|
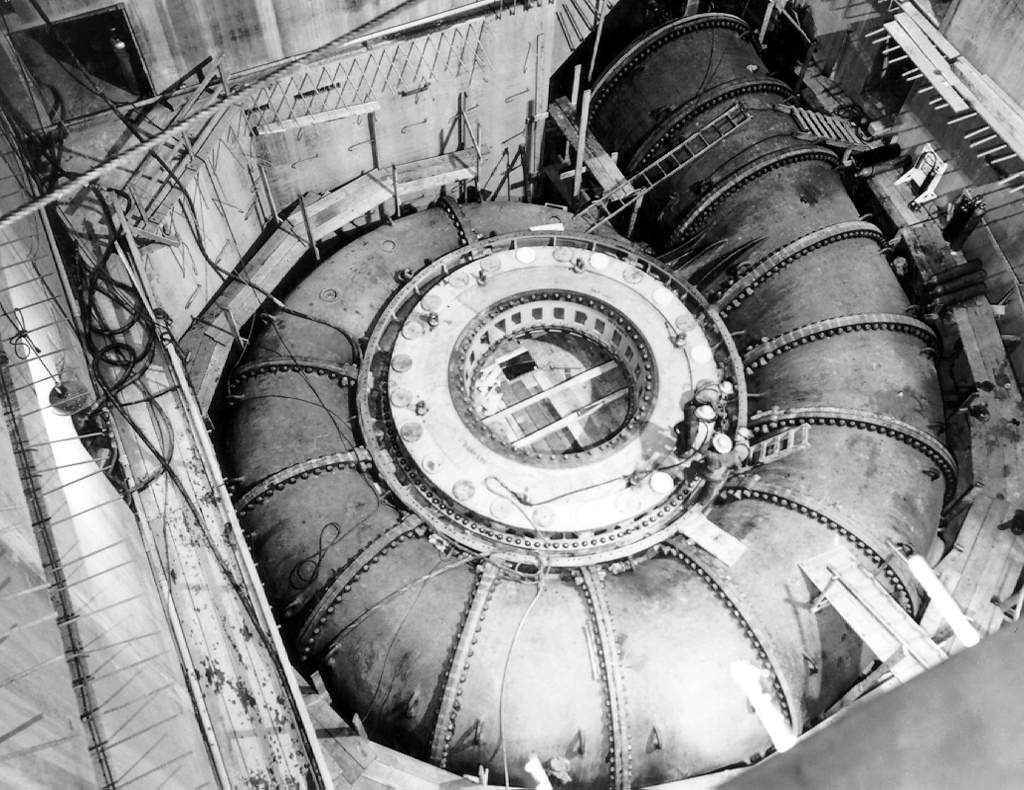
Shin-Takasegawa Pumped Storage Station
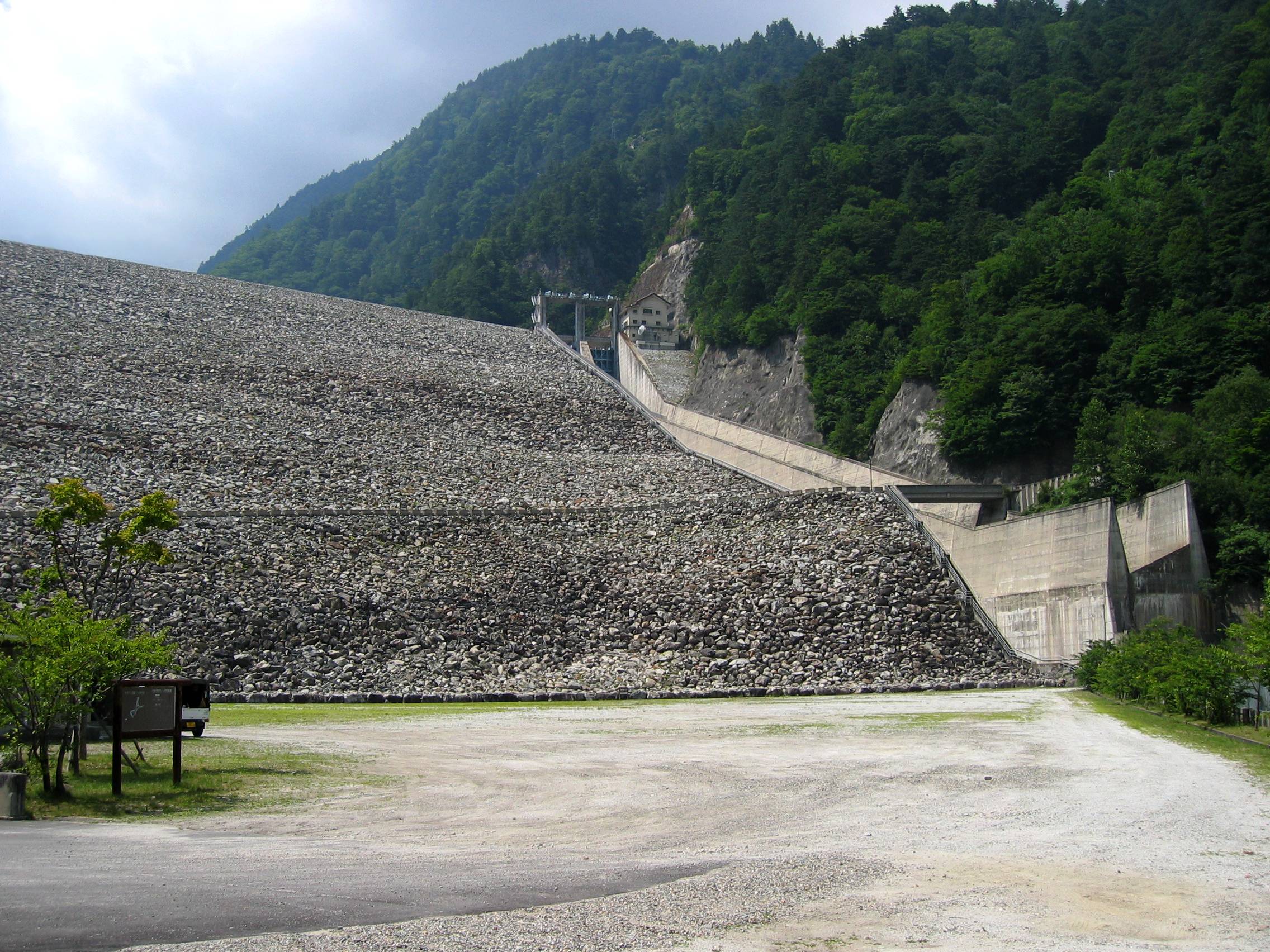
The Shin-Takasegawa Pumped Storage Station (新高瀬川発電所) uses the Takase River (a tributary of the Shinano River) to operate a pumped storage hydroelectric scheme about west of Ōmachi in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. Part of the system is within Chūbu-Sangaku National Park. Construction on the complex began in 1971, concluded in 1978 and the power station was commissioned in 1980. The power plant has a installed capacity and its upper reservoir is created by the Takase Dam, a rock-fill dam — which at in height is the tallest of its type in Japan. It is also the second tallest dam in Japan, next to Kurobe Dam. Design and operation When energy demand is low and therefore electricity less expensive, the turbines reverse and pump water from the lower reservoir back into the upper reservoir. This process repeats depending upon energy demand and water availability. Water released from the lower reservoir is used to power the Nakanosawa Power Station which uses of hydrau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōmachi, Nagano
is a city located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 27,559 in 11861 households, and a population density of 49 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Ōmachi is located west of Nagano, the capital of Nagano Prefecture, in the of the prefecture. The 3000 meter Northern Japanese Alps (or Hida Mountains) are to the west ranges to the west of the city and mountains of around 1000 meters form the eastern border. The Takase River runs through the city, which is located in the northern Matsumoto basin. The Itoigawa-Shizuoka Tectonic Line active fault system is also running through the city. *Mountains: Mount Yarigatake, , , , , , , , , , , *Rivers: Takase River *Lakes and marshes: (, , ) Surrounding municipalities *Nagano Prefecture ** Matsumoto ** Nagano ** Azumino ** Matsukawa ** Ikeda ** Hakuba ** Ikusaka ** Ogawa * Toyama Prefecture ** Toyama ** Tateyama ** Kurobe * Gifu Prefecture ** Takayama Demographics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penstock
A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydro turbines and sewerage systems. The term is inherited from the earlier technology of mill ponds and watermills. Hydroelectric systems and dams Penstocks for hydroelectric installations are normally equipped with a gate system and a surge tank. They can be a combination of many components such as anchor block, drain valve, air bleed valve, and support piers depending on the application. Flow is regulated by turbine operation and is nil when turbines are not in service. Penstocks, particularly where used in polluted water systems, need to be maintained by hot water washing, manual cleaning, antifouling coatings, and desiccation. The term is also used in irrigation dams to refer to the channels leading to and from high-pressure sluice gates. Penstocks are also used in mine tailings dam construction. The penstock is usually situated fairly close to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumped-storage Hydroelectric Power Stations In Japan
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential energy of water, pumped from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is typically used to run the pumps. During periods of high electrical demand, the stored water is released through turbines to produce electric power. Although the losses of the pumping process make the plant a net consumer of energy overall, the system increases revenue by selling more electricity during periods of peak demand, when electricity prices are highest. If the upper lake collects significant rainfall or is fed by a river then the plant may be a net energy producer in the manner of a traditional hydroelectric plant. Pumped-storage hydroelectricity allows energy from intermittent sources (such as solar, win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In Nagano Prefecture
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions. The earliest known dam is the Jawa Dam in Jordan, dating to 3,000 BC. The word ''dam'' can be traced back to Middle English, and before that, from Middle Dutch, as seen in the names of many old cities, such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam. History Ancient dams Early dam building took place in Mesopotamia and the Middle East. Dams were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hida Mountains
The , or , is a Japanese mountain range which stretches through Nagano, Toyama and Gifu prefectures. A small portion of the mountains also reach into Niigata Prefecture. William Gowland coined the phrase "Japanese Alps" during his time in Japan, but he was only referring to the Hida Mountains when he used that name. The Kiso and Akaishi mountains received the name in the ensuing years. Geography The layout of the Hida Mountains forms a large Y-shape. The southern peaks are the lower portion of the Y-shape, with the northern peaks forming two parallel bands separated by a deep V-shaped valley. It is one of the steepest V-shaped valleys in Japan. The Kurobe Dam, Japan's largest dam, is an arch dam located in the Kurobe Valley in the central area of the mountains. The western arm of mountains, also known as the Tateyama Peaks (立山連峰 ''Tateyama Renpō''), are dominated by Mount Tsurugi and Mount Tate. The eastern arm, known as the Ushiro Tateyama Peaks (後立山連峰 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Dams In The World
This is a list of the tallest dams in the world over in height. The tallest dam in the world is the Jinping-I Dam, an arch dam in China at . The tallest embankment dam and second tallest dam in the world is the Nurek Dam in Tajikistan. The tallest gravity dam is the high Grande Dixence Dam in Switzerland. The tallest natural dam, the Usoi Dam in Tajikistan, is taller than the tallest existing man-made one. Existing Under construction Gallery File:BarrageDeLaGrandeDixenceFaceValee.JPG, The Grande Dixence Dam in Switzerland File:Enguri Dam, Georgia.jpg, The Inguri Dam in Georgia File:VajontDiga.jpg, The Vajont Dam in Italy File:Tehri dam india.jpg, The Tehri Dam in India File:MicaDam.JPG, The Mica Dam in Canada File:Саяно-Шушенская ГЭС.jpg, The Sayano Shushenskaya Dam in Russia File:OrovilleDam.jpg, The Oroville Dam in the United States File:El Cajon Dam Honduras.jpg, The El Cajón Dam in Honduras File:Bhakra Dam Aug 15 2008.JPG, The Bhakra D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Pumped-storage Hydroelectric Power Stations
The following page lists all pumped-storage hydroelectric power stations that are larger than in installed generating capacity, which are currently operational or under construction. Those power stations that are smaller than , and those that are decommissioned or only at a planning/proposal stage may be found in regional lists, listed at the end of the page. List of plants larger than 1000 MW capacity The table below lists currently operational power stations. Some of these may have additional units under construction, but only current installed capacity is listed. Under construction This table lists future 1,000 MW or larger stations that are under construction; some may be partially operational with a current installed capacity under 1,000 MW. See also * List of energy storage projects * List of hydroelectric power station failures * Lists of hydroelectric power stations * List of largest power stations * United States Department of Energy Global En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōmachi Dam
The Ōmachi Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the just west of Ōmachi in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. Construction of the dam began in 1975 and it was completed in 1985. The primary purpose of the dam is water supply and it also supports a 13 MW hydroelectric power station. It is owned by TEPCO. See also *Shin-Takasegawa Pumped Storage Station The Shin-Takasegawa Pumped Storage Station (新高瀬川発電所) uses the Takase River (a tributary of the Shinano River) to operate a pumped storage hydroelectric scheme about west of Ōmachi in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. Part of the system is ... - upstream References {{DEFAULTSORT:Omachi Dam Dams in Nagano Prefecture Hydroelectric power stations in Japan Gravity dams Dams completed in 1985 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Power Station
An underground power station is a type of hydroelectric power station constructed by excavating the major components (e.g. machine hall, penstocks, and tailrace) from rock, rather than the more common surface-based construction methods. One or more conditions impact whether a power station is constructed underground. The terrain or geology around a dam is taken into consideration, as gorges or steep valleys may not accommodate a surface power station. A power station within bedrock may be less expensive to construct than a surface power station on loose soil. Avalanche-prone valleys often make a surface station unfeasible as well. After World War II, large hydroelectric power stations were placed underground more often in order to protect them from airstrikes. Often underground power stations form part of pumped storage hydroelectricity schemes, whose basic function is to level load: they use cheap or surplus off-peak power to pump water from a lower lake to an upper lake. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embankment Dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface and a dense, impervious core. This makes the dam impervious to surface or seepage erosion. Such a dam is composed of fragmented independent material particles. The friction and interaction of particles binds the particles together into a stable mass rather than by the use of a cementing substance. Types Embankment dams come in two types: the earth-filled dam (also called an earthen dam or terrain dam) made of compacted earth, and the rock-filled dam. A cross-section of an embankment dam shows a shape like a bank, or hill. Most have a central section or core composed of an impermeable material to stop water from seeping through the dam. The core can be of clay, concrete, or asphalt concrete. This type of dam is a good choice for sites w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagano Prefecture
is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has a geographic area of . Nagano Prefecture borders Niigata Prefecture to the north, Gunma Prefecture to the northeast, Saitama Prefecture to the east, Yamanashi Prefecture to the southeast, Shizuoka Prefecture and Aichi Prefecture to the south, and Gifu Prefecture and Toyama Prefecture to the west. Nagano is the capital and largest city of Nagano Prefecture, with other major cities including Matsumoto, Ueda, and Iida. Nagano Prefecture has impressive highland areas of the Japanese Alps, including most of the Hida Mountains, Kiso Mountains, and Akaishi Mountains which extend into the neighbouring prefectures. The abundance of mountain ranges, natural scenic beauty, and rich history has gained Nagano Prefecture international recognition as a world-class winter sports tourist destination, including hosting the 1998 Winter Olympics and a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)