|
Solar Chimney
:''This article refers to a device for ventilation. For the power generation technology, see Solar updraft tower.'' A solar chimney often referred to as a thermal chimney is a way of improving the natural ventilation of buildings by using convection of air heated by passive solar energy. A simple description of a solar chimney is that of a vertical shaft utilizing solar energy to enhance the natural stack ventilation through a building. The solar chimney has been in use for centuries, particularly in the Middle East and Near East by the Persians, as well as in Europe by the Romans. Description In its simplest form, the solar chimney consists of a black-painted chimney. During the day solar energy heats the chimney and the air within it, creating an updraft of air in the chimney. The suction created at the chimney's base can be used to ventilate and cool the building below. In most parts of the world it is easier to harness wind power for such ventilation as with a windcatch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Updraft Tower
The solar updraft tower (SUT) is a design concept for a renewable-energy power plant for generating electricity from low temperature solar heat. Sunshine heats the air beneath a very wide greenhouse-like roofed collector structure surrounding the central base of a very tall chimney tower. The resulting convection causes a hot air updraft in the tower by the chimney effect. This airflow drives wind turbines, placed in the chimney updraft or around the chimney base, to produce electricity. As of mid 2018, although several prototype models have been built, no full-scale practical units are in operation. Scaled-up versions of demonstration models are planned to generate significant power. They may also allow development of other applications, such as to agriculture or horticulture, to water extraction or distillation, or to improvement of urban air pollution. Commercial investment may have been discouraged by the high initial cost of building a very large novel structure, the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight to a hot spot, often to drive a steam turbine. Photovoltaics were initially solely used as a source of electricity for small and medium-sized applications, from the calculator powered by a single solar cell to remote homes powered by an off-grid rooftop PV system. Commercial concentrated solar power plants were first developed in the 1980s. Since then, as the cost of solar electricity has fallen, grid-connected solar PV systems have grown more or less exponentially. Millions of installations and gigawatt-scale photovoltaic power stations continue to be built, with half of new generation capacity being solar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zion Visitors Center Cool Tower
Zion ( he, צִיּוֹן ''Ṣīyyōn'', LXX , also variously transliterated ''Sion'', ''Tzion'', ''Tsion'', ''Tsiyyon'') is a placename in the Hebrew Bible used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole (see Names of Jerusalem). The name is found in 2 Samuel (5:7), one of the books of the Hebrew Bible dated to before or close to the mid-6th century BCE. It originally referred to a specific hill in Jerusalem ( Mount Zion), located to the south of Mount Moriah (the Temple Mount). According to the narrative of 2 Samuel 5, Mount Zion held the Jebusite fortress of the same name that was conquered by David and was renamed the City of David. That specific hill ("mount") is one of the many squat hills that form Jerusalem, which also includes Mount Moriah (the Temple Mount), the Mount of Olives, etc. Over many centuries, until as recently as the Ottoman era, the city walls of Jerusalem were rebuilt many times in new locations, so that the particular hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device's temperature. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool CPUs, GPUs, and some chipsets and RAM modules. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature. A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Research Establishment
The Building Research Establishment (BRE) is a centre of building science in the United Kingdom, owned by charitable organisation the BRE Trust. It is a former UK government national laboratory that was privatised in 1997. BRE provides research, advice, training, testing, certification and standards for both public and private sector organisations in the UK and abroad. It has its headquarters in Garston, Hertfordshire, England, with regional sites in Glasgow, Swansea, the US, India, the Middle East and China. Programmes BRE is now funded with income from commissioned research, commercial programmes and by a number of digital tools for use in the construction sector. BRE's certification arm – BRE Global – is an independent, third-party certification body responsible for sustainability certification schemes such as BREEAM (for buildings and communities), CEEQUAL (for infrastructure), the Home Quality Mark (for housing) and LPCB certification (for fire and security produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Chimney TAS Model
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. " solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Solar, Erode, India * Solar, Iran, Iran Companies * Solar Entertainment Corporation Solar Entertainment Corporation (simply known as Solar or SEC) is a Filipino media company based in Makati, Philippines. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Cooling
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior (heat gain prevention) or by removing heat from the building (natural cooling). Natural cooling utilizes on-site energy, available from the natural environment, combined with the architectural design of building components (e.g. building envelope), rather than mechanical systems to dissipate heat. Therefore, natural cooling depends not only on the architectural design of the building but on how the site's natural resources are used as heat sinks (i.e. everything that absorbs or dissipates heat). Examples of on-site heat sinks are the upper atmosphere (night sky), the outdoor air (wind), and the earth/soil. Passive cooling is an important tool for design of buildings for climate change adaptationreducing dependenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or alternatively a variety of other methods, including passive cooling or ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them to both heat and also cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used within vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a ''loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the top floor of a building and the slanted roof, they are known for being awkwardly shaped spaces with exposed rafters and difficult-to-reach corners. While some attics are converted into bedrooms, home offices, or attic apartments complete with windows and staircases, most remain difficult to access (and are usually entered using a loft hatch and ladder). Attics help control temperatures in a house by providing a large mass of slowly moving air, and are often used for storage. The hot air rising from the lower floors of a building is often retained in attics, further compounding their reputation as inhospitable environments. However, in recent years attics have been insulated to help decrease heating costs, since, on average, uninsulated at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
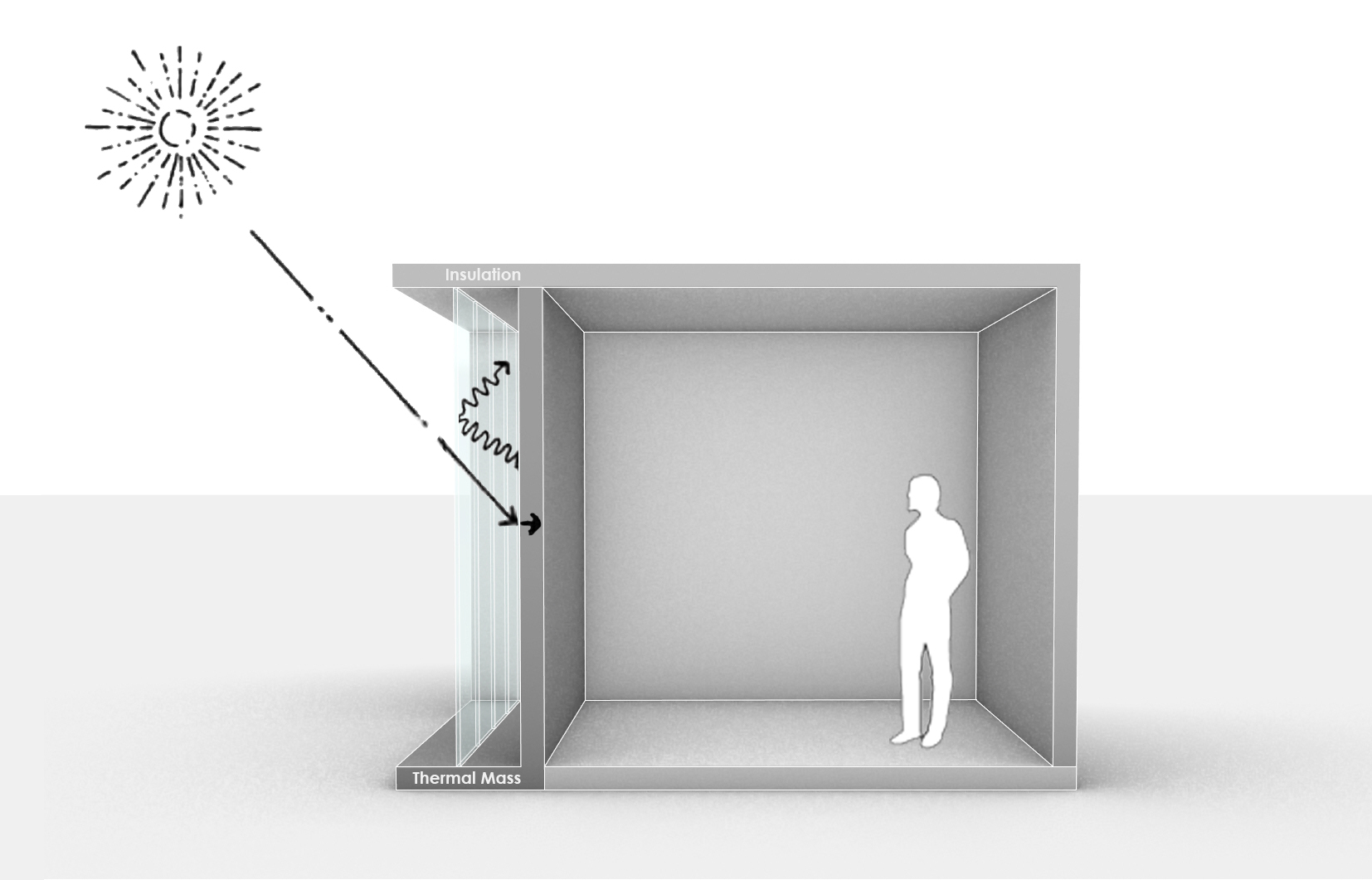
Trombe Wall
A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface which covers thermal mass located between the Sun and the space. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space. Trombe walls are also named mass walls, solar wall, or thermal storage wall. However, due to the extensive work of professor Félix Trombe and architect Jacques Michel in the design of passively heated and cooled solar structure, they are often called Trombe Walls. This system is similar to the air heater (as a simple glazed box on the south wall with a dark absorber, air space, and two sets of vents at top and botto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Cooling Tubes
A ground-coupled heat exchanger is an underground heat exchanger that can capture heat from and/or dissipate heat to the ground. They use the Earth's near constant subterranean temperature to warm or cool air or other fluids for residential, agricultural or industrial uses. If building air is blown through the heat exchanger for heat recovery ventilation, they are called earth tubes (or Canadian well, Provençal well, Solar chimney, also termed earth cooling tubes, earth warming tubes, earth-air heat exchangers (EAHE or EAHX), air-to-soil heat exchanger, earth channels, earth canals, earth-air tunnel systems, ground tube heat exchanger, hypocausts, subsoil heat exchangers, thermal labyrinths, underground air pipes, and others). Earth tubes are often a viable and economical alternative or supplement to conventional central heating or air conditioning systems since there are no compressors, chemicals or burners and only blowers are required to move the air. These are used for either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prevailing Wind
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze/land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind; in areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow. Wind roses are tools used to display the direction of the prevailing wind. Knowledge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_16_-_17_May_1943_C(AM)1603.jpg)