|
STS-56
STS-56 was a NASA Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' mission to perform special experiments. The mission was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on April 8, 1993. Crew Mission highlights The primary payload of the flight was the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science-2 (ATLAS-2), designed to collect data on the relationship between the Sun's energy output and Earth's middle atmosphere and how these factors affect the ozone layer. It included six instruments mounted on a Spacelab pallet in the cargo bay, with the seventh mounted on the wall of the bay in two Get Away Special (GAS) canisters. Atmospheric instruments included the Atmospheric Trace Molecule Spectroscopy (ATMOS) experiment, the Millimeter Wave Atmospheric Sounder (MAS), and the Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV/A) spectrometer (on the cargo bay wall). Solar science instruments were the solar spectrometry instrument SOLSPEC, the Solar Ultraviolet Irradiance Monitor (SUSIM), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Cockrell
Kenneth Dale "Taco" Cockrell (born April 9, 1950) is a retired American astronaut, engineer and a veteran of five Space Shuttle missions. He served as Chief of the Astronaut Office from 1997 to 1998. Pre-NASA career Cockrell was born in Austin, Texas to Buford Dale Cockrell and Jewell Moorman. He graduated from Rockdale High School in nearby Rockdale, Texas in 1968. He earned a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin in 1972 and received his commission in the United States Navy that same year. He also earned a master's in aeronautical systems from the University of West Florida in 1974. He was trained as a pilot and was stationed from 1975 to 1978 aboard the aircraft carrier . Cockrell then became a test pilot for several years before serving two tours of duty aboard . In 1987, Cockrell resigned from the Navy and joined the Aircraft Operations Division of Johnson Space Center as a research pilot. NASA experience Selected by NASA in Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Foale
Colin Michael Foale (; born 6 January 1957) is a British-American astrophysicist and former NASA astronaut. He is a veteran of six space missions, and is the only NASA astronaut to have flown extended missions aboard both Mir and the International Space Station. He was the second Briton in space and the first to perform a space walk. Until 17 April 2008 he held the record for most time spent in space by a US citizen: 374 days, 11 hours, 19 minutes, and he still holds the cumulative-time-in-space record for a UK citizen. Life and career Foale was born in Louth, Lincolnshire to a British father, Colin, and an American mother, Mary. He was raised in Cambridge and educated at The King's School, Canterbury. A member of the Air Training Corps, he studied at Queens' College, Cambridge, (with Stephen Fry who was entertained by his ambition of going to space) receiving a first-class honours degree in natural sciences in 1978 and a doctorate in laboratory astrophysics in 1982, where hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellen Ochoa
Ellen Ochoa (born May 10, 1958) is an American engineer, former astronaut and former director of the Johnson Space Center. In 1993, Ochoa became the first Hispanic woman to go to space when she served on a nine-day mission aboard the Space Shuttle ''Discovery''. Ochoa became director of the center upon the retirement of the previous director, Michael Coats, on December 31, 2012. She was the first Hispanic director and the second female director of Johnson Space Center. Early life and education Ellen Lauri Ochoa was born on May 10, 1958 in Los Angeles, California to Joseph and Rosanne (née Deardorff) Ochoa. Her paternal grandparents immigrated from Sonora, Mexico to Arizona and later to California where her father was born. She grew up in La Mesa, California. Ochoa was the middle child of five and neither parent had college degrees. Ochoa graduated from Grossmont High School in El Cajon in 1975. Her parents divorced when she was in high school and she lived with her mother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-55
STS-55, or Deutschland 2 (D-2), was the 55th overall flight of the NASA Space Shuttle and the 14th flight of Shuttle ''Columbia''. This flight was a multinational Spacelab flight involving 88 experiments from eleven different nations. The experiments ranged from biology sciences to simple Earth observations. Crew Backup crew Mission highlights ''Columbia'' carried to orbit the second reusable German Spacelab D-2 and demonstrated the shuttle's ability for international cooperation, exploration, and scientific research in space. The Spacelab module and an exterior experiment support structure contained in ''Columbia''s payload bay comprised the Spacelab D-2 payload. The first German Spacelab flight, D-1, flew Shuttle mission STS-61-A in October 1985. The United States and Germany gained valuable experience for future space station operations. The D-2 mission, as it was commonly called, augmented the German microgravity research program started by the D-1 mission. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-54
STS-54 was a NASA '' Space Transportation System'' ( Space Shuttle) mission using Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. This was the third flight for ''Endeavour'', and was launched on January 13, 1993 with Endeavour returning to the Kennedy Space Center on January 19, 1993. Crew Mission highlights The primary payload was the fifth TDRS satellite, TDRS-F, which was deployed on day one of the mission. It was later successfully transferred to its proper orbit by the Inertial Upper Stage (IUS). Also carried into orbit in the payload bay was a Hitchhiker experiment called the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer (DXS). This instrument collected data on X-ray radiation from diffuse sources in deep space. Other middeck payloads to test the effects of microgravity included the Commercial General Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGPA) for-life sciences research; the Chromosome and Plant Cell Division in Space Experiment (CHROMEX) to-study plant growth; the Physiological and Anatomical Rodent Experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, and other related hardware housed in the Shuttle's cargo bay. The components were arranged in various configurations to meet the needs of each spaceflight. Spacelab components flew on a total of about 32 Shuttle missions, depending on how such hardware and missions are tabulated. Spacelab allowed scientists to perform experiments in microgravity in geocentric orbit. There was a variety of Spacelab-associated hardware, so a distinction can be made between the major Spacelab program missions with European scientists running missions in the Spacelab habitable module, missions running other Spacelab hardware experiments, and other Space Transportation System (STS) missions that used some component of Spacelab hardware. There is some varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Discovery
Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' ( Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-103) is one of the orbiters from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the third of five fully operational orbiters to be built. Its first mission, STS-41-D, flew from August 30 to September 5, 1984. Over 27 years of service it launched and landed 39 times, aggregating more spaceflights than any other spacecraft to date. The Space Shuttle launch vehicle has three main components: the Space Shuttle orbiter, a single-use central fuel tank, and two reusable solid rocket boosters. Nearly 25,000 heat-resistant tiles cover the orbiter to protect it from high temperatures on re-entry. ''Discovery'' became the third operational orbiter to enter service, preceded by ''Columbia'' and ''Challenger''. It embarked on its final mission, STS-133, on February 24, 2011, and touched down for the last time at Kennedy Space Center on March 9, having spent a cumulative total of nearly a full year in space. ''Discovery'' performed bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Corona
A corona ( coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It consists of plasma. The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. It is most easily seen during a total solar eclipse, but it is also observable with a coronagraph. Spectroscopic measurements indicate strong ionization in the corona and a plasma temperature in excess of , much hotter than the surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere. The word ''corona'' is , in turn derived . History In 1724, French-Italian astronomer Giacomo F. Maraldi recognized that the aura visible during a solar eclipse belongs to the Sun, not to the Moon. In 1809, Spanish astronomer José Joaquín de Ferrer coined the term 'corona'. Based in his own observations of the 1806 solar eclipse at Kinderhook (New York), de Ferrer also proposed that the corona was part of the Sun and not of the Moon. English astronomer Norman Lockyer identified the first element unkn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
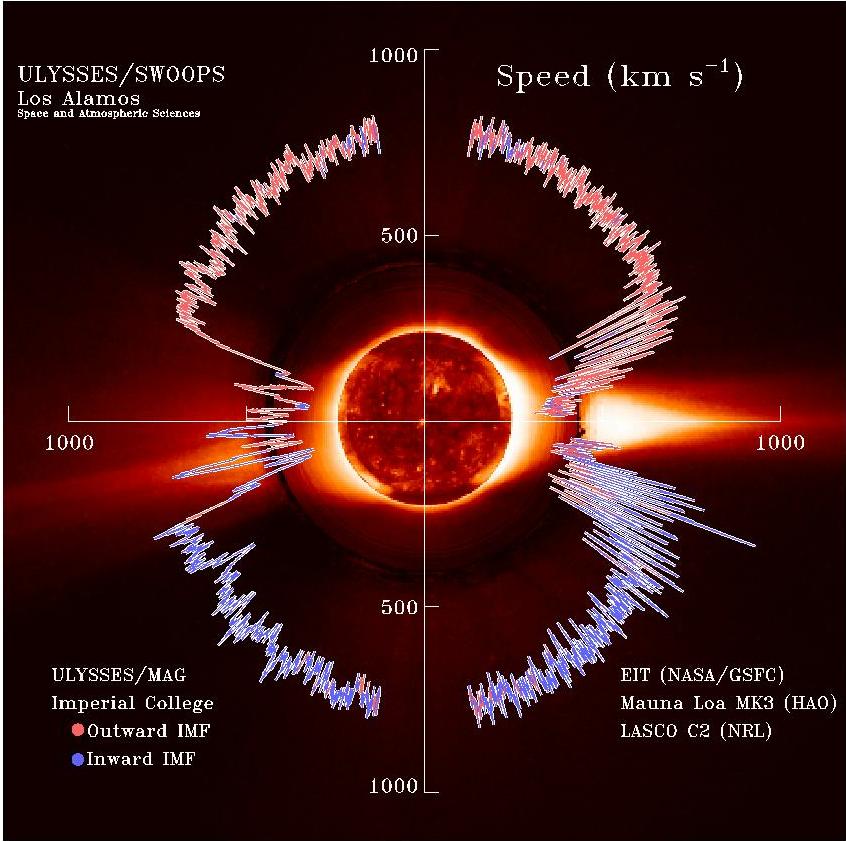
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Straits of Florida and Cuba; it is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Spanning , Florida ranks 22nd in area among the 50 states, and with a population of over 21 million, it is the third-most populous. The state capital is Tallahassee, and the most populous city is Jacksonville. The Miami metropolitan area, with a population of almost 6.2 million, is the most populous urban area in Florida and the ninth-most populous in the United States; other urban conurbations with over one million people are Tampa Bay, Orlando, and Jacksonville. Various Native American groups have inhabited Florida for at least 14,000 years. In 1513, Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadarm
Canadarm or Canadarm1 (officially Shuttle Remote Manipulator System or SRMS, also SSRMS) is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, the Canadarm was always paired with the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which was used to inspect the exterior of the shuttle for damage to the thermal protection system. Development In 1969, Canada was invited by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to participate in the Space Shuttle program. At the time what that participation would entail had not yet been decided but a manipulator system was identified as an important component. Canadian company DSMA ATCON had developed a robot to load fuel into CANDU nuclear reactors; this robot attracted NASA's attention. In 1975, NASA and the Canadian National Research Council (NRC) signed a memorandum of understanding that Canada would develop and const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-66
STS-66 was a Space Shuttle program mission that was flown by the Space Shuttle ''Atlantis''. STS-66 launched on 3 November 1994 at 11:59:43.060 am EDT from Launch Pad 39-B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. ''Atlantis'' landed at Edwards Air Force Base on 14 November 1994 at 10:33:45 am EST. Crew Mission highlights The Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Sciences – 3 (ATLAS-03) was the primary payload aboard STS-66. It continued the series of Spacelab flights to study the energy of the sun and how it affects the Earth's climate and environment. The ATLAS-03 mission made the first detailed measurements from the Shuttle of the Northern Hemisphere's middle atmosphere in late fall. The timing of the flight, when the Antarctic ozone hole is diminishing, allowed scientists to study possible effects of the ozone hole on mid-latitudes, the way Antarctic air recovers, and how the northern atmosphere changes as the winter season approaches. In addition to the ATLAS-03 inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |