|
Section 377 Of The Indian Penal Code
Section 377 of the British colonial penal code criminalized all sexual acts "against the order of nature". The law was used to prosecute people engaging in oral and anal sex along with homosexual activity. The penal code remains in many former colonies, such as India (but has been repealed in Singapore) and has been used to criminalize third gender people, such as the ''apwint'' in Myanmar. In 2018, British Prime Minister Theresa May acknowledged how the legacies of British colonial anti-sodomy laws continue to persist today in the form of discrimination, violence, and death. History Although the act of sodomy was sometimes prosecuted in England under British common law, it was first codified in the British empire as Section 377 in the Indian Penal Code as "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" in 1860. Section 377 was then exported to other colonies and even to England itself, providing the legal model for the act of ' buggery' in the Offenses Against the Person Act (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as " the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human rights abusers to denounce abuse and respect human rights, and the group often works on behalf of refugees, children, migrants, and political prisoners. Human Rights Watch, in 1997, shared the Nobel Peace Prize as a founding member of the International Campaign to Ban Landmines, and it played a leading role in the 2008 treaty banning cluster munitions. The organization's annual expenses totaled $50.6 million in 2011, $69.2 million in 2014, and $75.5 million in 2017. History Human Rights Watch was co-founded by Robert L. Bernstein Jeri Laber and Aryeh Neier as a private American NGO in 1978, under the name Helsinki Watch, to monitor the then- Soviet Union's compliance with the Helsinki Accords. Helsinki Watch adopted a practice of pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of India
The Supreme Court of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme judicial authority of India and is the highest court of the Republic of India under the constitution. It is the most senior constitutional court, has the final decision in all legal matters except for personal laws and interstate river disputes, and also has the power of judicial review. The Chief Justice of India is the Head and Chief Judge of the Supreme Court, which consists of a maximum of 34 judges, and has extensive powers in the form of original, appellate and advisory jurisdictions. New judges here are uniquely nominated by existing judges and other branches of government have neglible say as the court follows collegium system for appointments. As the apex and most powerful constitutional court in India, it takes up appeals primarily against verdicts of the High Courts of various states of the Union and other courts and tribunals. It is required to safeguard the fundamental rights of citizens and settles dispu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buggery Act 1533
The Buggery Act 1533, formally An Acte for the punishment of the vice of Buggerie (25 Hen. 8 c. 6), was an Act of the Parliament of England that was passed during the reign of Henry VIII. It was the country's first civil sodomy law, such offences having previously been dealt with by the ecclesiastical courts. The term buggery, not defined in the text of the legislation, was later interpreted by the courts to include only anal penetration and bestiality, regardless of the sex of the participants, but not oral penetration. The act remained in force until it was repealed and replaced by the Offences against the Person Act 1828. Buggery remained a capital offence until 1861, though the last executions were in 1835. Description The Act was piloted through Parliament by Henry VIII's minister Thomas Cromwell (though it is unrecorded who actually wrote the bill), and punished "the detestable and abominable Vice of Buggery committed with Mankind or Beast". Prior to the 1550s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rule Of India
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section 377A (Singapore)
Section 377A is a Singaporean law that criminalises sex between consenting adult males. It was introduced under British colonial rule in 1938 when added to the Penal Code by the colonial government. It remained part of the Singapore body of law after the Penal Code review of October 2007 that removed most of the other provisions in Section 377. On 29 November 2022, the Parliament of Singapore passed a bill to repeal Section 377A. The law, while retained ''de jure'' in the Penal Code, has for many years been ''de facto'' unenforced – there has been no convictions for sex between consenting male adults in decades. While a small number of people were convicted under the section for private consensual acts between adults from 1988 until 2007, enforcement effectively ceased outright following the Penal Code review, despite retention of section 377A. On 28 February 2022, the Court of Appeal of the Supreme Court of Singapore reaffirmed that 377A could not be used to prosecute men f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Codes
Penal is a town in south Trinidad, Trinidad and Tobago. It lies south of San Fernando, Princes Town, and Debe, and north of Moruga, Morne Diablo and Siparia. It was originally a rice- and cocoa-producing area but is now a rapidly expanding and developing town. The population is 12,281. The heart of Penal contains many businesses while the outskirts focus on agricultural development. Penal has a market, police station, branches of three banks (Scotiabank, Republic Bank and First Citizens Bank) health facilities, grocery stores, convenience stores, bars, fast food restaurants, service stations, restaurants, puja stores, an Indian expo, and clothing stores. Penal plays a major role in the energy supply to the nation's populace. Petrotrin, the national oil company, has a major sub-unit in Clarke Road and the National Gas Company has gas lines running through Penal that links the gas fields of the South East Coast and the industrial estates. One of the countries three major power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "state" is a polity that maintains a monopoly on the legitimate use of violence, although other definitions are not uncommon.Cudworth et al., 2007: p. 95Salmon, 2008p. 54 Absence of a state does not preclude the existence of a society, such as stateless societies like the Haudenosaunee Confederacy that "do not have either purely or even primarily political institutions or roles". The level of governance of a state, government being considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states, is used to determine whether it has failed. In a federal union, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated polities that make up the federation. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include “ province� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a dependent territory. The commemoration of the independence day of a country or nation celebrates when a country is free from all forms of foreign colonialism; free to build a country or nation without any interference from other nations. Definition of independence Whether the attainment of independence is different from revolution has long been contested, and has often been debated over the question of violence as legitimate means to achieving sovereignty. In general, revolutions aim only to redistribute power with or without an element of emancipation,such as in democratization ''within'' a state, which as such may remain unaltered. For example, the Mexican Revolution (1910) chiefly refers to a multi-factional conflict that ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminalization
Criminalization or criminalisation, in criminology, is "the process by which behaviors and individuals are transformed into crime and criminals". Previously legal acts may be transformed into crimes by legislation or judicial decision. However, there is usually a formal presumption in the rules of statutory interpretation against the retrospective application of laws, and only the use of express words by the legislature may rebut this presumption. The power of judges to make new law and retrospectively criminalise behaviour is also discouraged. In a less overt way, where laws have not been strictly enforced, the acts prohibited by those laws may also undergo ''de facto'' criminalization through more effective or committed legal enforcement. The process of criminalization takes place through societal institutions including schools, the family, and the criminal justice system. The problems There has been some uncertainty as to the nature and extent of the contribution to be mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section 377 Of The Indian Penal Code
Section 377 of the British colonial penal code criminalized all sexual acts "against the order of nature". The law was used to prosecute people engaging in oral and anal sex along with homosexual activity. The penal code remains in many former colonies, such as India (but has been repealed in Singapore) and has been used to criminalize third gender people, such as the ''apwint'' in Myanmar. In 2018, British Prime Minister Theresa May acknowledged how the legacies of British colonial anti-sodomy laws continue to persist today in the form of discrimination, violence, and death. History Although the act of sodomy was sometimes prosecuted in England under British common law, it was first codified in the British empire as Section 377 in the Indian Penal Code as "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" in 1860. Section 377 was then exported to other colonies and even to England itself, providing the legal model for the act of ' buggery' in the Offenses Against the Person Act (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
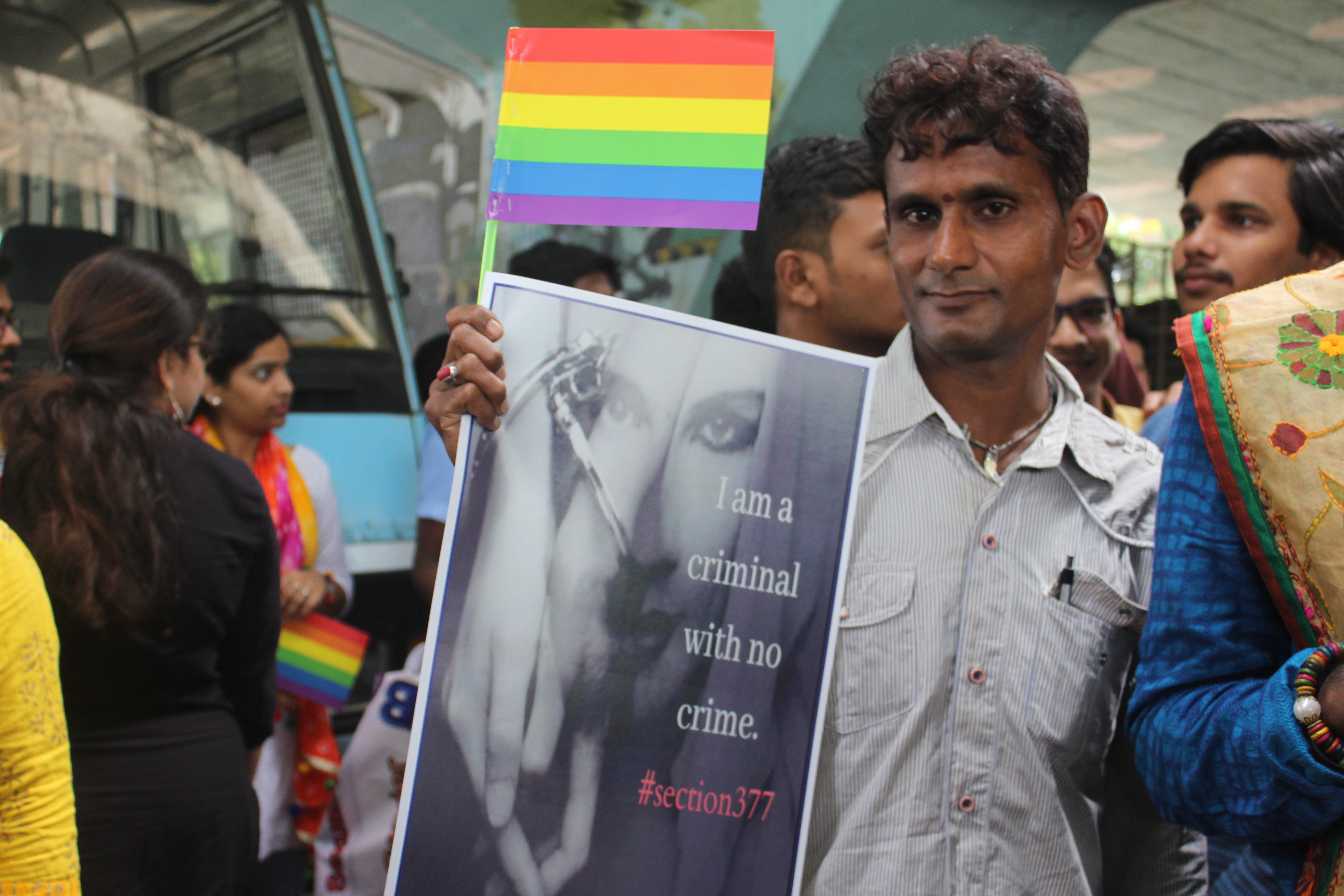






%2C_by_John_Trumbull.jpg)
.jpg)