|
Sisupalgarh
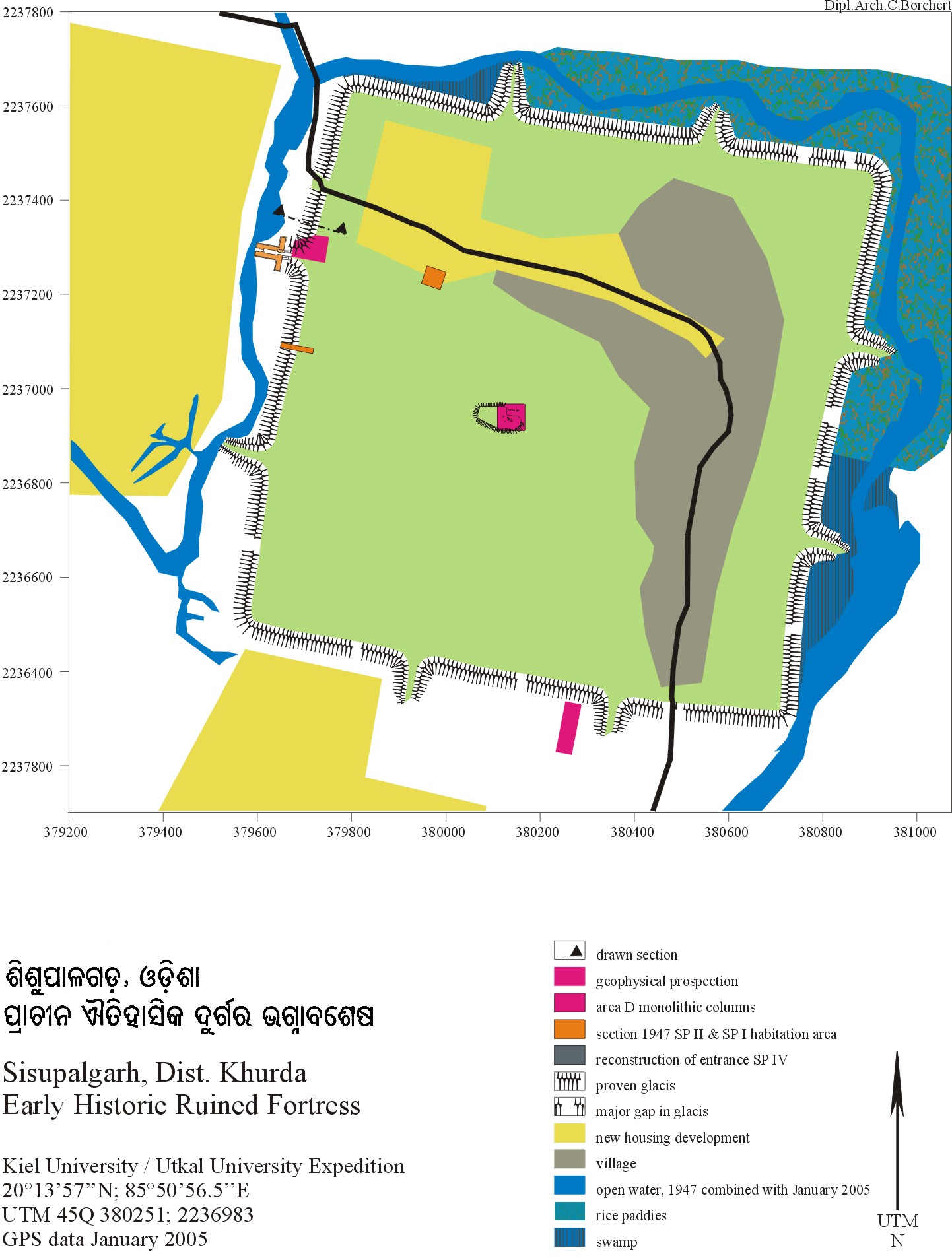
Sisupalgarh or Sisupalagada is situated in Khurda District in Odisha, India and houses ruined fortifications. It used to be the capital of ancient Kalinga. It is identified with Kalinganagara of Kharavela and Tosali of Ashoka. It is one of the largest and best preserved early historic fortifications in India, with the earliest occupation both inside and outside the later site´s northern rampart around 7th to 6th centuries BCE. Description The remains of the ancient city Sisupalgarh has been discovered near Bhubaneswar, today, the capital of the Odisha state in India. Sisupalgarh was a nationally protected monument. On the basis of the architectural pattern and artefacts discovered during the early excavations, B.B. Lal concluded that this fort city flourished between 3rd century BC and 4th century AD. On the basis of the new findings, M.L. Smith and R. Mohanty claimed in 2001 that the fortified city flourished from around 5th century BC and probably lasted well after the 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sisupalgarh Fortified Urban Center
Sisupalgarh or Sisupalagada is situated in Khurda District in Odisha, India and houses ruined fortifications. It used to be the capital of ancient Kalinga. It is identified with Kalinganagara of Kharavela and Tosali of Ashoka. It is one of the largest and best preserved early historic fortifications in India, with the earliest occupation both inside and outside the later site´s northern rampart around 7th to 6th centuries BCE. Description The remains of the ancient city Sisupalgarh has been discovered near Bhubaneswar, today, the capital of the Odisha state in India. Sisupalgarh was a nationally protected monument. On the basis of the architectural pattern and artefacts discovered during the early excavations, B.B. Lal concluded that this fort city flourished between 3rd century BC and 4th century AD. On the basis of the new findings, M.L. Smith and R. Mohanty claimed in 2001 that the fortified city flourished from around 5th century BC and probably lasted well after the 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Alan Yule
Paul Alan Yule is a German archaeologist at the Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg (habilitation). His main work targets the archaeology of Oman, Yemen, previously India. Education and career Yule studied at the University of Minnesota (BA), New York University (MA and PhD) and Marburg University. His dissertation, ''Early Cretan Seals'', classified and dated the seals from the Early and Middle Bronze Ages of Minoan Crete. In 1995 his habilitationsschrift at Heidelberg University analysed some 365 pre-Islamic graves in the eastern central part of Oman Within the framework of the Open Access movement Yule emphasises the archiving of his research materials and publications as soon as possible so as to make them publicly available. He does this largely by means of the image bank heidICON and the virtual library Propylaeum-Dok of the Heidelberg University Library. Since 2005 Yule has experimented in 3D recording and animation in India and Oman with the Fachhochschule Main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosali
Tosali or Toshali was an ancient city in the present day Odisha state in eastern India. It was the capital of the eastern province of the Kalinga Kingdom. While some scholars tried to identify this ancient city with Dhauli, 7 km away from Bhubaneshwar, other scholars were inclined to identify this city with Shishupalgarh, 5 km away from Bhubaneshwar. Recent archaeological excavations showing fort ruins and major ancient era weapons, inscriptions and presence of Kushan era gold coins gives credence to the sites at Radhanagar near Brahmani river in Jajpur district to be the most likely location of Tosali. Excavations at Shishupalgarh In 1948, the first excavation in Shishupalgarh was conducted by an Archaeological Survey of India team led by B.B. Lal, followed by another in 1950. These excavations led to the discovery of an ancient fortied urban centre in Shishupalgarh. The mud fortification, constructed in the early 2nd century BCE is almost square shaped and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar (; ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. The region, especially the old town, was historically often depicted as ''Ekamra Kshetra'' (area (''kshetra'') adorned with mango trees (''ekamra'')). Bhubaneswar is dubbed the "Temple City", a nickname earned because of the 700 temples which once stood there. In contemporary times, it has emerged as an education hub and an attractive business destination. Although the modern city of Bhubaneswar was formally established in 1948, the history of the areas in and around the present-day city can be traced to the 7th century BCE and earlier. It is a confluence of Hindu, Buddhist and Jain heritage and includes several Kalingan temples, many of them from 6th–13th century CE. With Puri and Konark it forms the 'Swarna Tribhuja' ("Golden Triangle"), one of Eastern India's most visited destinations. Ramesh Prasad Mohapatra, ''Archaeology in Orissa'', Vol I, Page 47, B. R. Publishing Corporation, Delhi, 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinga (historical Region)
Kalinga (Sanskrit: ), is a historical region of India. It is generally defined as the eastern coastal region between the Mahanadi and the Godavari rivers, although its boundaries have fluctuated with the territory of its rulers. The core territory of Kalinga now encompasses a large part of Odisha and northeastern part of Andhra Pradesh. At its widest extent, the Kalinga region also included parts of present-day Chhattisgarh, extending up to Amarkantak in the west. The Kalingas have been mentioned as a major tribe in the legendary text ''Mahabharata''. In the 3rd century BCE, the region came under Mauryan control as a result of the Kalinga War. It was subsequently ruled by several regional dynasties whose rulers bore the title ''Kalingādhipati'' ("Lord of Kalinga"); these dynasties included Mahameghavahana, Vasishtha, Mathara, Pitrbhakta, Shailodbhava, Somavamshi, and Eastern Ganga. The medieval era rulers to rule over the Kalinga region were the Suryavamsa Gajapatis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacis
A glacis (; ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis is any slope, natural or artificial, which fulfils the above requirements. The etymology of this French word suggests a slope made dangerous with ice, hence the relationship with ''glacier''. A ''glacis plate'' is the sloped front-most section of the hull of a tank or other armoured fighting vehicle. Ancient fortifications A glacis could also appear in ancient fortresses, such as the one the ancient Egyptians built at Semna in Nubia. Here it was used by them to prevent enemy siege engines from weakening defensive walls. Hillforts in Britain started to incorporate glacis around 350 BC. Those at Maiden Castle, Dorset were high. Medieval fortifications Glacis, also called talus, were incorporated into medieval fortifications t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Indian Cities
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Monuments In Odisha
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forts In Odisha
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)


.jpg)
