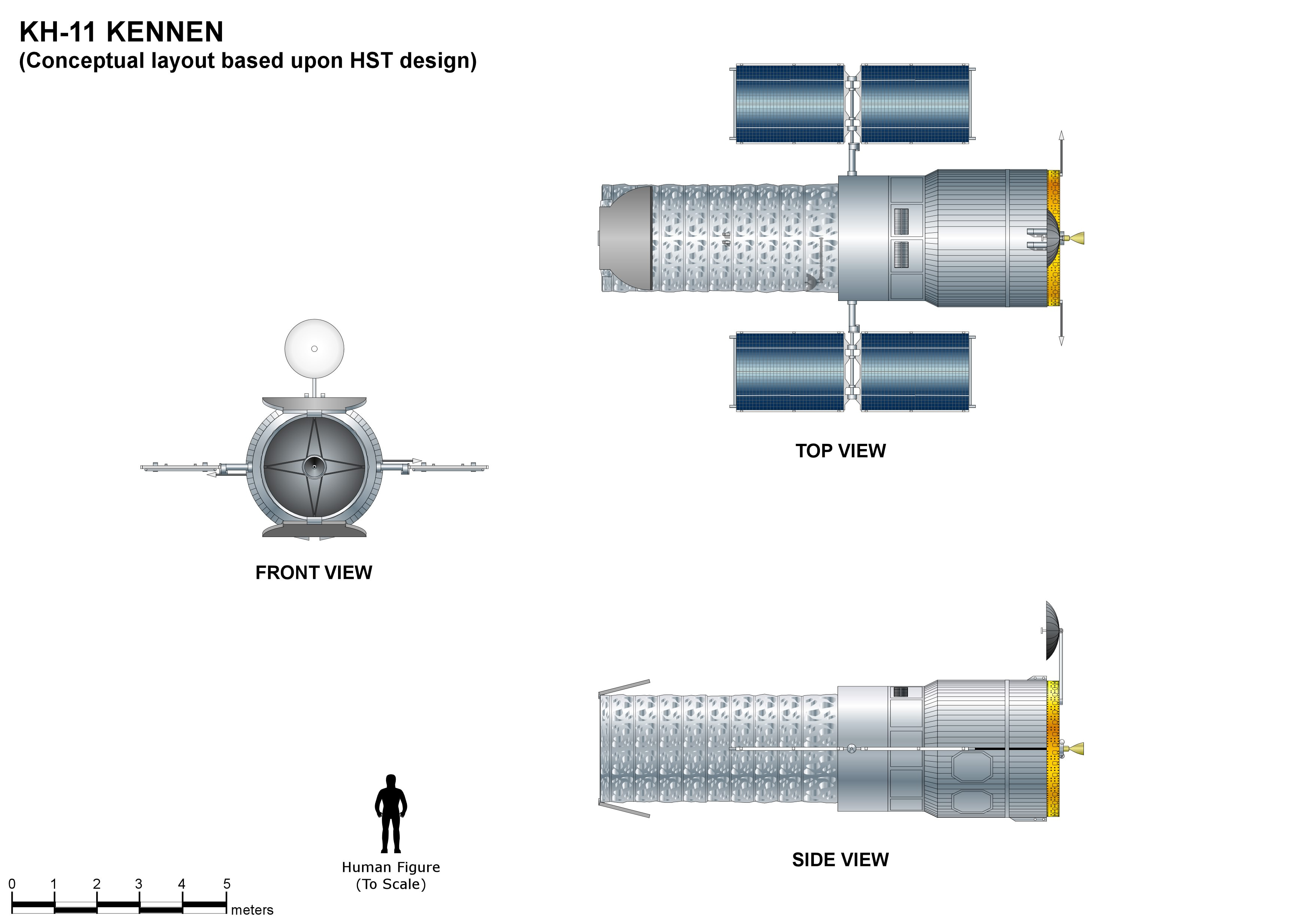
KH-11
The KH-11 KENNEN (later renamed CRYSTAL,p.199-200 then Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System, and codenamed 1010 and Key Hole) is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and so offer real-time optical observations. Later KH-11 satellites have been referred to by outside observers as KH-11B or KH-12, and by the names "Advanced KENNEN", "Improved Crystal" and "Ikon". Official budget documents refer to the latest generation of electro-optical satellites as ''Evolved Enhanced CRYSTAL System''. The Key Hole series was officially discontinued in favor of a random numbering scheme after repeated public references to KH-7 GAMBIT, KH-8 GAMBIT 3, KH-9 HEXAGON, and KH-11 KENNEN satellites. The capabilities of the KH-11 are highly classified, as are images they produce. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vodka
Vodka ( pl, wódka , russian: водка , sv, vodka ) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impurities and flavourings. Traditionally, it is made by distilling liquid from fermented cereal grains, and potatoes since introduced in Europe in the 1700's. Some modern brands use fruits, honey, or maple sap as the base. Since the 1890s, standard vodkas have been 40% alcohol by volume (ABV) (80 U.S. proof). The European Union has established a minimum alcohol content of 37.5% for vodka. Vodka in the United States must have a minimum alcohol content of 40%. Vodka is traditionally drunk "neat" (not mixed with water, ice, or other mixers), and it is often served ''freezer chilled'' in the vodka belt of Belarus, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and Ukraine. It is also used in cocktails and mixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/ oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persians, Mongols, and Indians as early as the 13th century. All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant up until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications for their simplicity and reliability. Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation and because they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. The lower performance of solid propellants (as compared to liquids) does not favor their use as primary propu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shield
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is also often used to refer to the thermal energy contained in a system as a component of its internal energy and that is reflected in the temperature of the system. For both uses of the term, heat is a form of energy. An example of formal vs. informal usage may be obtained from the right-hand photo, in which the metal bar is "conducting heat" from its hot end to its cold end, but if the metal bar is considered a thermodynamic system, then the energy flowing within the metal bar is called internal energy, not heat. The hot metal bar is also transferring heat to its surroundings, a correct statement for both the strict and loose meanings of ''heat''. Another example of informal usage is the term '' heat content'', used despite the fact that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grid Fin
Grid fins (or lattice fins) are a type of flight control surface used on rockets and bombs, sometimes in place of more conventional control surfaces, such as planar fins. They were developed in the 1950s by a team led by and used since the 1970s in various Soviet ballistic missile designs such as the SS-12 ''Scaleboard'', SS-20 ''Saber'', SS-21 ''Scarab'', SS-23 ''Spider'', and SS-25 ''Sickle'', as well as the N-1 (the intended rocket for the Soviet moon program). In Russia, they are thus often referred to as ' grid fins. Grid fins have also been used on conventional missiles and bombs such as the Vympel R-77 air-to-air missile; the 3M-54 Klub (SS-N-27 Sizzler) family of cruise missiles; and the American Massive Ordnance Air Blast (MOAB) large-yield conventional bomb, and on specialized devices such as the Quick-MEDS delivery system and as part of the launch escape system for the Soyuz spacecraft. In 2014, SpaceX tested grid fins on a first-stage demonstration test ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reentry Capsule
A reentry capsule is the portion of a space capsule which returns to Earth following a spaceflight. The shape is determined partly by aerodynamics; a capsule is aerodynamically stable falling blunt end first, which allows only the blunt end to require a heat shield for atmospheric entry. A crewed capsule contains the spacecraft's instrument panel, limited storage space, and seats for crew members. Because a capsule shape has little aerodynamic lift, the final descent is via parachute, either coming to rest on land, at sea, or by active capture by an aircraft. In contrast, the development of spaceplane reentry vehicles attempts to provide a more flexible reentry profile. Structure Reentry capsules have typically been smaller than in diameter due to launch vehicle aerodynamic requirements. The capsule design is both volumetrically efficient and structurally strong, so it is typically possible to construct small capsules of performance comparable to lifting body or spaceplane d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Module
The orbital module is a compartment of some space capsules used only in orbit. It is separated from the crewed reentry capsule before reentry. The orbital module provides 'habitat' space to use in orbit, while the reentry capsule tends to be focused on the machinery needed to get seated passengers back safely, with heavy structural margins. These have developed for the Soyuz spacecraft. Soyuz orbital module The orbital module is a spherical part of Soviet-Russian Soyuz space capsule series. Designed for use only in orbit, the module does not need to be strengthened to survive re-entry, allowing it to provide more usable space for less weight than other manned capsule designs. It serves mainly as a living compartment during orbital flight, and when used as a space station ferry it stores cargo on ascent and is filled with trash which burns up on descent. On early Soyuz missions the module was used for experiments and even as an airlock for the Soyuz 4/ Soyuz 5 EVA crew transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payload Shroud
A payload fairing is a nose cone used to protect a spacecraft payload against the impact of dynamic pressure and aerodynamic heating during launch through an atmosphere. An additional function on some flights is to maintain the cleanroom environment for precision instruments. Once outside the atmosphere the fairing is jettisoned, exposing the payload to outer space. The standard payload fairing is typically a cone-cylinder combination, due to aerodynamic considerations, although other specialized fairings are in use. The type of fairing which separates into two halves upon jettisoning is called a clamshell fairing by way of analogy to the bifurcating shell of a clam. In some cases the fairing may enclose both the payload and the upper stage of the rocket, such as on Atlas V and Proton M. If the payload is attached both to the booster's core structures and to the fairing, the payload may still be affected by the fairing's bending loads, as well as inertia loads due to vib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |