|
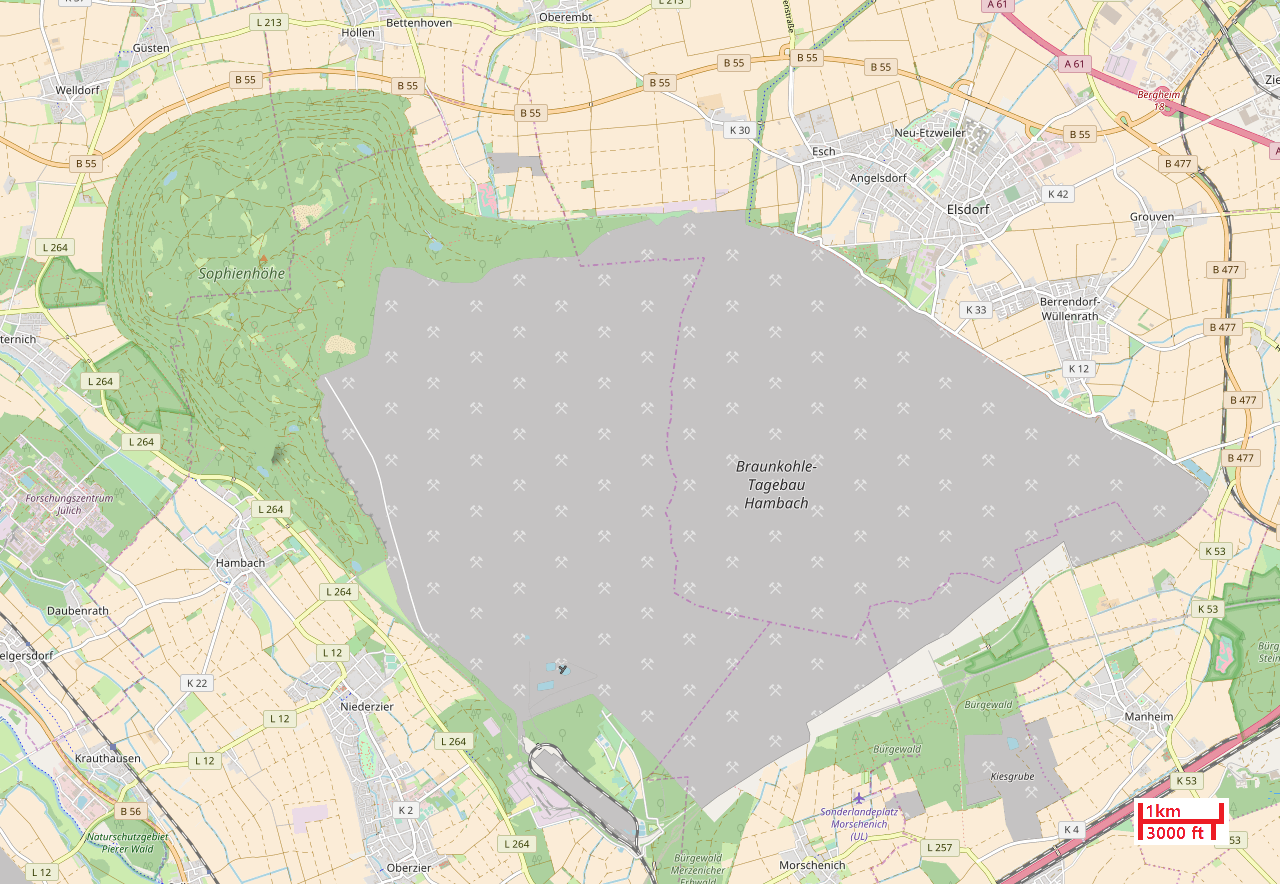
Sophienhöhe
The Sophienhöhe (301.8 m AMSL) is the largest artificial hill worldwide, created by surface mining at the open cast lignite mine Tagebau Hambach operated by RWE Power AG in Düren (district), North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Location Sophienhöhe is about 6 km east of the city centre of Jülich bordering Niederzier and Titz at the north-end of the open pit Tagebau Hambach. The distance (in respect to sea-level) between the top of Sophienhöhe and the lowest point of the pit is 594.8 meters. Tagebau Hambach is the lowest surface point in Europe, lying 293 meters below sea level Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise .... The CIA still maintains that Neuendorf bei Wilster is Germany's lowest point. The highest points of Sophienhöhe are Höller Horn (291.5 m A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagebau Hambach
The Tagebau Hambach is a large open-pit coal mine (german: Tagebau) in Niederzier and Elsdorf, North Rhine–Westphalia, Germany. It is operated by RWE and used for mining lignite. The mine is on the site of the ancient Hambach Forest, which was purchased by RWE in 1978. The company then cut most of the forest down and cleared it to mine. Only 10% of the forest area remains. RWE planned to clear half of the remaining area between 2018 and 2020. This plan was met with massive protests in the autumn of 2018 and was temporarily stopped in October 2018 by the supreme administrative court of North Rhine–Westphalia (Oberverwaltungsgericht für das Land Nordrhein-Westfalen). Begun in 1978, the mine's operation area currently (as of end of 2017) has a size of 43.8 km2, with the total area designated for mining having a size of 85 km2. It is the deepest open pit mine with respect to sea level: the bottom of the pit, with up to from the surface, is below sea level, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophienhöhe L
The Sophienhöhe (301.8 m AMSL) is the largest artificial hill worldwide, created by surface mining at the open cast lignite mine Tagebau Hambach operated by RWE Power AG in Düren (district), North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Location Sophienhöhe is about 6 km east of the city centre of Jülich bordering Niederzier and Titz at the north-end of the open pit Tagebau Hambach. The distance (in respect to sea-level) between the top of Sophienhöhe and the lowest point of the pit is 594.8 meters. Tagebau Hambach is the lowest surface point in Europe, lying 293 meters below sea level. The CIA still maintains that Neuendorf bei Wilster is Germany's lowest point. The highest points of Sophienhöhe are Höller Horn (291.5 m AMSL), Jülicher Kopf (285.8 m AMSL) and the Roman Tower (301.8 m AMSL). See also * List of mountains and hills in North Rhine-Westphalia * Hambach Forest Hambach Forest (german: Hambacher Wald, Hambacher Forst (), Bürgewald, Die Bürge) is an anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hambach Forest
Hambach Forest (german: Hambacher Wald, Hambacher Forst (), Bürgewald, Die Bürge) is an ancient forest located near in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany, between Cologne and Aachen. It was planned to be cleared as part of the Hambach surface mine by owner RWE AG. There were protests and occupations from 2012 against this, and in 2020 a law was passed to preserve it. The forest Hambach Forest is rich in biodiversity and home to 142 species regarded as important for conservation. The forest has been called ''"the last remnant of a sylvan ecosystem that has occupied this part of the Rhine River plain between Aachen and Cologne since the end of the last ice age"''. Only ten percent of Hambach Forest still remains, and the remaining forest is severely threatened by mining for brown coal. Of special interest is the rare Bechstein's bat population, which is strictly protected according to annex II and annex IV of the European Habitats Directive. An Environmental Impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
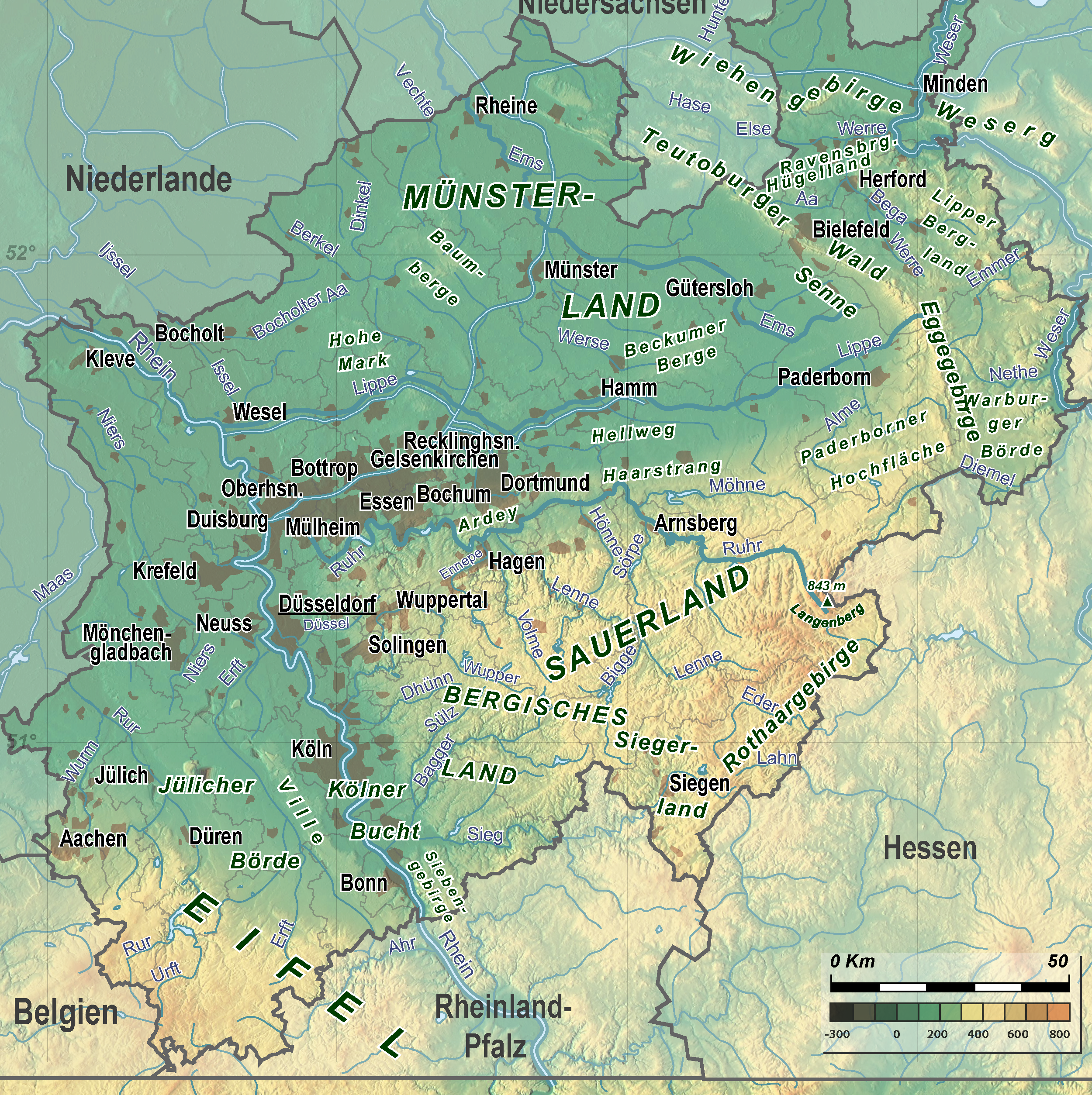
List Of Mountains And Hills In North Rhine-Westphalia
This list of the mountains and hills in North Rhine-Westphalia shows a selection of high or well-known mountains and hills in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia (''in order of height''). Highest points of the North Rhine-Westphalian provinces The following table gives the highest hill or point in the five provinces (''Regierungsbezirke'') of North Rhine-Westphalia. By clicking on the word "List" in the "Lists" column you will be taken to a list of other hills in the respective region or hill range (some of which lie partly outside of North Rhine-Westphalia}. The table is listed in order of height, but can be sorted by other columns by clicking on the symbol at the head. *The highest point in the Province of Detmold is on the flank of the Totenkopf in the Sauerland near Bad Wünnenberg. The provincial boundary runs up to a height of . Highest points of the North Rhine-Westphalian regions In the following table are the highest mountains and hills in the various Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jülich
Jülich (; in old spellings also known as ''Guelich'' or ''Gülich'', nl, Gulik, french: Juliers, Ripuarian: ''Jöllesch'') is a town in the district of Düren, in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. As a border region between the competing powers in the Lower Rhine and Meuse areas, the town and the Duchy of Jülich played a historic role from the Middle Ages up to the 17th century. Geography Jülich stands in the Rur valley on the banks of the river Rur. The town is bordered by the town of Linnich in the north, the municipality of Titz in the northeast, the municipality of Niederzier in the southeast, the municipality of Inden in the south, and by the municipality of Aldenhoven in the west. Its maximum size is 13.3 km from east to west and 10.9 km from north to south. The highest point in Jülich is in Bourheim, 110 m above sea level (excepting Sophienhöhe, an extensive artificial mountain made up of overburden from a nearby open-pit l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains And Hills Of North Rhine-Westphalia
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMSL
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''. The combination of unit of measurement and the physical quantity (height) is called "metres above mean sea level" in the metric system, while in United States customary and imperial units it would be called " feet above mean sea level". Mean sea levels are affected by climate change and other factors and change over time. For this and other reasons, recorded measurements of elevation above sea level at a reference time in history might differ from the actual elevation of a given location over sea level at a given moment. Uses Metres above sea level is the standard measurement of the elevation or altitude of: * Geographic locations such as towns, mountains and other landmarks. * The top of buildings and other structures. * Flying objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuendorf Bei Wilster
Neuendorf-Sachsenbande is a municipality in Wilstermarsch, in the district of Steinburg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town is notable for containing the lowest accessible point in Germany, which is 3.54 m (11.61 ft) below sea level. History The history of the town only dates back to April 15, 2003, when the town was formed from the merger of the municipalities of ''Neuendorf bei Wilster'' and ''Sachsenbande'' to the municipality of ''Bredensee.'' This new agglomeration was renamed ''Neuendorf-Sachsenbande.'' Economy The land making up the municipality is mainly rural and involved in agriculture Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ..., but local registries indicate 30 small businesses in the municipality. Politics The local council counts one member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niederzier
Niederzier is a municipality in the district of Düren in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located approximately 10 km north of Düren, and 10 km south-east of Jülich. Personalities * Viktor Schroeder (1922-2011), industrialist, patron and honorary citizen * Karl Lauterbach Karl Wilhelm Lauterbach (; born 21 February 1963) is a German scientist, physician, and politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) who has served as Federal Minister of Health since 8 December 2021. He is professor of health eco ... (born 1963), doctor and politician (SPD), since 2005 Bundestag deputy * Andrea Tillmanns (born 1972), author References External links Düren (district) {{Düren-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titz
Titz is a municipality in the district of Düren in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located approximately north-east of Jülich and south of Mönchengladbach. Since the local government reform of 1975, Titz Municipality consists from 16 districts: Ameln, Bettenhoven, Gevelsdorf, Hasselsweiler, Höllen, Hompesch, Jackerath, Kalrath, Müntz, Mündt, Opherten, Ralshoven, Rödingen, Sevenich, Spiel and Titz. Museum * The LVR-Cultural Centre Village Synagogue Rödingen is dedicated to Jewish Life in rural Rhineland of past and present Notable person *Petra Hammesfahr (b. 1951), bestselling German novelist A novelist is an author or writer of novels, though often novelists also write in other genres of both fiction and non-fiction. Some novelists are professional novelists, thus make a living writing novels and other fiction, while others aspire ... References External links Düren (district) {{Düren-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35%, and is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat content. When removed from the ground, it contains a very high amount of moisture which partially explains its low carbon content. Lignite is mined all around the world and is used almost exclusively as a fuel for steam-electric power generation. The combustion of lignite produces less heat for the amount of carbon dioxide and sulfur released than other ranks of coal. As a result, environmental advocates have characterized lignite as the most harmful coal to human health. Depending on the source, various toxic heavy metals, including naturally occurring radioactive materials may be present in lignite which are left over in the coal fly ash produced from its combustion, further increasing health risks. Characteristics Lignite is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
