|
Sexmission
''Sexmission'' ( pl, Seksmisja) is a 1984 Polish cult comedy science fiction action film. It also contains a hidden political satire layer specific to the time and place of its production (the socialist-feminist system as proposed by the Communist Party), but with relevance still today. Plot On 9 August 1991 Maksymilian "Max" Paradys (Jerzy Stuhr), looking for adventure, and Albert Starski (Olgierd Łukaszewicz), biologist, volunteer themselves for the first human hibernation experiment, created by professor Wiktor Kuppelweiser, a Nobel Prize laureate, who previously successfully hibernated a chimpanzee for half a year. The experiment is considered as an epochal event and is broadcast on television. The hibernation is scheduled to last for 3 years. Instead of being awakened 3 years later in 1994 as planned, they wake up in the year 2044, in a post-nuclear world. Both are 86 years old, but haven't aged a day outwardly. They are being taken care of by women, which they enjoy at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juliusz Machulski
Juliusz Machulski (born 10 March 1955 in Olsztyn) is a Poles, Polish film director and screenplay writer. Son of noted actor Jan Machulski, Juliusz became notable for his comedies ridiculing the life in communist-ruled Poland of the 1970s and 1980s. Biography Juliusz Machulski was born 10 March 1955 in Olsztyn, Poland, to parents, Jan Machulski and Halina Machulska. In 1973, he moved to Warsaw, where he was admitted to the Polish Philology faculty of the Warsaw University. However, in 1975 he moved to Łódź, where he graduated from the Łódź Film School. His film debut was ''Vabank'' (1981), a comedy describing a story of two Polish gangsters of the 1930s. The film was a striking success, as was the science-fiction comedy ''Seksmisja'' of 1984. Often seen as either a golden child or enfant terrible of the Polish cinema, Machulski quickly became one of the most popular Polish directors, both in Poland and abroad. His ''Seksmisja'', although significantly shortened by the Sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KADR (studio)
KADR (since 1989 Studio Filmowe Kadr) is a major Polish film production and distribution company, founded in 1955 and still producing films as of 2016. Between its founding and 2003, KADR released 150 films in total, including many classics of Polish cinema. History "Arguably the most important Polish film studio," Kadr was founded on May 1, 1955, by filmmaker Jerzy Kawalerowicz, and its initial output is closely associated with him. Along with Krzysztof Teodor Toeplitz and Tadeusz Konwicki, Kawalerowicz was a primary influence on the development of the Polish Film School in the 1950s. With a few exceptions, its landmark films were produced at Kadr. The organization began as one of a few "film units" (''zespoły filmowe'') set up as state enterprises, and with close connections to the establishment National Film School in Łódź. By 1968 Kadr was a major studio, producing perhaps four titles annually, including the big-budget three-year period production of ''Pharaoh'', nominate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Stuhr
Jerzy Oskar Stuhr (; born 18 April 1947) is a Polish film and theatre actor. He is one of the most popular, influential and versatile Polish actors. He also works as a screenwriter, film director and drama professor. He served as the Rector of the Ludwik Solski Academy for the Dramatic Arts in Kraków for two terms: from 1990 to 1996 and again from 2002 to 2008. Life and career Stuhr was born in Kraków. His ancestors, Leopold Stuhr and Anna Thill, migrated within Austria-Hungary from Mistelbach to Cracow shortly after their wedding in 1879. Having obtained a degree in Polish literature from the Jagiellonian University in 1970, Stuhr spent the next two years studying acting at the Academy for the Dramatic Arts in Kraków ( often shortened to ''PWST''), where he became a professor. From the early 1970s, Stuhr appeared in Polish theatre and worked in film productions, making his debut with the role of Beelzebub in Adam Mickiewicz's directed by Konrad Swinarski. Having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olgierd Łukaszewicz
Olgierd Łukaszewicz (born 7 September 1946) is a Polish film actor. He has appeared in more than 60 films since his 1969 graduation from the Ludwik Solski Academy for the Dramatic Arts in Kraków. Between 2002 and 2005, he was the President of the Polish Union of Stage Actors (Związek Artystów Scen Polskich). Selected filmography * 1970: '' Salt of the Black Earth'' (''Sól ziemi czarnej'') as Gabriel Basista * 1972: '' Pearl in the Crown'' (''Perła w koronie'') as Jaś * 1972: '' The Wedding'' (''Wesele'') as Phantom * 1977: '' The Story of Sin'' (''Dzieje grzechu'') as Zygmunt Szczerbic * 1975: '' Nights and Days'' (''Noce i dnie'') as Janusz Ostrzeński * 1978: '' Jörg Ratgeb – Painter'' as Bishop * 1981: ''Fever'' (''Gorączka: Dzieje jednego pocisku'') as Marek * 1982: ''Interrogation'' (''Przesłuchanie'') as Konstnty * 1984: '' Sexmission'' (''Seksmisja'') as Albert Starski * 1986: ''Boris Godunov'' as Mikolaj Czernikowski * 1987: ''Magnat'' as Franzel * 1987: ''K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
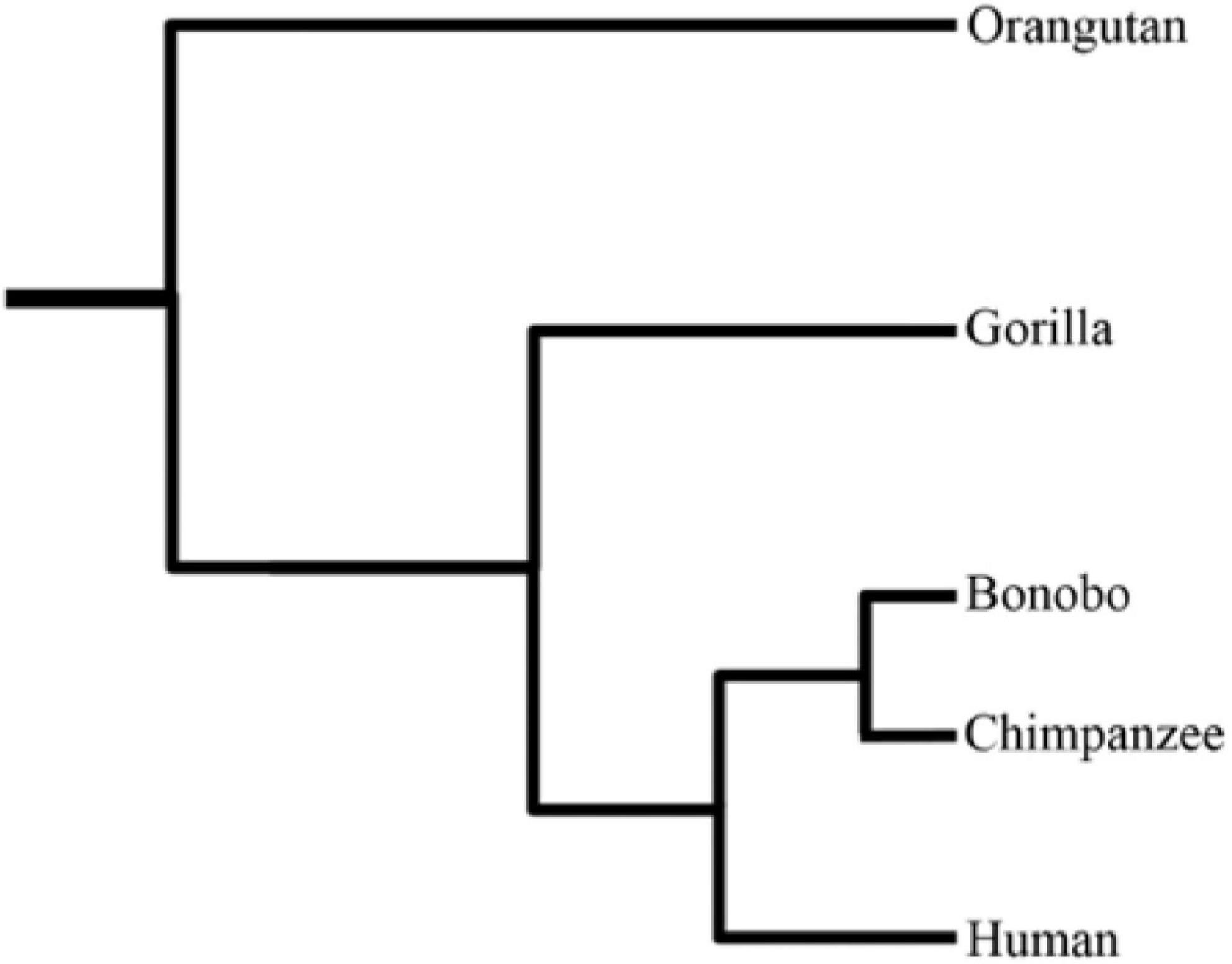
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-apocalyptic Science Fiction
Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction is a subgenre of speculative fiction in which the Earth's (or another planet's) civilization is collapsing or has collapsed. The apocalypse event may be climatic, such as runaway climate change; astronomical, such as an impact event; destructive, such as nuclear holocaust or resource depletion; medical, such as a pandemic, whether natural or human-caused; end time, such as the Last Judgment, Second Coming or Ragnarök; or more imaginative, such as a zombie apocalypse, cybernetic revolt, technological singularity, dysgenics or alien invasion. The story may involve attempts to prevent an apocalypse event, deal with the impact and consequences of the event itself, or it may be post-apocalyptic, set after the event. The time may be directly after the catastrophe, focusing on the psychology of survivors, the way to keep the human race alive and together as one, or considerably later, often including that the existence of pre-catastrophe ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Women's Day
International Women's Day (IWD) is a global holiday celebrated annually on March 8 as a focal point in the women's rights movement, bringing attention to issues such as gender equality, reproductive rights, and violence and abuse against women. Spurred on by the universal female suffrage movement that had begun in New Zealand, IWD originated from labor movements in North America and Europe during the early 20th century. The earliest version was purportedly a "Women's Day" organized by the Socialist Party of America in New York City February 28, 1909. This inspired German delegates at the 1910 International Socialist Women's Conference to propose "a special Women's Day" be organized annually, albeit with no set date; the following year saw the first demonstrations and commemorations of International Women's Day across Europe. After women gained suffrage in Soviet Russia in 1917 (the beginning of the February Revolution), IWD was made a national holiday on March 8; it was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryos occur in a gamete (egg or sperm) without combining with another gamete (e.g., egg and sperm fusing). In animals, parthenogenesis means development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell. In plants, parthenogenesis is a component process of apomixis. In algae, parthenogenesis can mean the development of an embryo from either an individual sperm or an individual egg. Parthenogenesis occurs naturally in some plants, algae, invertebrate animal species (including nematodes, some tardigrades, water fleas, some scorpions, aphids, some mites, some bees, some Phasmatodea and parasitic wasps) and a few vertebrates (such as some fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds). This type of reproduction has been induced artificially i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, '' Malus sieversii'', is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after planting. Rootstocks are used to control the speed of growth and the size of the resulting tree, allowing for easier harvesting. There are mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthanasia
Euthanasia (from el, εὐθανασία 'good death': εὖ, ''eu'' 'well, good' + θάνατος, ''thanatos'' 'death') is the practice of intentionally ending life to eliminate pain and suffering. Different countries have different euthanasia laws. The British House of Lords select committee on medical ethics defines euthanasia as "a deliberate intervention undertaken with the express intention of ending a life, to relieve intractable suffering". In the Netherlands and Belgium, euthanasia is understood as "termination of life by a doctor at the request of a patient". The Dutch law, however, does not use the term 'euthanasia' but includes the concept under the broader definition of "assisted suicide and termination of life on request". Euthanasia is categorized in different ways, which include voluntary, non-voluntary, or involuntary. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most commonly occurs during winter months. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and utilise similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on the species, ambient temperatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



