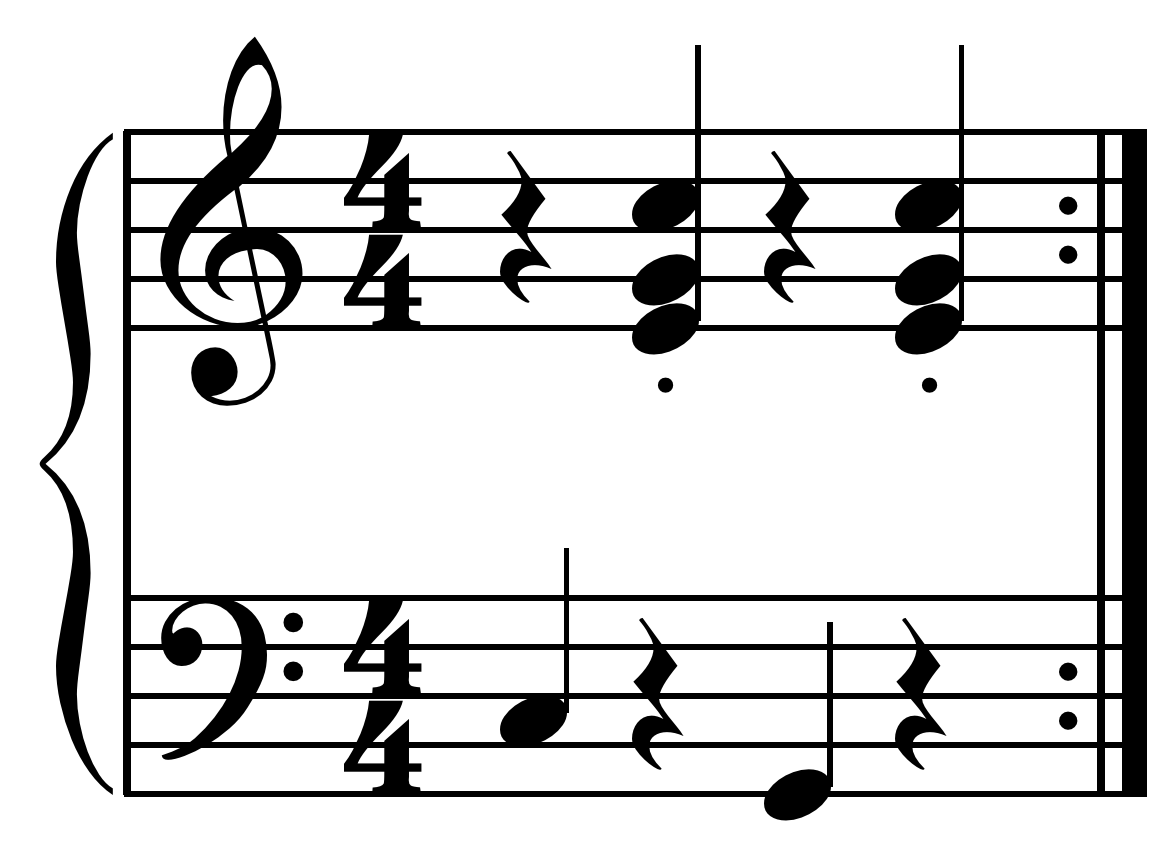|
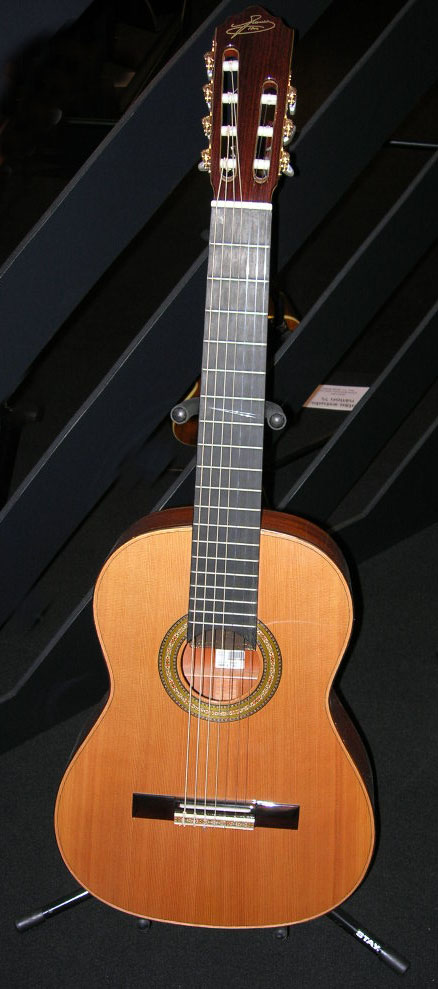
Seven-string Guitar
The seven-string guitar adds one additional string to the more common six-string guitar, commonly used to extend the bass range (usually a low B) or also to extend the treble range. The additional string is added in one of two different ways: by increasing the width of the fingerboard such that the additional string may be fretted by the left hand; or, by leaving the fingerboard unchanged and adding a "floating" bass string. In the latter case, the extra bass string lies next to the existing bass strings, but free of the fingerboard in similar fashion as the archlute and theorbo. Such unfrettable bass strings were historically known as diapasons or bourdons. Some types of seven-string guitars are specific to certain cultures such as the Russian, Mexican, and Brazilian guitars. History The history of the seven-string guitar stretches back more than 230 years. During the Renaissance period (), the European guitar generally had four courses, each strung with two gut strings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
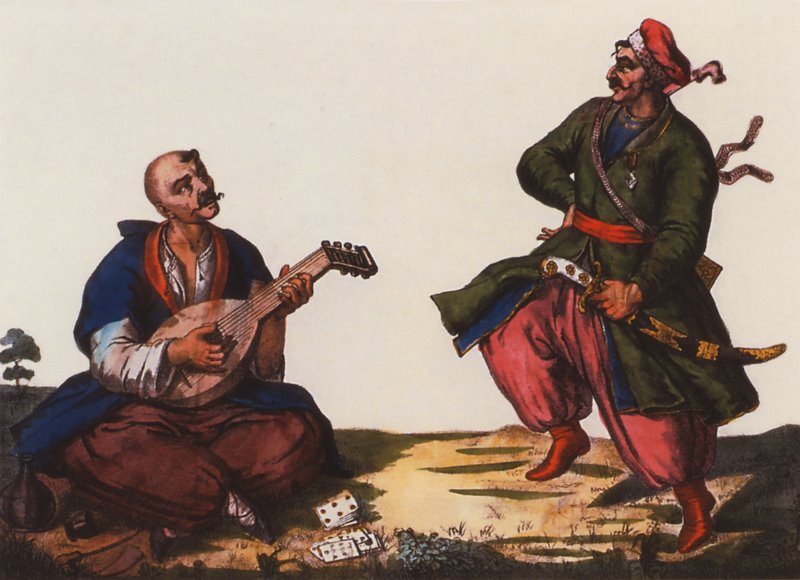
Tropinin Gitarist
Vasily Andreevich Tropinin (russian: Васи́лий Андре́евич Тропи́нин; – ) was a Russian Romantic painter. Much of his life was spent as a serf; he didn't attain his freedom until he was more than forty years old. Three of his more important works are a portrait of Alexander Pushkin and paintings called '' The Lace Maker'' and '' The Gold-Embroideress''. Biography Vasily was born as a serf of Count Munnich in the village Korpovo of Novgorod guberniya. He was transferred to Count Morkov as part of the dowry of Munnich's daughter. Soon he was sent to Saint Petersburg to study the trade of a confectioner. Instead of learning his trade Tropinin secretly attended free drawing lessons in the Imperial Academy of Arts. In 1799, his owner allowed Tropinin's to study at the Academy as a non-degree student (''Postoronny uchenik''). He took lessons from S. S. Schukin and was supported by the President of the Academy Alexander Sergeyevich Stroganov. In 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignác František Held
Ignác, also sometimes spelled Ignac in English, is the Hungarian version of the name Ignatius. Ignac is also a surname, among the most common surnames in the Međimurje County of Croatia. Notable people with this name include: * Ignác Alpár (1855–1928), Hungarian architect * Jozef Ignác Bajza (1755–1836), Slovak writer, satirist and Catholic priest *Ignác Batthyány (1741–1798), Hungarian Roman Catholic Bishop of Transylvania * Jan Josef Ignác Brentner (1689–1742), Czech composer of baroque era * Ignác Frank (1788–1850), Hungarian jurist and private law scholar *Ignác Goldziher (1850–1921), Hungarian orientalist *Ignác Gyulay (1763–1831), Hungarian military officer * Ignác Irhás (born 1985), Hungarian football player * Jiří Ignác Linek (1725–1791), renowned Czech late-Baroque composer and pedagogue * Ignác Raab (1715–1787), Czech Jesuit and painter * Ignác Šechtl (1840–1911), pioneer of Czech photography and cinematography * Ignác Šustala (182 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Bass
In music, alternate bass is a performance technique on many instruments where the bass alternates between two notes, most often the root and the fifth of a triad or chord. The perfect fifth is often, but not always, played below the root, transposed down an octave creating a fourth interval. The alternation between the root note and the fifth scale degree below it creates the characteristic sound of the alternate bass. On the guitar and bass guitar this is accomplished with the right hand alternating between two or more strings, often the bottom two on the guitar. In the following example in the C major chord C is located on the fifth string while G is located on the adjacent sixth (lowest) string and in the F major chord F is located on the adjacent fourth string: Alternate bass lines are also used on the double bass in country music, bluegrass music and related genres. On the Stradella bass system commonly found on accordions, the left-hand bass-note buttons are arran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bard (Soviet Union)
The term bard ( rus, бард, p=bart) came to be used in the Soviet Union in the early 1960s, and continues to be used in Russia today, to refer to singer-songwriters who wrote songs outside the Soviet establishment, similarly to folk singers of the American folk music revival. Because in bard music songwriters perform their own songs, the genre is also commonly referred to as author song (russian: авторская песня, ''avtorskaya pesnya'') or bard song (russian: бардовская песня, ''bardovskaya pesnya''). Bard poetry differs from other poetry mainly in being sung with simple guitar accompaniment as opposed to being spoken. Another difference is that it focuses less on style and more on meaning. This means that fewer stylistic devices are used, and the poetry is often in the form of a narrative. What separates bard poetry from other songs is that the music is far less important than the lyrics; chord progressions are often very simple and tend to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or concerts. Its most common form is triangular in shape and made of wood. Some have multiple rows of strings and pedal attachments. Ancient depictions of harps were recorded in Current-day Iraq (Mesopotamia), Iran (Persia), and Egypt, and later in India and China. By medieval times harps had spread across Europe. Harps were found across the Americas where it was a popular folk tradition in some areas. Distinct designs also emerged from the African continent. Harps have symbolic political traditions and are often used in logos, including in Ireland. History Harps have been known since antiquity in Asia, Africa, and Europe, dating back at least as early as 3000 BCE. The instrument had great popularity in Europe during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent ( Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutheil
Gutheil is a German surname of: * Emil Arthur Gutheil (1889–1959), Polish-American psychiatrist * (1868–1914), German conductor and composer, husband of Marie Gutheil-Schoder * Marie Gutheil-Schoder (1874–1935), German soprano * (born 1959), German jurist See also * Gutheil (publisher), founded in 1859 by Alexander Bogdanovich Gutheil, later an imprint of Serge Koussevitzky's Editions Russes {{surname, Gutheil German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Sychra
Andrei Osipovich Sychra (Sikhra, Sichra, in Russian Андрей Осипович Сихра ''Andrej Osipovič Sixra'') (born 1773 (?1776) in Vilnius; died November 21/December 3, 1850, in St Petersburg) was a Russian guitarist, composer and teacher of Czech ancestry. Sychra holds a prominent position within Russia, where he is often referred to as the patriarch of the seven-string guitar, and also as its inventor, disputed though that may be. He was a major force in the development of Russian guitar music and one of its most prolific composers, as well as an important teacher who trained a number of students. Sychra initially played the harp and possibly the torban on which he was reputed to have been a great virtuoso, before dedicating himself to the seven-string guitar. He moved to Moscow early in 1801, and became the dominant figure in the field, gaining a huge following. In 1812, perhaps because of Napoleon’s campaign and the Moscow fire of that year, he moved t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torban
The torban ( ua, Торбан, also ''teorban'' or ''Ukrainian theorbo'') is a Ukrainian musical instrument that combines the features of the Baroque lute with those of the psaltery. The Тorban differs from the more common European bass lute known as the theorbo in that it had additional short unfretted treble strings (known as ''prystrunky'') strung along the treble side of the soundboard. Overview It appeared ca. 1700, probably influenced by the central European Theorbo and the Angelique which, according to Ukrainian sources Cossack mercenaries would have encountered in the Thirty Years' War. According to Marcin Ludwicki and Roman Turovsky, the torban's inventor was Tuliglowski, a Paulite monk from Jasna Gora. The Torban was manufactured and used mainly in Ukraine, but also occasionally encountered in neighbouring Poland and Russia (only 3 luthiers could be identified from the surviving instruments). There are about 40 torbans in museums around the world, with the largest gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobza
The kobza ( uk , кобза), also called bandurka ( uk , бандурка) is a Ukrainian folk music instrument of the lute family ( Hornbostel-Sachs classification number 321.321-5+6), a relative of the Central European mandora. The term ''kobza'' however, has also been applied to a number of other Eastern European instruments distinct from the Ukrainian kobza. Construction The Ukrainian kobza was a traditionally gut-strung, lute-like stringed musical instrument with a body hewn from a single block of wood. Instruments with a staved assembly also exist. The kobza has a medium-length neck which may or may not have tied-on frets, which were usually made of gut. It was single-strung (sometimes also double-strung) and the strings were played with fingertips or occasionally with a plectrum threaded through a ring placed on the middle finger. History The term kobza is of Turkic origin and is related to the terms kobyz and komuz, thought to have been introduced into the Ukrainian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |