Adrenal Insufficiency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the
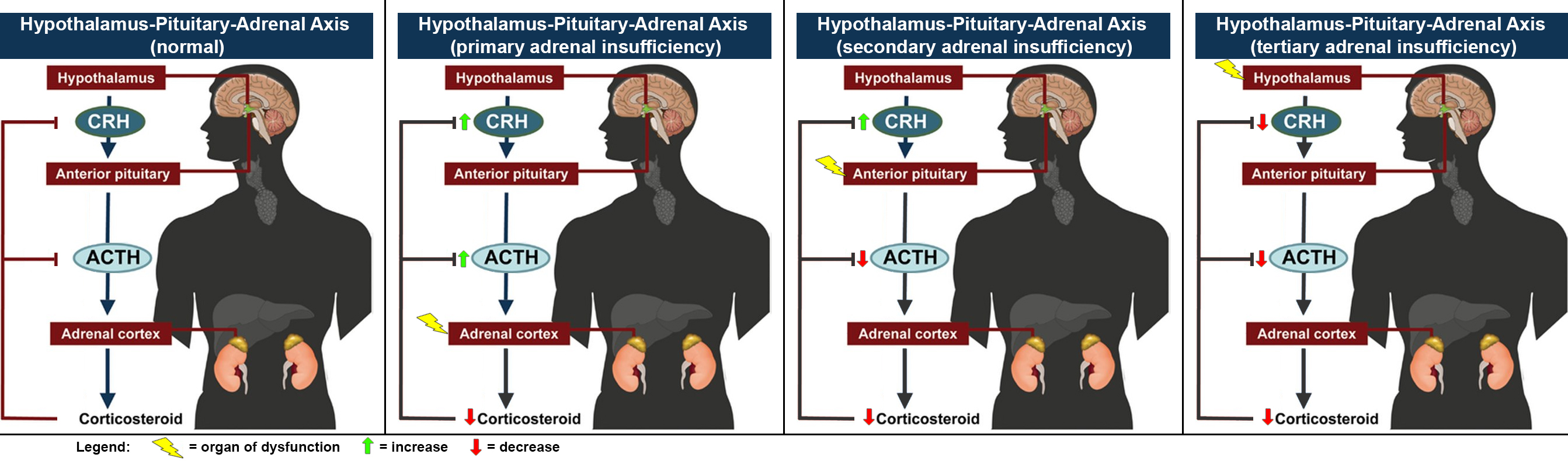 When functioning normally, the adrenal glands secrete
When functioning normally, the adrenal glands secrete
adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
s do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
), mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s (primarily aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
), and androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, muscle weakness and fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure
Organ dysfunction is a condition where an organ does not perform its expected function. Organ failure is organ dysfunction to such a degree that normal homeostasis cannot be maintained without external clinical intervention or life support. It i ...
and shock (in severe cases). Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow.
Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g., Addison's disease), failure of development (e.g., adrenal dysgenesis), or enzyme deficiency (e.g., congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
). Adrenal insufficiency can also occur when the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
or the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
do not produce adequate amounts of the hormones that assist in regulating adrenal function. This is called secondary adrenal insufficiency (when caused by lack of production of adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important ...
(ACTH) in the pituitary gland) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (when caused by lack of corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that b ...
(CRH) in the hypothalamus).
Types
There are three major types of adrenal insufficiency, depending on the affected organ. * Primary adrenal insufficiency is due to impairment of the adrenal glands, resulting in a lack ofglucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
production. Since the adrenal glands are directly affected, mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
production is also reduced. Principal causes include:
** Autoimmune: e.g., Addison's disease (also called autoimmune adrenalitis), which has been identified to be the cause of 80–90% of primary adrenal insufficiency cases since 1950.
** Congenital: e.g. congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
, adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a genetic disorder, disease linked to the X chromosome. It is a result of fatty acid buildup caused by failure of peroxisome#Metabolic functions, peroxisomal fatty acid beta oxidation which results in the accumulation ...
** Infection: e.g. tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, CMV, histoplasmosis
** Drugs: e.g. anticonvulsants
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatment ...
, etomidate
Etomidate (United States Adopted Name, USAN, International Nonproprietary Name, INN, British Approved Name, BAN; marketed as Amidate) is a short-acting intravenous anaesthetic agent used for the induction of general anaesthesia and sedation for ...
, metyrapone, rifampicin
** Vascular: e.g. hemorrhage from sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
, adrenal vein thrombosis, hypercoagulable states such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and antiphospholipid syndrome
** Neoplasia: e.g. adenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelium, epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organ (anatomy), organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prosta ...
(tumor) of the adrenal gland
** Deposition disease: e.g. hemochromatosis, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph n ...
** Idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent spontaneous origin.
For some medical conditions, one or more causes are somewhat understood, but in a certain percentage of people with the condition, the cause ...
: undetermined cause
** Acquired: Bilateral Adrenalectomy to treat recurrent Cushing's Disease/Syndrome
* Secondary adrenal insufficiency is caused by impairment of the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
, resulting in a lack of adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important ...
(ACTH) production and subsequent decreased adrenal stimulation. Since the adrenal glands are not directly affected, the effect on mineralocorticoid production is minimal, as ACTH primarily affects glucocorticoid production. Principal causes include:
** Pituitary adenoma or craniopharyngioma
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak inciden ...
: Tumors in the pituitary gland can suppress production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). High-dose irradiation (>30 Gy) to the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland can cause ACTH deficiency.
** Surgery or radiation: Pituitary gland surgery and/or radiation can lead to destruction of ACTH-producing tissue.
** Exogenous corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
use: Exogenous corticosteroids suppress the stimulation of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland to secrete CRH and ACTH, respectively. These cases may present with symptoms of cortisol excess (see Cushing's syndrome).
** Sheehan's syndrome: Loss of blood flow to the pituitary gland following childbirth
** Pituitary apoplexy: Bleeding or impaired blood supply to the pituitary gland
* Tertiary adrenal insufficiency is caused by impairment of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, resulting in a lack of corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that b ...
(CRH) production, causing downstream reduction in ACTH production and subsequently decreasing adrenal stimulation. Since the adrenal glands are not directly affected, the effect on mineralocorticoid production is minimal, as ACTH primarily affects glucocorticoid production. Principal causes include:
** Sudden withdrawal from long-term exogenous steroid use
** Brain tumors
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms include:hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's tria ...
, hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation, also known as the dark spots or circles on the skin, is the darkening of an area of Human skin, skin or nail (anatomy), nails caused by increased melanin.
Causes
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by sun damage, inflammation, or ...
, dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
, and disorientation. Additional signs and symptoms include weakness, tiredness, dizziness, low blood pressure that falls further when standing (orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when they are standing up ( orthostasis) or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as ne ...
), cardiovascular collapse, muscle aches, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, and diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
. These problems may develop gradually and insidiously. Addison's disease can present with tanning of the skin that may be patchy or even all over the body. Characteristic sites of tanning are skin creases (e.g., of the hands) and the inside of the cheek ( buccal mucosa). Goitre and vitiligo
Vitiligo (, ) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes patches of skin to lose pigment or color. The cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be related to immune system changes, genetic factors, stress, or sun exposure, and susceptibili ...
may also be present. Eosinophilia may also occur. Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the Serum (blood), blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symp ...
is a sign of secondary insufficiency.
Pathophysiology
 When functioning normally, the adrenal glands secrete
When functioning normally, the adrenal glands secrete glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s (primarily cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
) in the '' zona fasciculata'' and mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s (primarily aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
) in the '' zona glomerulosa'' to regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance. Adrenal hormone production is controlled by the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis or HTPA axis) is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three components: the hypothalamus (a part of the brain located below the thalamus), the pituitary gland ( ...
, in which the hypothalamus produces corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that b ...
(CRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important ...
(ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal gland to produce cortisol. High levels of cortisol inhibit the production of both CRH and ACTH, forming a negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
loop. The types of adrenal insufficiency thus refer to the level of the axis in which the dysfunction originates: primary, secondary, and tertiary for adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus, respectively.
In adrenal insufficiency, cortisol production is deficient, which may be accompanied by a deficiency in aldosterone production (predominantly in primary adrenal insufficiency). Depending on the cause and type of adrenal insufficiency, the mechanism of the disease differs. Generally, the symptoms manifest through the systemic effects of cortisol and aldosterone. In secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency, there is no effect on the production of aldosterone within the ''zona glomerulosa'' as this process is regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), not ACTH.
Adrenal insufficiency can also affect the ''zona reticularis'' and disrupt production of androgens, which are precursors to testosterone and estrogen. This leads to a deficiency of sex hormones and can contribute to symptoms of depression and menstrual irregularities.
Cortisol deficiency
Cortisol increases blood sugar by inducinggluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
(glucose production) in the liver, lipolysis (fat breakdown) in adipose tissue, and proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis o ...
(muscle breakdown) in muscle while increasing glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medic ...
secretion and decreasing insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
secretion in the pancreas. Overall, these actions cause the body to use fat stores and muscle for energy. Deficiency results in hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's tria ...
, with associated nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness.
Cortisol potentiates the effectiveness of angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
and catecholamines such as norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
in vasoconstriction. Thus, a deficiency can contribute to hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
, though this effect is most pronounced in mineralocorticoid deficiency.
In primary adrenal insufficiency, the lack of negative feedback from cortisol leads to increased production of CRH and ACTH. ACTH is derived from pro-opiomelanocortin
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is Protein biosynthesis, synthesized in Corticotropic cell, corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 267-amino-acid-long Precursor polypeptide, pol ...
(POMC), which is cleaved into ACTH as well as α-MSH, which regulates production of melanin in the skin. The overproduction of α-MSH leads to the characteristic hyperpigmentation of Addison's disease.
Aldosterone deficiency
Although the production of aldosterone occurs within the adrenal cortex, it is not induced by adrenocorticotropic (ACTH); instead, it is regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS). Renin production in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney is induced by decreased arterial blood pressure, decreased sodium content in the distal convoluted tubule, and increased sympathetic tone. Renin initiates the downstream sequence of cleavage of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I toangiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
, in which angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone production in the ''zona glomerulosa''. Thus, dysfunction of the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus does not affect the production of aldosterone. However, in primary adrenal insufficiency, damage to the adrenal cortex (e.g. autoimmune adrenalitis a.k.a. Addison's disease) can lead to destruction of the ''zona glomerulosa'' and therefore a loss of aldosterone production.
Aldosterone acts on mineralocorticoid receptors on epithelial cells lining the distal convoluted tubule, activating epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) and the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pump. This results in the absorption of sodium (with resulting retention of fluid) and the excretion of potassium. Deficiency of aldosterone leads to urinary loss of sodium and effective circulating volume, as well as retention of potassium. This can cause hypotension (in severe cases, shock), dizziness (from orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when they are standing up ( orthostasis) or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as ne ...
), dehydration, and salt craving.
Unlike mineralocorticoid deficiency, glucocorticoid deficiency does not cause a negative sodium balance (in fact, a positive sodium balance may occur).
Causes
Causes of acute adrenal insufficiency are mainly sudden withdrawal of long-termcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
therapy, Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome, and stress in people with underlying chronic adrenal insufficiency.Table 20-7 in: 8th edition. The latter is termed critical illness–related corticosteroid insufficiency.
For chronic adrenal insufficiency, the major contributors are autoimmune adrenalitis (Addison's Disease), tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
, and metastatic disease. Minor causes of chronic adrenal insufficiency are systemic amyloidosis, fungal infections, hemochromatosis, and sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph n ...
.
Causes of adrenal insufficiency can be categorized by the mechanism through which they cause the adrenal glands to produce insufficient cortisol. These are adrenal destruction (disease processes leading to glandular damage), impaired steroidogenesis (the gland is present but is biochemically unable to produce cortisol), or adrenal dysgenesis (the gland has not formed adequately during development).
Adrenal destruction
Autoimmune adrenalitis (Addison's disease) is the most common cause of primary adrenal insufficiency in the industrialised world, causing 80–90% of cases since 1950.Autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
destruction of the adrenal cortex is caused by an immune reaction against the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (a phenomenon first described in 1992). This may be isolated or in the context of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (APS type 1 or 2), in which other hormone-producing organs, such as the thyroid and pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, may also be affected.
Autoimmune adrenalitis may be part of type 2 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, which can include type 1 diabetes, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
, and autoimmune thyroid disease (also known as autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Hashimoto's disease). Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the human gonad, gonads—the testicles or the ovary, ovaries—that may result in diminished biosynthesis, production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred t ...
may also present with this syndrome. Other diseases that are more common in people with autoimmune adrenalitis include premature ovarian failure, celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, and autoimmune gastritis with pernicious anemia.
Adrenal destruction is a feature of adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a genetic disorder, disease linked to the X chromosome. It is a result of fatty acid buildup caused by failure of peroxisome#Metabolic functions, peroxisomal fatty acid beta oxidation which results in the accumulation ...
(ALD). Destruction also occurs when the adrenal glands are involved in metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
(seeding of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
cells from elsewhere in the body, especially lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
), hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
(e.g. in Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome or antiphospholipid syndrome), particular infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s which can spread to the adrenal cortex (tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis (, ) is a mammalian mycosis, fungal disease caused by ''Coccidioides immitis'' or ''Coccidioides posadasii''. It is commonly known as cocci, Valley fever, California fever, desert rheumatism, or San Joaquin Valley fever. Cocci ...
), or the deposition of abnormal protein in amyloidosis.
Impaired steroidogenesis
To form cortisol, the adrenal gland requirescholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
, which is then converted biochemically into steroid hormones. Interruptions in the delivery of cholesterol include Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome is an inborn error of metabolism, inborn error of cholesterol synthesis. It is an autosome, autosomal recessive (genetics), recessive, multiple malformation syndrome caused by a mutation in the enzyme 7-Dehydrochole ...
and abetalipoproteinemia.
Of the synthesis problems, congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
is the most common (in various forms: 21-hydroxylase, 17α-hydroxylase, 11β-hydroxylase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase), lipoid CAH due to deficiency of StAR
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
and mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
mutations. Some medications interfere with steroid synthesis enzymes (e.g. ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral, among others, is an antiandrogen, antifungal drug, antifungal, and antiglucocorticoid medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin inf ...
), while others accelerate the normal breakdown of hormones by the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
(e.g. rifampicin, phenytoin).
Adrenal insufficiency can also result when a patient has a brain mass in the pituitary gland (e.g. pituitary adenoma, craniopharyngioma
A craniopharyngioma is a rare type of brain tumor derived from pituitary gland embryonic tissue that occurs most commonly in children, but also affects adults. It may present at any age, even in the prenatal and neonatal periods, but peak inciden ...
) which can take up space and interfere with the secretion of pituitary hormones such as ACTH, therefore leading to decreased adrenal stimulation (secondary adrenal insufficiency). The same can occur with masses in the hypothalamus (tertiary adrenal insufficiency).
Corticosteroid withdrawal
Use of high-dosesteroids
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter mem ...
for more than a week begins to produce suppression of the person's adrenal glands because the exogenous glucocorticoids suppress release of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). With prolonged suppression, the adrenal glands atrophy (physically shrink), and can take months to recover full function after discontinuation of the exogenous glucocorticoid. During this recovery time, the person is vulnerable to adrenal insufficiency during times of stress, such as illness, due to both adrenal atrophy and suppression of CRH and ACTH release. Use of steroids joint injections may also result in adrenal suppression after discontinuation.
Adrenal dysgenesis
All causes in this category are genetic and generally very rare. These includemutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
to the '' SF1'' transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
, congenital adrenal hypoplasia due to ''DAX-1'' gene mutations and mutations to the ACTH receptor
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a Adrenocorticotropic hormone (medication), medication and ...
gene (or related genes, such as in the Triple A or Allgrove syndrome). ''DAX-1'' mutations may cluster in a syndrome with glycerol kinase deficiency with a number of other symptoms when ''DAX-1'' is deleted together with a number of other genes.
Diagnosis
The first step of diagnosing adrenal insufficiency is confirming inappropriately low cortisol secretion. This is followed by determining the origin of dysfunction (adrenal glands, pituitary gland, or hypothalamus) and therefore the type of adrenal insufficiency (primary, secondary, or tertiary). After narrowing down the source, further testing can elucidate the cause of insufficiency. If a patient is suspected to be experiencing an acute adrenal crisis, immediate treatment with IV corticosteroids is imperative and should not be delayed for any testing, as the patient's health can deteriorate rapidly and result in death without replacing the corticosteroids. Dexamethasone should be used as the corticosteroid of choice in these cases as it is the only corticosteroid that will not affect diagnostic test results. To confirm inappropriately low cortisol secretion, testing may include baseline morning cortisol level in the blood or morning cortisol level in the saliva. Cortisol levels typically peak in the morning; thus, low values indicate true adrenal insufficiency. Urinary free cortisol can also be measured, but is not necessary for diagnosis. To determine the origin of dysfunction, theACTH stimulation test
The ACTH test (also called the cosyntropin, tetracosactide, or Synacthen test) is a medical test usually requested and interpreted by endocrinologists to assess the functioning of the adrenal glands' stress response by measuring the adrenal res ...
is the best initial test as it can differentiate between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency. If cortisol levels remain low following ACTH stimulation, then the diagnosis is primary adrenal insufficiency. If cortisol levels increase following ACTH stimulation, then the diagnosis is either secondary or tertiary adrenal insufficiency. The corticotropin-releasing hormone test can then differentiate between secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency. Additional testing can include basal plasma ACTH, renin, and aldosterone concentrations, as well as a blood chemistry panel to check for electrolyte imbalances.
Depending on the type of adrenal insufficiency, there are several possible causes and therefore many different avenues of testing (see Causes above). For primary adrenal insufficiency, the most common cause is autoimmune adrenalitis ( Addison's disease); therefore, 21-hydroxylase autoantibodies should be checked. Structural abnormalities of the adrenal glands can be detected on CT imaging. For secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency, an MRI of the brain can be obtained to detect structural abnormalities such as masses, metastasis, hemorrhage, infarction, or infection.
Effects
Treatment
In general, the treatment of adrenal insufficiency requires replacement of deficient hormones, as well as treatment of any underlying cause. All types of adrenal insufficiency will require glucocorticoid repletion. Many cases (typically, primary adrenal insufficiency) will also require mineralocorticoid repletion. In rarer cases, repletion of androgens may also be indicated, typically in female patients with mood disturbances and changes in well-being. * Adrenal crisis (acute) treatment ** Intravenous fluids ** Intravenous glucocorticoids *** typicallyhydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenit ...
(Cortef) but dexamethasone (Decadron) may be used if diagnostic studies are necessary, as dexamethasone does not affect testing results
** Supportive measures and correction of any additional issues such as electrolyte abnormalities
* Chronic adrenal insufficiency treatment
** Glucocorticoid deficiency (low cortisol)
*** Oral glucocorticoids
**** Hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenit ...
(brand name: Cortef), or
**** Prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
(brand name: Deltasone), or
**** Dexamethasone (brand name: Decadron)
** Mineralocorticoid deficiency (low aldosterone) treatment
*** Oral mineralocorticoids
**** Fludrocortisone (brand name: Florinef)
** Sex hormone deficiency (low androgen)
*** Oral androgens
**** Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
Prognosis
Primary adrenal insufficiency predisposes to a higher risk of death, mostly due to infection, cardiovascular disease, and adrenal crisis. Delayed diagnosis can impair quality of life, and lack of treatment brings high mortality. However, with proper diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment, people with adrenal insufficiency can live normally.Epidemiology
The most common cause of primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease) overall is autoimmune adrenalitis. The prevalence of Addison's disease ranges from 5 to 221 per million in different countries. In children,congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
(CAH) is the most common cause of adrenal insufficiency, with an incidence of 1 in 14,200 live births.
See also
* Addison's disease – primary adrenocortical insufficiency * Adrenal fatigue (hypoadrenia) – a term used in alternative medicine to describe a believed exhaustion of the adrenal glands * Cushing's syndrome – overproduction of cortisol * Insulin tolerance test – another test used to identify sub-types of adrenal insufficiency * Adrenal gland disorderReferences
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Adrenal Insufficiency Adrenal gland disorders de:Nebennierenrindeninsuffizienz