|
Szakoly Power Plant
The Szakoly Power Plant is one of Hungary's largest biomass Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ... power plants having an installed electric capacity of 20 MW. References Energy infrastructure completed in 2008 Biomass power stations in Hungary {{powerstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szakoly
Szakoly is a village in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary. It is 135 miles (217 km) to the east of Budapest and 21 miles (33 km) to the north east of Debrecen. It is home to the Szakoly Power Plant. Szakoly was first mentioned in 1290. Geography It covers an area of and has a population of 2952 people (2004). There is a lake on the southern border of the settlement. Average annual precipitation is about 560–590 mm, and the annual average temperature is between 9.5 to 9.6 °C (49.1 to 49.3 °F). History Szakoly was first mentioned in 1290. Inhabited area as early as the Avars age was built by B.C. II.-I. century. This is evidenced by several archaeological finds. During the reign of King of Bela III. of Hungary, it was a hospital in Szakoly. Here was a county assembly in 1320. It were owned by the Zakoly family in 1487, hence the name of the settlement known today. The Turks almost completely destroyed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
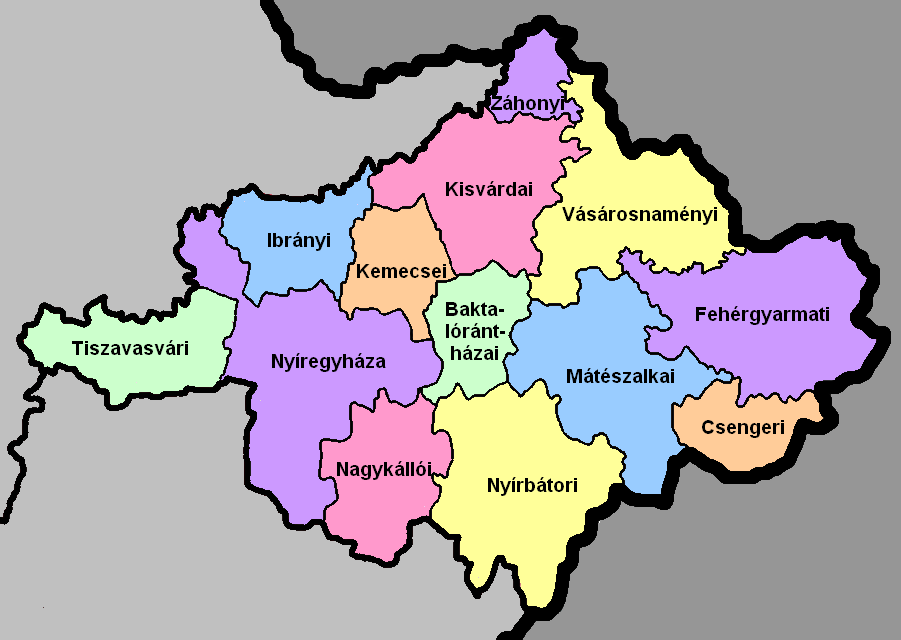
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg ( hu, Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg megye, ) is an administrative county (Hungarian: ''megye'') in north-eastern Hungary, bordering Slovakia (Košice Region), Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), and Romania ( Bihor and Satu Mare counties). It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Hajdú-Bihar and Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén. The capital of Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county is Nyíregyháza. Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County was organised after World War II from the previous counties Szatmár-Ugocsa-Bereg and Szabolcs. Before 1991, it was called Szabolcs-Szatmár County. Geography Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg is located in the north-eastern tip of Hungary. It borders Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), Slovakia (Košice Region), and Romania ( Bihor and Satu Mare counties), and has good connections both by road and rail. Within Hungary, the county is bordered by Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County and the Tisza River to the north-west and Hajdú-Bihar County to the south-west. The earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tohoku Electric Power
is an electric utility, servicing 7.6 million individual and corporate customers in six prefectures in Tōhoku region plus Niigata Prefecture. It provides electricity at 100 V, 50 Hz, though some area use 60 Hz. Tohoku Electric Power is the fourth-largest electric utility in Japan in terms of revenue, behind TEPCO, KEPCO and Chubu Electric Power. Shareholders * Nippon Life Insurance Company 3.9% * Japan Trustee Services Bank 3.8% * The Master Trust Bank of Japan 3.6% Accidents On 11 March 2011, several nuclear reactors in Japan were badly damaged by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. In the Onagawa Nuclear Power Plant a fire broke out in the turbine section of the plant. In order to make up for the loss of electricity from the damaged reactor plant, Tohoku announced it would restart a mothballed natural gas power plant. The liquefied natural gas and oil-fired No. 1 unit at the Higashi Niigata plant in Niigata prefecture has a 350-megawatt capacity and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biomass and biofuel interchangeably, while others consider biofuel to be a ''liquid'' or ''gaseous'' fuel used for transportation, as defined by government authorities in the US and EU. The European Union's Joint Research Centre defines solid biofuel as raw or processed organic matter of biological origin used for energy, such as firewood, wood chips, and wood pellets. In 2019, biomass was used to produce 57 EJ (exajoules) of energy, compared to 190 EJ from crude oil, 168 EJ from coal, 144 EJ from natural gas, 30 EJ from nuclear, 15 EJ from hydropower, hydro and 13 EJ from wind power, wind, solar power, solar and geothermal energy, geothermal combined. Approximately 86% of modern bioenergy is used for heating applications, with 9% used for tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non- Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms biomass and biofuel interchangeably, while others consider biofuel to be a ''liquid'' or ''gaseous'' fuel used for transportation, as defined by government authorities in the US and EU. The European Union's Joint Research Centre defines solid biofuel as raw or processed organic matter of biological origin used for energy, such as firewood, wood chips, and wood pellets. In 2019, biomass was used to produce 57 EJ (exajoules) of energy, compared to 190 EJ from crude oil, 168 EJ from coal, 144 EJ from natural gas, 30 EJ from nuclear, 15 EJ from hydropower, hydro and 13 EJ from wind power, wind, solar power, solar and geothermal energy, geothermal combined. Approximately 86% of modern bioenergy is used for heating applications, with 9% used for tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Infrastructure Completed In 2008
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that has mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |