|
Sarcophaga
''Sarcophaga'' is a genus of true flies and the type genus of the flesh-fly family (Sarcophagidae). The members of this cosmopolitan genus are frequently known as common flesh flies. This genus occurs essentially worldwide. These flies are generally well-sized and of a greyish color; like many of their relatives, the typical patterns are lengthwise darker stripes on the thorax and dark and light square dots on the abdomen. Many have conspicuous red compound eyes. These are set further apart in females than in males; the females are also larger on average. As typical for this family, it is almost impossible to tell the species apart from their outward appearance, and many can only be reliably identified by microscopic examination of the males' genitalia. As the common name implies, their larvae typically feed on decaying meat. Some, however, instead eat the bacteria and other small organisms living on carrion. Many species have adapted to humans, and while they are usually nuis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Haemorrhoidalis
''Sarcophaga pernix'', also known as the red-tailed flesh fly, is a fly in the Sarcophagidae family. This fly often breeds in carrion and feces, making it a possible vector for disease. The larvae of this species can cause myiasis, as well as accidental myiasis. It is potentially useful in forensic entomology. Taxonomy ''Sarcophaga pernix'' was first described by Moses Harris, an English entomologist, in 1780. ''Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis'' was first described by Carl Fredrik Fallén (1764–1830), a Swedish botanist and entomologist, in 1817 during his tenure at Lund University between 1814–1827. Fallén first named this species ''Musca haemorrhoidalis'' in 1817 not knowing that Charles Joseph de Villers had already named an unrelated species ''Musca haemorrhoidalis'' in 1789. In 1826, Johann Wilhelm Meigen, a German entomologist famous for his pioneering work on Diptera, described the same species that Fallén had described in 1817 as ''Sarcophaga cruentata'' following Mei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Bullata
''Sarcophaga bullata'', or the grey flesh fly, is a species of fly belonging to the family Sarcophagidae. It varies in size from small to large, 8 to 17 millimeters in length and is very similar in appearance and behavior to a closely related species, ''Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis''. ''S. bullata'' is a common scavenger species in the Eastern United States, but is found throughout the Nearctic region. Identification down to the species level in the family Sarcophagidae is notably difficult and relies primarily on the male genitalia. Though limited information is available regarding ''S. bullata'', it has gained increasing recognition in the field of forensic entomology as a forensically-relevant fly species, as it may be among the first species to colonize human remains. In these instances, recovered maggots may be analyzed for post-mortem interval (PMI) estimations, which may be used as evidence in courts of law. Current studies regarding ''S. bullata'' have revealed a maternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Carnaria
''Sarcophaga carnaria'' is a European(globalized) species of flesh fly within the common flesh fly genus, ''Sarcophaga''. Identification Only males can be identified with certainty, and then only by examining genitalia. Biology Larvae mostly feed on earthworms. Adults are attracted to rotting meat and faeces. Distribution European, from the U.K. and southern Europe, east to the Altai mountains and north to the Kola Peninsula sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк , image_name= Kola peninsula.png , image_caption= Kola Peninsula as a part of Murmansk Oblast , image_size= 300px , image_alt= , map_image= Murmansk in Russia.svg , map_caption = Location of Murmansk Oblast .... left, Video References Sarcophagidae Insects described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus {{Oestroidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagidae
Sarcophagidae () are a family of flies commonly known as flesh flies. They differ from most flies in that they are ovoviviparous, opportunistically depositing hatched or hatching maggots instead of eggs on carrion, dung, decaying material, or open wounds of mammals, hence their common name. Some flesh fly larvae are internal parasites of other insects such as Orthoptera, and some, in particular the Miltogramminae, are kleptoparasites of solitary Hymenoptera. The adults mostly feed on fluids from animal bodies, nectar, sweet foods, fluids from animal waste and other organic substances. Juveniles need protein to develop and may be laid on carrion, dung or sweet plant foods (including fruit, nuts, and artificial foodstuffs). Diagnostic characteristics Members of the subfamily Sarcophaginae are small to large flies with black and gray longitudinal stripes on the thorax and checkering on the abdomen. Other key features include red eyes and a bristled abdomen. Abdominal sternit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Crassipalpis
''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' is a species of flesh flies (insects in the family Sarcophagidae. It is a common laboratory animal used in the study of gene expression and the study of diapause in insects. ''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' conforms to the basic bilateral symmetry body plan for arthropods and insects by possessing jointed-appendages, a sclerotized external cuticle, and an internal muscular system that functions as levers for movement. The six legs possess a tarsus, or foot, with a pair of claws for gripping rough surfaces. Beneath the claws is a fleshy, glandular adhesive pad called a pulvillus, which is used on smooth surfaces. ''Sarcophaga crassipalpis'' is an insect in the order Diptera, meaning “two-winged”. As with other flies, ''S. crassipalpis'' has one pair of wings used for flying. Posterior to the wings is a small pair of knob-like structures (called halteres), which function as organs of balance. Like other dipterans, ''S. crassipalpis'' reproduces ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Africa
''Sarcophaga (Bercaea) africa'' is a species of fly belonging to the family Sarcophagidae, the flesh-flies. It is the best known species in its genus. ''S. africa'' feeds on living and dead tissue, including snails, and other decomposing matter, and feces. ''Sarcophaga africa'' is a synanthropic species known to cause myiasis in humans and livestock. The species is considered useful in forensic entomology Forensic entomology is the scientific study of the colonization of a dead body by arthropods. This includes the study of insect types commonly associated with cadavers, their respective life cycles, their ecological presences in a given environme ... due to this quality. ''S. africa'' is coprophagus, lays eggs in feces, and can be cultured from human and animal feces. The fly also lays eggs in decaying flesh and can be cultured from the decaying matter. References Sarcophagidae Forensic entomology Insects described in 1824 {{Oestroidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophaga Aldrichi
The friendly fly or large flesh fly, ''Sarcophaga aldrichi'', is a fly that is a parasitoid of the forest tent caterpillar. It strongly resembles the house fly but is in a different family, the Sarcophagidae, or flesh-flies. It is a little larger than the house fly, and has the same three black stripes on its thorax. It has red eyes, a grayish body, and a checkered abdomen. In early summer it emerges from pupae in the ground and seeks out forest tent caterpillar cocoons, where it deposits live larvae which bore into the cocoons and feed on the pupating insects, killing them. Eventually the fly maggot A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies. Entom ...s drop to the ground and pupate and go dormant over the winter. Population explosions of this species usually occur during the summe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrophagy
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding behavior. Scavengers play an important role in the ecosystem by consuming dead animal and plant material. ''Decomposers'' and detritivores complete this process, by consuming the remains left by scavengers. Scavengers aid in overcoming fluctuations of food resources in the environment. The process and rate of scavenging is affected by both biotic and abiotic factors, such as carcass size, habitat, temperature, and seasons. Etymology Scavenger is an alteration of ''scavager,'' from Middle English ''skawager'' meaning "customs collector", from ''skawage'' meaning "customs", from Old North French ''escauwage'' meaning "inspection", from ''schauwer'' meaning "to inspect", of Germanic origin; akin to Old English ''scēawian'' and German ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
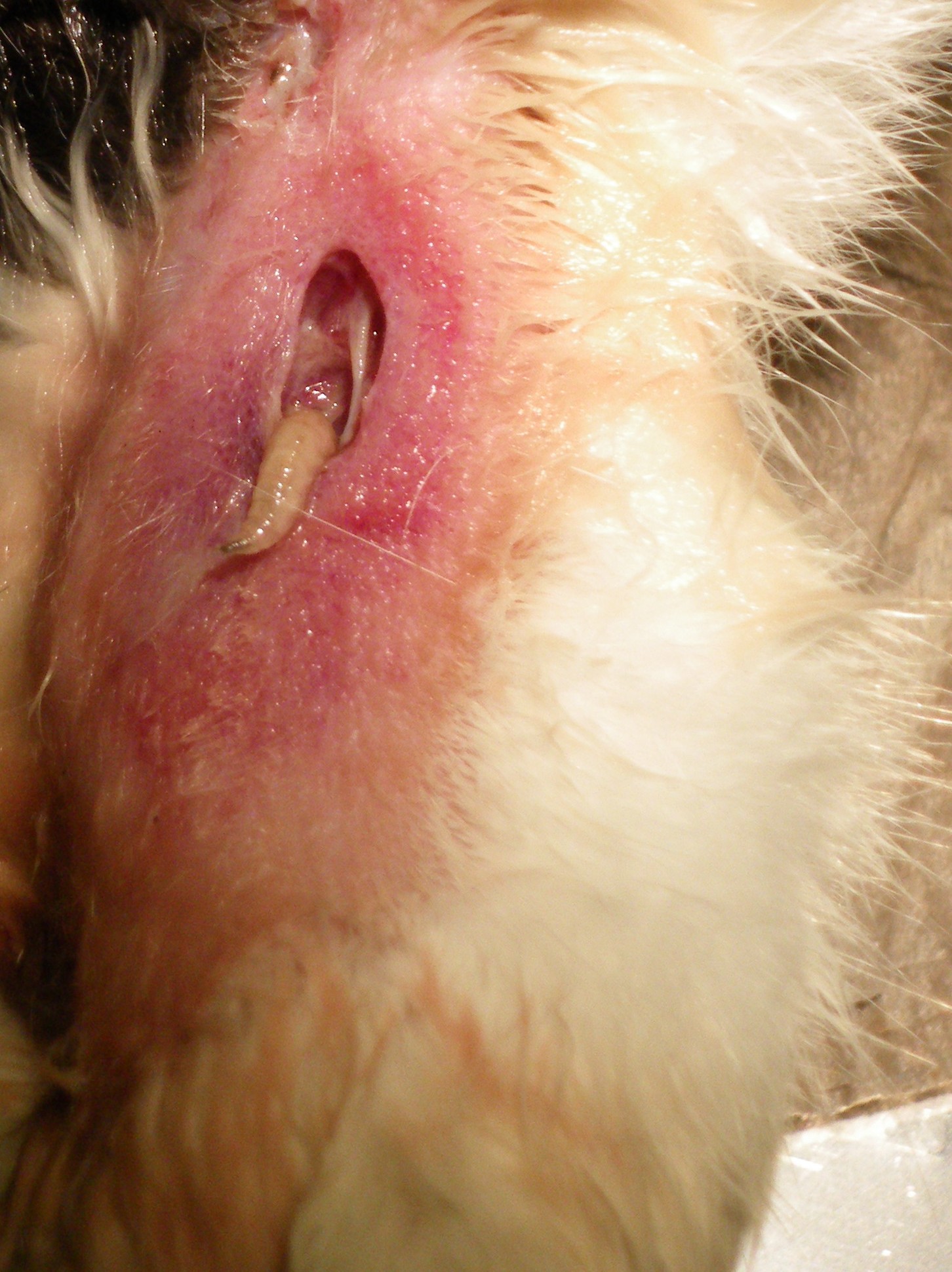
Myiasis
Myiasis is the parasitic infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larvae (maggots) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wounds and urine- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly, blowfly, and screwfly) can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies (such as the common housefly) as vector agents for their parasitic larvae. Because some animals (particularly non-native domestic animals) cannot react as effectively as humans to the causes and effects of myiasis, such infestations present a severe and continuing problem for livestock industries worldwide, causing severe economic losses where they are not mitigated by human action. Although typically a far greater issue for animals, myiasis is also a relatively frequent disease for humans in rural tropical regions where myiatic flies thrive, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pest (organism)
A pest is any animal or plant harmful to humans or human concerns. The term is particularly used for creatures that damage crops, livestock, and forestry or cause a nuisance to people, especially in their homes. Humans have modified the environment for their own purposes and are intolerant of other creatures occupying the same space when their activities impact adversely on human objectives. Thus, an elephant is unobjectionable in its natural habitat but a pest when it tramples crops. Some animals are disliked because they bite or sting; snakes, wasps, ants, bed bugs, fleas and ticks belong in this category. Others enter the home; these include houseflies, which land on and contaminate food, beetles, which tunnel into the woodwork, and other animals that scuttle about on the floor at night, like cockroaches, which are often associated with unsanitary conditions. Agricultural and horticultural crops are attacked by a wide variety of pests, the most important being insects, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |