|
Sarira (Vedanta)
According to Sarira Traya, the Doctrine of the Three bodies in Hinduism, the human being is composed of three shariras or "bodies" emanating from Brahman by avidya, "ignorance" or "nescience". They are often equated with the five koshas (sheaths), which cover the atman. The ''Three Bodies Doctrine'' is an essential doctrine in Indian philosophy and religion, especially Yoga, Advaita Vedanta, Tantra and Shaivism. The Three Bodies Karana sarira ŌĆō causal body ''Karana sarira'' or the causal body is merely the cause or seed of the subtle body and the gross body. It has no other function than being the seed of the subtle and the gross body. It is ''nirvikalpa rupam'', "undifferentiated form". It originates with ''avidya'', "ignorance" or "nescience" of the real identity of the atman, instead giving birth to the notion of ''jiva''. Swami Sivananda characterizes the causal body as "The beginningless ignorance that is indescribable". Siddharameshwar Maharaj, the guru of Nisargada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2ŌĆō1.35 billion followers, or 15ŌĆō16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' San─ütana Dharma'' ( sa, ÓżĖÓż©ÓżŠÓżżÓż© Óż¦Óż░ÓźŹÓż«, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purusa
''Purusha'' (' or ) is a complex concept whose meaning evolved in Vedic and Upanishadic times. Depending on source and historical timeline, it means the cosmic being or self, awareness, and universal principle.Karl Potter, Presuppositions of IndiaŌĆÖs Philosophies, Motilal Banarsidass, , pp 105-109 In early Vedas, ''Purusha'' was a cosmic being whose sacrifice by the gods created all life. This was one of many creation myths discussed in the Vedas. In the Upanishads, the ''Purusha'' concept refers to the abstract essence of the Self, Spirit and the Universal Principle that is eternal, indestructible, without form, and is all-pervasive. In Sankhya philosophy, Purusha is the plural immobile cosmic principle, pure consciousness, unattached and unrelated to anything, which is ŌĆ£nonactive, unchanging, eternal, and pureŌĆØ. Purusha uniting with Prakß╣øti (matter) gives rise to life. In Kashmir Shaivism, Purusha is enveloped in five sheaths of time ('' K─üla''), desire (''Raga''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for various mental phenomena, like perception, pain experience, belief, desire, intention, and emotion. Various overlapping classifications of mental phenomena have been proposed. Important distinctions group them according to whether they are ''sensory'', ''propositional'', ''intentional'', ''conscious'', or ''occurrent''. Minds were traditionally understood as substances but it is more common in the contemporary perspective to conceive them as properties or capacities possessed by humans and higher animals. Various competing definitions of the exact nature of the mind or mentality have been proposed. ''Epistemic definitions'' focus on the privileged epistemic access the subject has to these states. ''Consciousness-based approaches'' give primacy to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhi
:''In Hindu mythology, Buddhi is one of the wives of Ganesha.'' Buddhi (Sanskrit: Óż¼ÓźüÓż”ÓźŹÓż¦Óż┐) refers to the intellectual faculty and the power to "form and retain concepts, reason, discern, judge, comprehend, understand". Etymology ''Buddhi'' ( sa, Óż¼ÓźüÓż”ÓźŹÓż¦Óż┐) is derived from the Vedic Sanskrit root ''Budh'' (Óż¼ÓźüÓż¦ÓźŹ ), which literally means "to wake, be awake, observe, heed, attend, learn, become aware of, to know, be conscious again". The term appears extensively in Rigveda and other Vedic literature. ''Buddhi'' means, states Monier Williams, the power to "form, retain concepts; intelligence, reason, intellect, mind", the intellectual faculty and the ability to "discern, judge, comprehend, understand" something. Buddhi is a feminine Sanskrit noun derived from ''*budh'', to be awake, to understand, to know. The same root is the basis for the more familiar masculine form ''Buddha'' and the abstract noun ''bodhi''. Buddhi contrasts from ''manas'' (Óż«Óż©ÓżĖÓ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antahkarana
AntaßĖźkaraß╣ća (Sanskrit: ÓżģÓż©ÓźŹÓżżÓżāÓżĢÓż░ÓżŻ) is a concept in Hindu philosophy, referring to the totality of the mind, including the thinking faculty, the sense of I-ness, and the discriminating faculty. AntaßĖź means 'inner' and karaß╣ća means 'instrument', or, 'function'. Therefore, the word ''AntaßĖźkaraß╣ća'' can be understood as 'inner organ', 'inner functions', or, 'inner instrument'. It also refers to the four functions of the mind, namely the manas (the mind or lower mind), buddhi (the intellect or higher mind), chitta (memory, or, consciousness), and ahamkara (ego, or, I-maker). ''AntaßĖźkaraß╣ća'' has also been called the link between the middle and higher mind, the reincarnating part of the mind. In Ved─üntic literature, this (''internal organ'') is organised into four parts: # ahaß╣āk─üra (''ego'')ŌĆöidentifies the Atman (''self'') with the body as 'I'. The attachment or identification of the ego, also known as the 'I-maker'. # buddhi (''intellect'')ŌĆöthe de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prajna (Vedic) , a Buddhist concept
{{disambig ...
Prajna or Praj├▒─ü may refer to: * Praj├▒─ü (Hinduism), a Hindu concept * Praj├▒─ü (Buddhism), a Buddhist concept * Prajna (Buddhist monk), an important 9th century Buddhist monk from Gandhara See also * Prajnaparamita A Tibetan painting with a Praj├▒─üp─üramit─ü s┼½tra at the center of the mandala Praj├▒─üp─üramit─ü ( sa, Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░Óż£ÓźŹÓż×ÓżŠÓż¬ÓżŠÓż░Óż«Óż┐ÓżżÓżŠ) means "the Perfection of Wisdom" or "Transcendental Knowledge" in Mah─üy─üna and Therav─üda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhi
:''In Hindu mythology, Buddhi is one of the wives of Ganesha.'' Buddhi (Sanskrit: Óż¼ÓźüÓż”ÓźŹÓż¦Óż┐) refers to the intellectual faculty and the power to "form and retain concepts, reason, discern, judge, comprehend, understand". Etymology ''Buddhi'' ( sa, Óż¼ÓźüÓż”ÓźŹÓż¦Óż┐) is derived from the Vedic Sanskrit root ''Budh'' (Óż¼ÓźüÓż¦ÓźŹ ), which literally means "to wake, be awake, observe, heed, attend, learn, become aware of, to know, be conscious again". The term appears extensively in Rigveda and other Vedic literature. ''Buddhi'' means, states Monier Williams, the power to "form, retain concepts; intelligence, reason, intellect, mind", the intellectual faculty and the ability to "discern, judge, comprehend, understand" something. Buddhi is a feminine Sanskrit noun derived from ''*budh'', to be awake, to understand, to know. The same root is the basis for the more familiar masculine form ''Buddha'' and the abstract noun ''bodhi''. Buddhi contrasts from ''manas'' (Óż«Óż©ÓżĖÓ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manas-vijnana
Manas-vijnana (Skt. "'Óż«ÓżŠÓż©ÓżĖ-ÓżĄÓż┐Óż£ÓźŹÓż×ÓżŠÓż©"'; m─ünas-vij├▒─üna; "mind-knowledge", compare '' man-tra'', j├▒─üna) is the seventh of the eight consciousnesses as taught in Yogacara and Zen Buddhism, the higher consciousness or intuitive consciousness that on the one hand localizes experience through thinking and on the other hand universalizes experience through intuitive perception of the universal mind of alayavijnana. Manas-vijnana, also known as klista-manas-vijnana or simply manas, is not to be confused with ''manovijnana'' which is the sixth consciousness. Overlapping Pali terms for "mind" According to Bhikkhu Bodhi, the post-canonical Pali commentary uses the three terms ''vi├▒├▒─üa'', ''mano'' and ''citta'' as synonyms for the mind sense base (''mana- ayatana''); however, in the Sutta Pitaka, these three terms are generally contextualized differently: * ''Vi├▒├▒─üa'' refers to awareness through a specific internal sense base, that is, through the eye, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manas (early Buddhism)
''Manas'' (Pali: Óż«Óż©ÓżĖÓźŹ) is one of three overlapping terms used in the nikayas to refer to the mind, the others being ''citta'' and '' vi├▒├▒─üß╣ća''. Comparison with ''citta'' and ''vi├▒├▒─üß╣ća'' ''Manas'', ''citta'', and ''vi├▒├▒─üß╣ća'' are each sometimes used in the generic and non-technical sense of "mind" in general, and the three are sometimes used in sequence to refer to one's mental processes as a whole. Their primary uses are, however, distinct. In the distinction of Abhidhamma Pitaka of Theravada Buddhism, mana or mano is sort of the notion of mind as a whole, whereas a citta is each of instant steps or processes of mind, and vi├▒├▒─üß╣ća is one of the several forms of citta, also being a step of a vithi or mental procedure, which is an orderly sequence of citta. Relationship with thinking and volition Manas often indicates the general thinking faculty. Thinking is closely associated with volitions, because mental activity is one of the ways that volit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
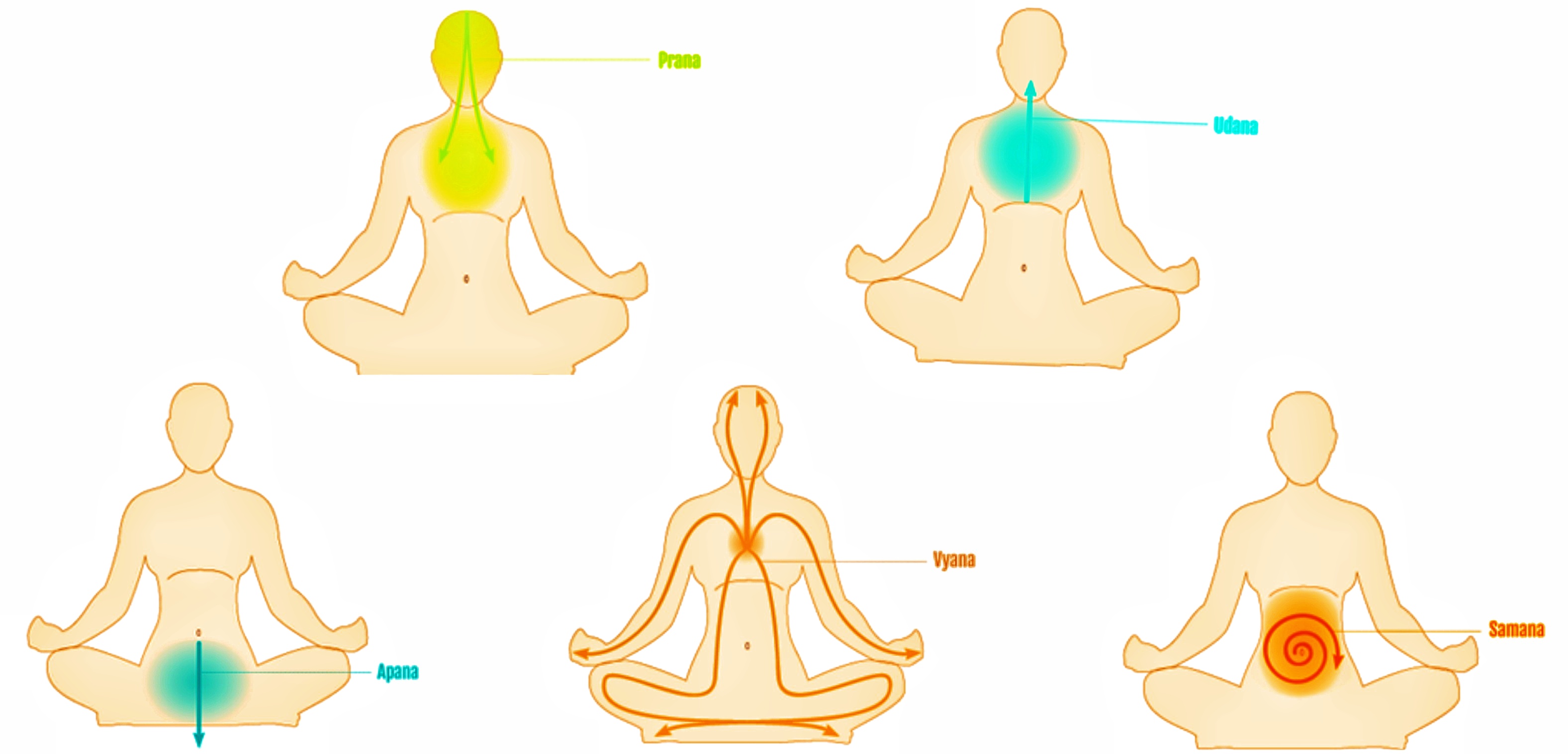
Prana
In yoga, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts, prana ( sa2, Óż¬ÓźŹÓż░ÓżŠÓżŻ, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, "life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, pr─üß╣ća is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of pr─üß╣ća, collectively known as the five '' v─üyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''pr─üß╣ća v─üyu'' as the basic v─üyu from which the other v─üyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas ŌĆō Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana ŌĆō and the five Upa-Pranas ŌĆō Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana. Etymology V. S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchikarana
''Pancikarana'' ( sa, Óż¬Óż×ÓźŹÓżÜÓźĆÓżĢÓż░ÓżŻ, Pa├▒c─½karaß╣ća, quintuplication) is a Vedantic theory of how matter came into existence, originating from the primordial five subtle elements. History Adi Shankara wrote a treatise on this theory, titled ŌĆō ''Pancikaranam'', which was elaborated by his disciple Sureshvaracharya, and later on commented upon in 2400 slokas by Ramananda Saraswati, disciple of Ramabhadra, and in 160 slokas by Ananda Giri, disciple of Suddhananda Yati. The Chandogya Upanishad teaches the doctrine of tripartition () from which developed the Vedantic theory of ''pancikarana'' with regard to the creation of the transformed evolutes of the original elements. This theory is also found narrated to Narada in the '' Srimad Devi Bhagavatam''. Overview ''Pancikarana'' is the creation of the elements (''bh┼½tasarga'') by a process in which subtle matter (or the prior stage of matter) transforms itself into gross matter. Intelligence is the subtle manife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anandamaya Kosha
The Anandamaya kosha or "sheath made of bliss" ( ananda) is in Vedantic philosophy the most subtle or spiritual of the five levels of embodied self. It has been interpreted differently according to specific schools of Indian (and also Theosophical) thought. The Anandamaya kosha in traditional Advaita Vedanta In Advaita Vedanta the Anandamaya kosha is the innermost of the five koshas or "sheaths" that veil the Atman or Supreme Self. Unlike the next three more outer koshas, it constitutes the ''karana sarira'' or causal body. It is associated with the state of dreamless sleep and samadhi. The Anandamaya kosha in Krsna Consciousness The ānanda-maya stage is explained by A. C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada as the "brahma-bhūta" stage in the Bhagavad-gītā. There it is said that in the brahma-bhūta stage of life there is no anxiety and no hankering. This stage begins when one becomes equally disposed toward all living entities, and it then expands to the stage of KṠ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |