|
Schneifel
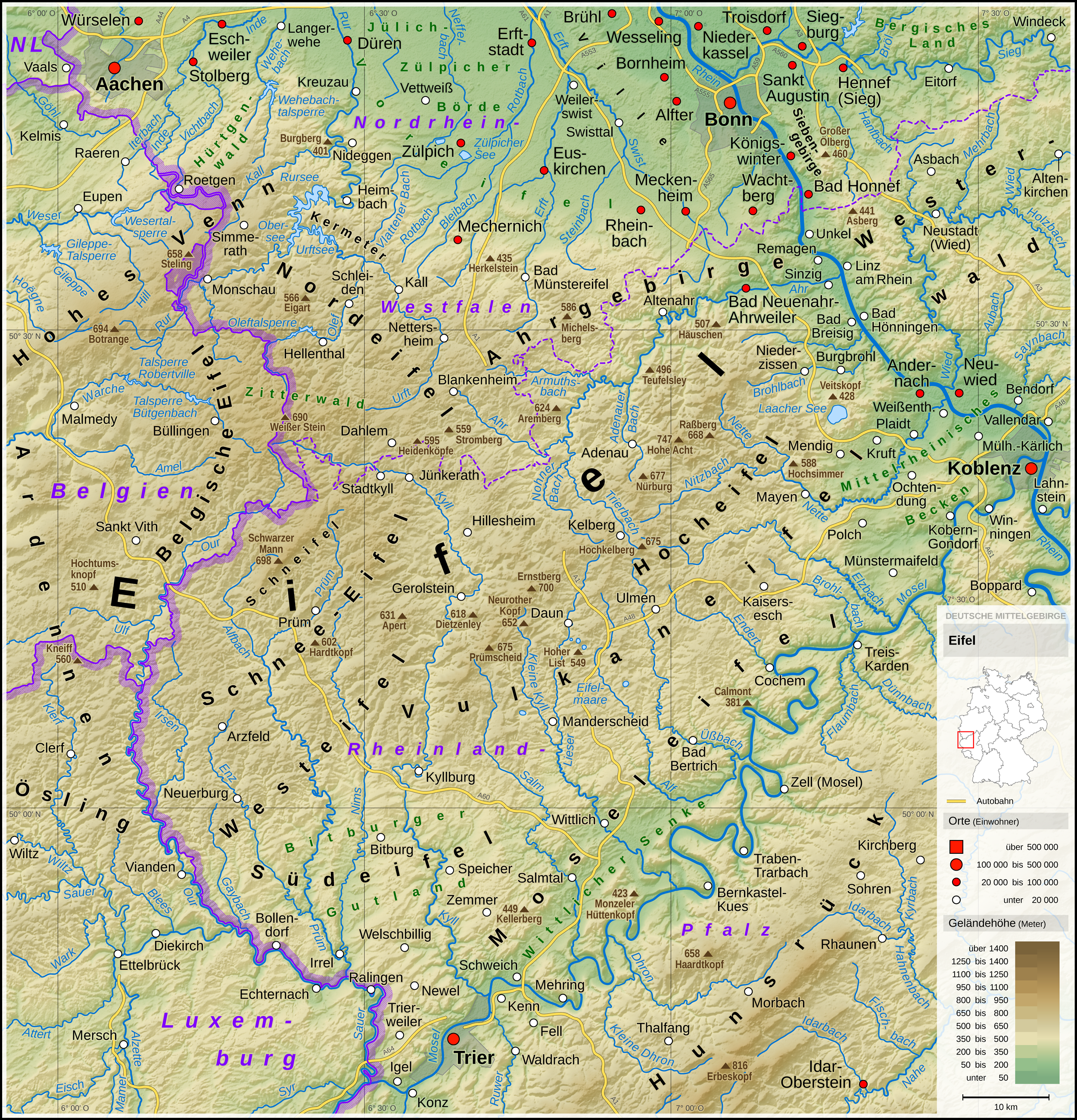
The Schneifel is a range of low mountains, up to , in the western part of the Eifel in Germany, near the Belgian border. It runs from Brandscheid near Prüm in a northeasterly direction to Ormont. The name Schneifel has nothing to do with the German words ''Schnee'' (snow) and ''Eifel''. It is derived from the former dialect of this region and means something like ''Schneise'' ("swathe"). This swathe ran over the mountains. The term was "Germanised" during the Prussian era and the term Schnee-Eifel ("Snow Eifel") was born, albeit referring to a larger area. Winters in this low mountainous region are unusually cold and snowy for western and parts of central Europe and snow lies here for longer than anywhere else in the Eifel. As a result, the winter sports season is longer here than in the surrounding region. The highest point of the Schneifel is the 699.1-metre-high Schwarze Mann ("Black Man"), which is also the third highest point of the Eifel range after the Hohe Acht and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifel
The Eifel (; lb, Äifel, ) is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Community of Belgium. The Eifel is part of the Rhenish Massif; within its northern portions lies the Eifel National Park. Geography Location The Eifel lies between the cities of Aachen to the north, Trier to the south and Koblenz to the east. It descends in the northeast along a line from Aachen via Düren to Bonn into the Lower Rhine Bay. In the east and south it is bounded by the valleys of the Rhine and the Moselle. To the west it transitions in Belgium and Luxembourg into the geologically related Ardennes and the Luxembourg Ösling. In the north it is limited by the Jülich-Zülpicher Börde. Within Germany it lies within the states of Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia; in the Benelux the area of Eupen, St. Vith and Luxembour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schnee-Eifel
The Schnee Eifel is a heavily wooded landscape in Germany's Central Uplands, up to , that forms part of the western Eifel in the area of the German-Belgian border. The name may have been derived in the 19th century from the Schneifel chain of hills which had nothing to do with snow (''Schnee''), but with the name for a forest swathe (''Schneise''). Geography The Schnee Eifel natural region is formed by the southern part of the Hohes Venn-Eifel Nature Park. To the north it is bounded by the river Kyll, the border with the North Eifel, that begins near Hallschlag and Kronenburg with the Zitter Forest; To the east the Kyll forms the boundary river with the High Eifel. To the south the Schnee Eifel merges into the South Eifel to Pronsfeld in the Prümer Land. Its highest elevation is found on the Schneifel ridge: the high Schwarzer Mann ("Black Man"). The term ''Schneifel'' is frequently employed in publications to mean the whole Schnee Eifel region, but they are not syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneifel
The Schneifel is a range of low mountains, up to , in the western part of the Eifel in Germany, near the Belgian border. It runs from Brandscheid near Prüm in a northeasterly direction to Ormont. The name Schneifel has nothing to do with the German words ''Schnee'' (snow) and ''Eifel''. It is derived from the former dialect of this region and means something like ''Schneise'' ("swathe"). This swathe ran over the mountains. The term was "Germanised" during the Prussian era and the term Schnee-Eifel ("Snow Eifel") was born, albeit referring to a larger area. Winters in this low mountainous region are unusually cold and snowy for western and parts of central Europe and snow lies here for longer than anywhere else in the Eifel. As a result, the winter sports season is longer here than in the surrounding region. The highest point of the Schneifel is the 699.1-metre-high Schwarze Mann ("Black Man"), which is also the third highest point of the Eifel range after the Hohe Acht and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ormont
Ormont is an '' Ortsgemeinde'' (a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality) situated in the Vulkaneifel district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Gerolstein, whose seat is in the municipality of Gerolstein. Name It is often supposed that Ormont's name is of French origin (''or'' = “gold”; ''mont'' = “mountain”), but this is not so. In the ''Liber Aureus'', the “Golden Book” of the town of Prüm, is a boundary description for the centres of Olzheim and Ormont. Here, the village is called ''Aurimuncio'', in Mediaeval Latin. Nonetheless, this does have the same literal meaning as the supposed French derivation (''aurum'' = “gold”; ''mons/montem'' = “mountain”). Either way, therefore, the municipality's name means “Gold Mountain”. Geography Location The municipality lies at the foot of the Schneifel in the Vulkaneifel, a part of the Eifel known for its volcanic histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prüm
Prüm () is a town in the Westeifel (Rhineland-Palatinate), Germany. Formerly a district capital, today it is the administrative seat of the '' Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Prüm. Geography Prüm lies on the river Prüm (a tributary of the Sauer) at the southeastern end of the Schneifel, which is 697 m high. Prüm is eponymous for the Prüm syncline (Ger. '' Prümer Kalkmulde''), the largest of the Eifel-lime-synclines. Here, the only GSSP-point in Germany identifies the geological border between the lower Devonian Emsian and the middle Devonian Eifelian. History See main article on the town's former monastery, Prüm Abbey. In 2005, the Prüm Convention was signed in the city by several European countries. Ninety-two percent of the town was destroyed by bombing and ground fighting during the Second World War. In 1949, it was wrecked again by an explosion on the Kalvarienberg hill caused by a fire in an underground ammunition bunker. Twelve people were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohe Acht
The Hohe Acht () is the highest mountain ( ) in the Eifel mountains of Germany. It is located on the boundary between the districts of Ahrweiler and Mayen-Koblenz in Rhineland-Palatinate. Geography and geology The Hohe Acht is located in the High Eifel east of Adenau. The mountain is a Tertiary volcano, whose cone is composed of Lower Devonian rock and whose summit is made of basalt. Emperor William Tower In 1908/09 the Emperor William Tower (''Kaiser-Wilhelm-Turm'') was erected on the Hohe Acht. The occasion for the construction of this stone observation tower, based on plans by the architect, Freiherr von Tettau of Berlin, was the silver wedding of Emperor William II and Empress Augusta Victoria as well as the commemoration of Emperor William I The tower is high and its walls are one metre thick at ground level. The work was carried out by master masons, Karl and Johannes Leidinger, from Adenau using local stone. The cost of construction was 18,000 marks. The tower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial TV
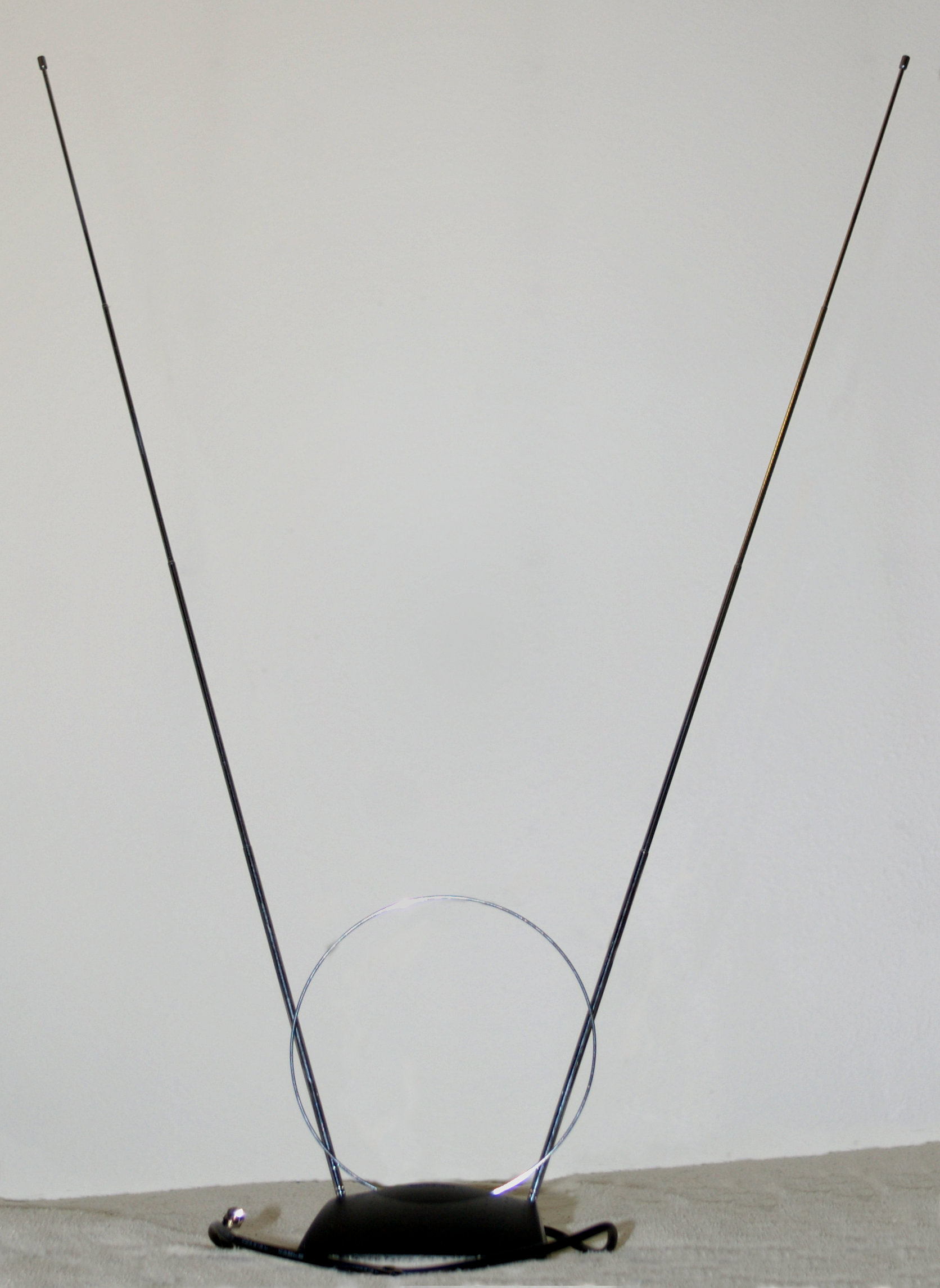
Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a TV station to a TV receiver having an antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast on television channels with frequencies between about 52 and 600 MHz in the VHF and UHF ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried Line
The Siegfried Line, known in German as the ''Westwall'', was a German defensive line built during the 1930s (started 1936) opposite the French Maginot Line. It stretched more than ; from Kleve on the border with the Netherlands, along the western border of Nazi Germany, to the town of Weil am Rhein on the border with Switzerland – and featured more than 18,000 bunkers, tunnels and tank traps. From September 1944 to March 1945 the Siegfried Line was subjected to a large-scale Allied offensive. Name The official name for the German defensive line construction program before and during the Second World War that collectively came to be known as the "Westwall" (and "Siegfried Line", or sometimes "West Wall", in English) changed several times during the late 1930s reflecting areas of progress. * Border Watch programme (pioneering programme) for the most advanced positions (1938) * Limes Programme (1938) * Western Air Defense Zone (1938) * Aachen–Saar Programme (1939) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunker
A bunker is a defensive military fortification designed to protect people and valued materials from falling bombs, artillery, or other attacks. Bunkers are almost always underground, in contrast to blockhouses which are mostly above ground. They were used extensively in World War I, World War II, and the Cold War for weapons facilities, command and control centers, and storage facilities. Bunkers can also be used as protection from tornadoes. Trench bunkers are small concrete structures, partly dug into the ground. Many artillery installations, especially for coastal artillery, have historically been protected by extensive bunker systems. Typical industrial bunkers include mining sites, food storage areas, dumps for materials, data storage, and sometimes living quarters. When a house is purpose-built with a bunker, the normal location is a reinforced below-ground bathroom with fiber-reinforced plastic shells. Bunkers deflect the blast wave from nearby explosions to prevent ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a " Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |