|
Systemic Symptom
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of Organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues, or affects the Human body, body as a whole. It differs from a localized disease, which is a disease affecting only part of the body (e.g., a mouth ulcer). Examples * Mastocytosis, including mast cell activation syndrome and eosinophilic esophagitis * Chronic fatigue syndrome * vasculitis, Systemic vasculitis e.g. Lupus erythematosus, SLE, Polyarteritis nodosa, PAN * Sarcoidosis – a disease that mainly affects the lungs, brain, joints and eyes, found most often in young African-American women. * Hypothyroidism – where the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormones. * Diabetes mellitus – an imbalance in blood glucose (sugar) levels. * Fibromyalgia * Ehlers-Danlos syndromes - an inherited connective tissue disorder with multiple subcategories * Adrenal insufficiency – where the adrenal glands don't produce enough steroid hormones * Coeliac disease – an autoimmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
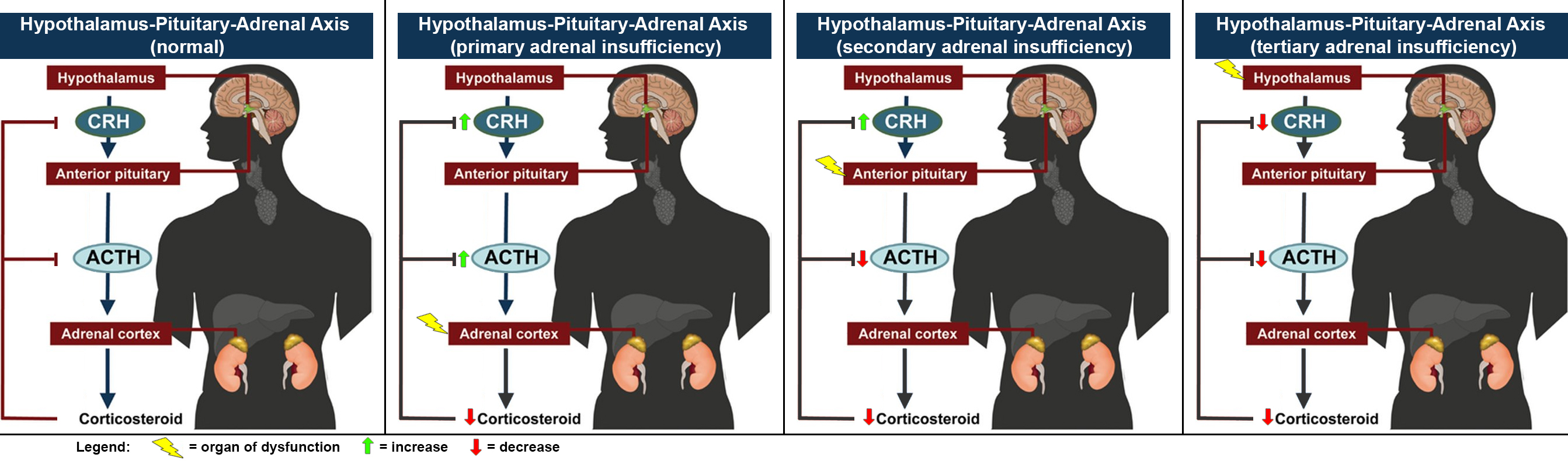
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardised geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organisation describing the region (e.g. United Nations, UN, World Health Organization, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union (AU) uses a different regional breakdown, recognising all 55 member states on the continent—grouping them into five distinct and standard regions. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited Hemoglobinopathy, haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to the red blood cells adopting an abnormal sickle-like shape under certain circumstances; with this shape, they are unable to deform as they pass through Capillary, capillaries, causing blockages. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis) in joints, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections, dizziness and stroke. The probability of severe symptoms, including long-term pain, increases with age. Without treatment, people with SCD rarely reach adulthood but with good healthcare, median life expectancy is between 58 and 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by elevated blood levels of cholesterol. These lesions may lead to narrowing of the arterial walls due to buildup of atheromatous plaques. At the onset, there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. In severe cases, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney disorders, depending on which body part(s) the affected arteries are located in the body. The exact cause of atherosclerosis is unknown and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking (both active and passive smoking), obesity, genetic factors, family history, lifes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affects the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. Children up to 18 years old develop a more severe form of SLE termed childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graves' Disease
Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter or Basedow's disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear, but symptoms are a result of antibodies binding to receptors on the thyroid causing over-expression of thyroid hormone. Persons are more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one monozygotic twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a preventable disease. It can be managed with treatment and become a manageable chronic health condition. While there is no cure or vaccine for HIV, antiretroviral treatment can slow the course of the disease, and if used before significant disease progression, can extend the life expectancy of someone living with HIV to a nearly standard level. An HIV-positive person on treatment can expect to live a normal life, and die with the virus, not of it. Effective treatment for HIV-positive people (people living with HIV) involves a life-long regimen of medicine to suppress the virus, making the viral load undetectable. Treatment is recommended as soon as the diagnosis is made. An HIV-positive person who has an undetectable viral load as a result of long-term treatmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Metabolic syndrome is associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. In the U.S., about 25% of the adult population has metabolic syndrome, a proportion increasing with age, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and prediabetes are closely related to one another and have overlapping aspects. The syndrome is thought to be caused by an underlying disorder of energy utilization and storage, but the cause of the syndrome is an area of ongoing medical research. Researchers debate whether a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome implies differential treatment or increases risk of cardiovascular disease beyond what is suggested by the sum of its individual components. Signs and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as essential hypertension, primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to non-specific lifestyle and Genetics, genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, overweight, excess body weight, smoking, physical inactivity and Alcohol (drug), alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary hypertension, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, uveitis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue (medical), fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections, as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer. Although the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental, Immunity (medical), immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals. It results in a Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's immune system defends the gastrointesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |