|
Synchro Software
A synchro (also known as selsyn and by other brand names) is, in effect, a transformer whose primary-to-secondary coupling may be varied by physically changing the relative orientation of the two windings. Synchros are often used for measuring the angle of a rotating machine such as an antenna platform or transmitting rotation. In its general physical construction, it is much like an electric motor. The primary winding of the transformer, fixed to the rotor, is excited by an alternating current, which by electromagnetic induction causes voltages to appear between the Y-connected secondary windings fixed at 120 degrees to each other on the stator. The voltages are measured and used to determine the angle of the rotor relative to the stator. Uses Synchro systems were first used in the control system of the Panama Canal in the early 1900s to transmit lock gate and valve stem positions, and water levels, to the control desks. Fire-control system designs developed during Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Picture
A film, also known as a movie or motion picture, is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, emotions, or atmosphere through the use of moving images that are generally, since the 1930s, synchronized with sound and (less commonly) other sensory stimulations. Etymology and alternative terms The name "film" originally referred to the thin layer of photochemical emulsion on the celluloid strip that used to be the actual medium for recording and displaying motion pictures. Many other terms exist for an individual motion-picture, including "picture", "picture show", "moving picture", "photoplay", and "flick". The most common term in the United States is "movie", while in Europe, "film" is preferred. Archaic terms include "animated pictures" and "animated photography". "Flick" is, in general a slang term, first recorded in 1926. It originates in the verb flicker, owing to the flickering appearance of early films. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
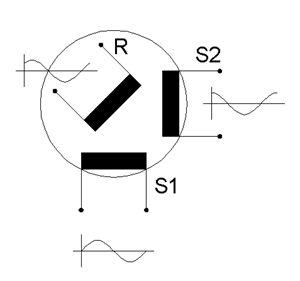
Resolver (electrical)
A resolver is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring degrees of rotation. It is considered an analog device, and has digital counterparts such as the digital resolver, rotary (or pulse) encoder. A rotating coil induces voltage in two stationary coils, and by comparing the phase of the signal in the two secondaries, the angle can be accurately determined. These systems were commonly used in mechanical control systems, for instance, counting the number of revolutions of a screw jack to move an aircraft's flaps to a specific extension. Description The most common type of resolver is the brushless transmitter resolver (other types are described at the end). On the outside, this type of resolver may look like a small electrical motor having a stator and rotor. On the inside, the configuration of the wire windings makes it different. The stator portion of the resolver houses three windings: an exciter winding and two two-phase windings, usually labeled "x" a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Transformer
A rotary (rotatory) transformer is a specialized transformer used to couple electrical signals between two parts that rotate in relation to each other. They may be either cylindrical or 'pancake' shaped. Slip rings can be used for the same purpose, but are subject to friction, wear, intermittent contact, and limitations on the rotational speed that can be accommodated without damage. Wear can be eliminated by using a pool of liquid Mercury (element), mercury or liquid metal alloy instead of a solid ring contact, but the Mercury poisoning, toxicity and slow corrosion of mercury are problematic, and very high rotational speeds are again difficult to achieve. A rotary transformer has none of these limitations. Rotary transformers are constructed by winding the primary and secondary windings into separate halves of a ''cup core''; these concentric halves face each other, with each half mounted to one of the rotating parts. Magnetic flux provides the coupling from one half of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an external circuit. In most generators which are rotating machines, a source of kinetic power rotates the generator's shaft, and the generator produces an electric current at its output terminals which flows through an external circuit, powering electrical loads. Sources of mechanical energy used to drive generators include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. Generators produce nearly all of the electric power for worldwide electric power grids. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mains Electricity
Mains electricity, utility power, grid power, domestic power, wall power, household current, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose Alternating current, alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electrical grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items (such as domestic appliances, televisions and lamps) by plugging them into a wall outlet. The voltage and utility frequency, frequency of electric power differs between regions. In much of the world, a voltage (nominally) of 230 volts and frequency of 50 Hz is used. In North America, the most common combination is 120 V and a frequency of 60 Hz. Other combinations exist, for example, 230 V at 60 Hz. Travellers' portable appliances may be inoperative or damaged by foreign electrical supplies. Non-interchangeable AC power plugs and sockets, plugs and sock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base units is 1/s or s−1, meaning that one hertz is one per second or the Inverse second, reciprocal of one second. It is used only in the case of periodic events. It is named after Heinrich Hertz, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For high frequencies, the unit is commonly expressed in metric prefix, multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brush (electric)
A brush or carbon brush is an electrical contact, often made from specially prepared carbon, which conducts current between stationary and rotating parts (the latter most commonly being a rotating shaft) of an electrical machine. Typical applications include electric motors, alternators and electric generators. The lifespan of a carbon brush depends on how much the motor is used, and how much power is put through the motor. Etymology For certain types of electric motors or generators to function, the coils of the rotor must be connected to complete an electrical circuit. Originally this was accomplished by affixing a copper or brass commutator or ' slip ring' to the shaft, with springs pressing braided copper wire 'brushes' onto the slip rings or commutator which conduct the current. Such brushes arced and even welded as the commutator rotated, because the brush short-circuited adjacent segments. The cure was the introduction of 'high resistance brushes' made from graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip Ring
A slip ring is an electromechanical device that allows the transmission of Electric power, power and electrical Signal, signals from a stationary to a rotating structure. A slip ring can be used in any Electromechanics, electromechanical system that requires rotation while transmitting power or signals. It can improve mechanical performance, simplify system operation and eliminate damage-prone wires dangling from movable joints. Also called rotary electrical interfaces, rotating electrical connectors, collectors, swivels, or electrical rotary joints, these rings are commonly found in slip ring motors, electrical generators for alternating current (AC) systems and alternators and in packaging machinery, cable reels, and wind turbines. They can be used on any rotating object to transfer power, control circuits, or Analog signal, analog or Digital signal, digital signals including data such as those found on aerodrome beacons, rotating tanks, power shovels, radio telescopes, telemet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomotor
A servomotor (or servo motor or simply servo) is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration in a mechanical system. It constitutes part of a servomechanism, and consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback and a controller (often a dedicated module designed specifically for servomotors). Servomotors are not a specific class of motor, although the term ''servomotor'' is often used to refer to a motor suitable for use in a closed-loop control system. Servomotors are used in applications such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing. Mechanism A servomotor is a closed-loop servomechanism that uses position feedback (either linear or rotational position) to control its motion and final position. The input to its control is a signal (either analog or digital) representing the desired position of the output shaft. The motor is paired with some type of positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller. These devices are typically made from semiconductor materials. Many components of a normal electronic design are available in a microelectronic equivalent. These include transistors, capacitors, inductors, resistors, diodes and (naturally) insulators and conductors can all be found in microelectronic devices. Unique wiring techniques such as wire bonding are also often used in microelectronics because of the unusually small size of the components, leads and pads. This technique requires specialized equipment and is expensive. Digital integrated circuits (ICs) consist of billions of transistors, resistors, diodes, and capacitors. Analog circuits commonly contain resistors and capacitors as well. Inductors are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |