|
Synanceia
''Synanceia'' is a genus of ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Synanceiinae, the stonefish, which is classified within the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfish and relatives. Stonefish are the most venomous fish known; stings can be fatal to humans. They are found in the coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific. They are sometimes confused with the freshwater lionfish. Taxonomy ''Synanceia'' was first described as a genus in 1801 by the German naturalists Marcus Elieser Bloch and Johann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider with ''Scorpaena horrida'', which had been described by Carl Linnaeus in 1766 from Ambon Island (Indonesia), as its type species. The genus ''Synanceia'' is classified within the tribe Synanceiini which is one of three tribes in the subfamily Synanceeinae within the family Scorpaenidae. Despite this, other authorities regard Synanceiidae as a valid family and the Synanceiini as the subfamily Synanceiinae. The genus name ''Synanceia'' is made up of ''syn'', mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
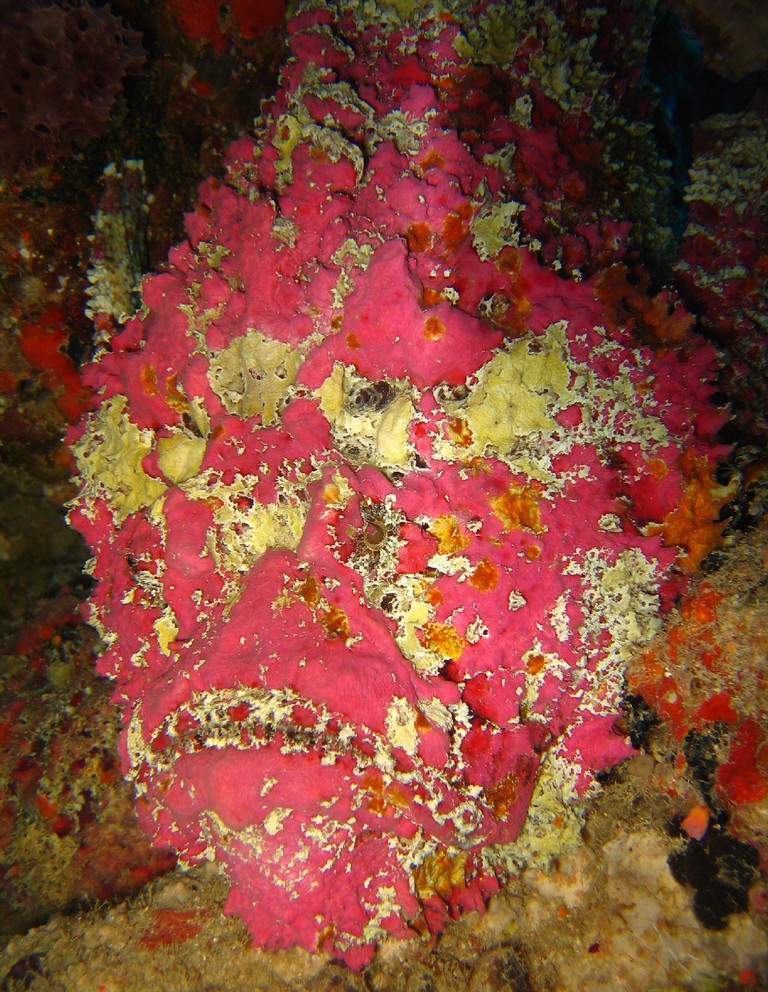
Synanceia Verrucosa
''Synanceia verrucosa'', the reef stonefish or simply stonefish, is a species of Venomous fish, venomous, marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the subfamily Synanceiinae which is Taxonomy (biology), classified as being within the Family (biology), family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is the most widespread species of stonefish, mostly found in shallow waters of the Red Sea and the Indo-Pacific. It possesses highly effective venom which can be lethal to humans. It is the type species of ''Synanceia''. Taxonomy ''Synanceia verrucosa'' was first formally Species description, described in 1801 by the German naturalists Marcus Elieser Bloch and Johann Gottlob Theaenus Schneider with the type locality given as India. Bloch and Schneider described a new genus, ''Synanceia'', for this species, but in 1856 Eugène Anselme Sébastien Léon Desmarest designated ''Synanceia horrida, Scorpaena horrida'' which had been described by Carl Linnaeus in 1766, as the type s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
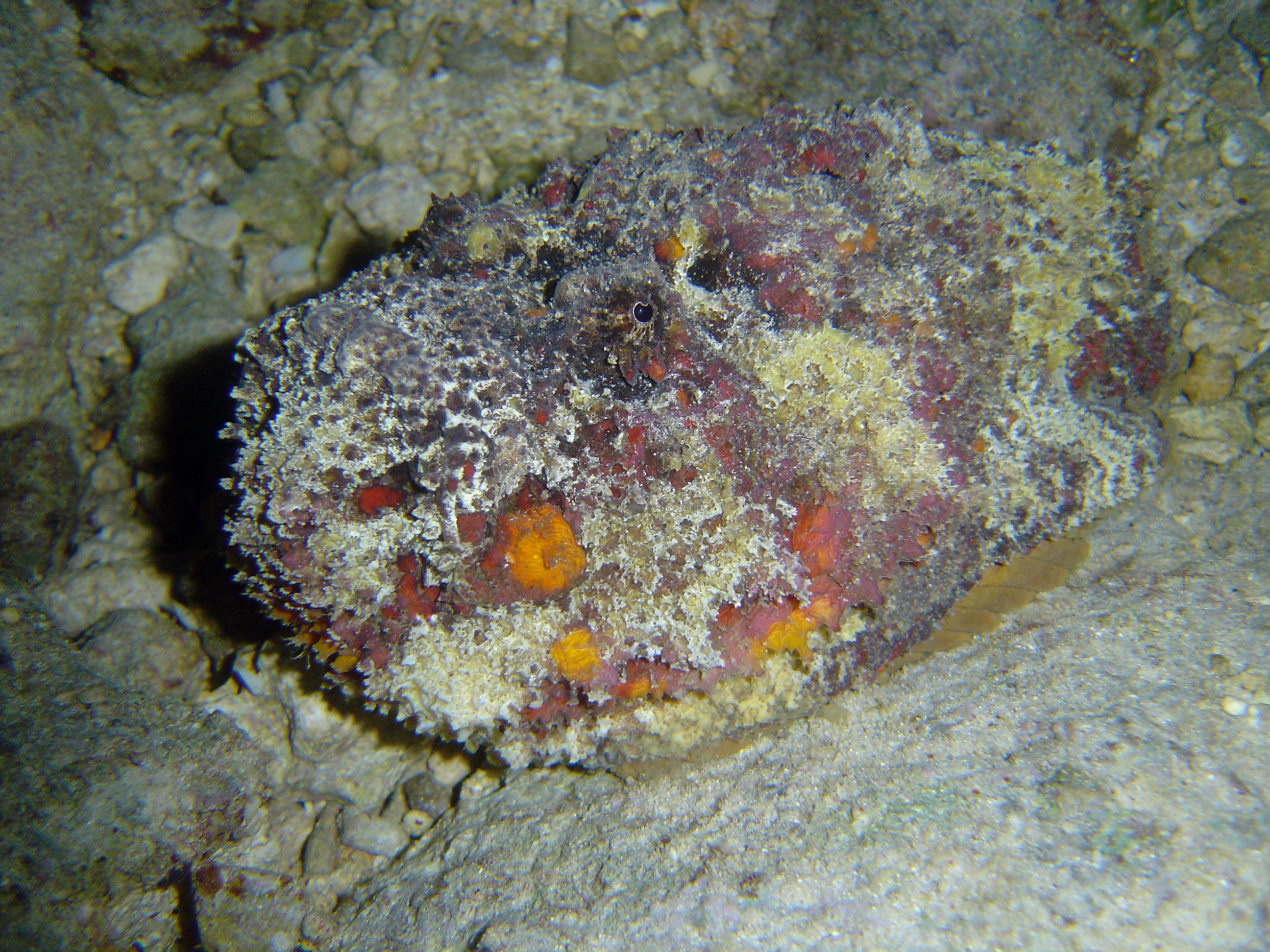
Synanceia Horrida
''Synanceia horrida'', the estuarine stonefish, hollow-cheek stonefish, horrid stonefish, rough stonefish or true stonefish, is a species of venomous, marine ray-finned fish, a stonefish belonging to the subfamily Synanceiinae which is classified as being within the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. It is a benthic fish which is found in the Indo-Pacific region. This species is considered to be one of the most dangerous venomous fish in the world. It is a popular exhibit in public aquaria and is found in the private aquarium trade. Taxonomy ''Synanceia horrida'' was first formally described in 1766 as ''Scorpaena horrida'' by Carl Linnaeus in volume 1 of his 1766 ''Systema naturae sive regna tria naturae'' with its type locality given as Ambon Island in Indonesia. In 1856 Eugène Anselme Sébastien Léon Desmarest designated this species as the type species of the genus ''Synanceia'', which had been described in 1801 by Marcus Elieser Bloch and Johann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synanceiinae
Synanceiinae is a subfamily of venomous ray-finned fishes, waspfishes, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are found in the Indo-Pacific oceans. They are primarily marine, though some species are known to live in fresh or brackish waters. The various species of this family are known informally as stonefish, stinger, stingfish and ghouls. Its species are known to have the most potent neurotoxins of all the fish venoms, secreted from glands at the base of their needle-like dorsal fin spines. The vernacular name, stonefish, for some of these fishes derives from their behaviour of camouflaging as rocks. The type species of the family is the reef stonefish ('' Synanceia verrucosa''). Taxonomy Synanceiinae, or the family Synanceiidae, was first named and recognised as a grouping of related taxa by the English naturalist William Swainson in 1839. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' treats this groupin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venomous Fish
Venomous fish are species of fish which produce strong mixtures of toxins harmful to humans (called venom) which they deliberately deliver by means of a bite, sting, or stab, resulting in an envenomation. As a contrast, poisonous fish also produce a strong toxin, but they do not bite, sting, or stab to deliver the toxin, instead being poisonous to eat because the human digestive system does not destroy the toxin they contain in their bodies. Venomous fish do not necessarily cause poisoning if they are eaten, as the digestive system often destroys the venom.Poisonous vs. Venomous fish: What’s the difference? Reef Biosearch. Retrieved 17 July 2009. There are at least 1200 species of venomous fish, Smith WL and Wheeler WC (2006 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synanceiini
Synanceiini commonly known as stonefishes, is a tribe of venomous ray-finned fishes classified within the subfamily Synanceiinae, the stonefishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are found in the Indo-Pacific. Genera Synanceiini contains the following genera: * '' Dampierosa'' Whitley, 1932 * '' Erosa'' Swainson, 1839 * '' Leptosynanceia'' Bleeker, 1874 * '' Pseudosynanceia'' Day, 1875 * ''Synanceia'' Bloch Bloch is a surname of German origin. Notable people with this surname include: A *Adele Bloch-Bauer (1881–1925), Austrian entrepreneur *Albert Bloch (1882–1961), American painter *Alexandre Bloch (1857–1919), French painter *Alfred Bloch ( ... & Schneider, 1801 * '' Trachicephalus'' Swainson, 1839 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q111519254 Synanceiinae Fish tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullrout
The bullrout (''Notesthes robusta''), also commonly called freshwater stonefish or kroki, is a pale yellowish to dark-brown coloured fish that lives in tidal estuaries and slow-flowing streams in eastern Australia, from southern New South Wales to northern Queensland. It has on a very infrequent occurrence been caught at sea. Its spines are venomous. It is the only member of the genus ''Notesthes''. It is often confused with the true stonefish. Taxonomy and etymology The bullrout was first formally described in 1860 as ''Centropogon robustus'' by the German-born British |
Anthony Curtiss
Anthony Curtiss, pen name of Roy Abijah Curtiss Jr (born in Brooklyn, New York 10 May 1910, died 12 July 1981 in Karachi, Pakistan), also known in his later life as Muhammad Abdullah al-Hussein, was an American naturalist who wrote a short, and somewhat eccentric, book on the zoology of Tahiti. Early life Roy Abijah Curtiss Jr. was born on 19 May 1910 in Brooklyn, New York, the son of Roy Abijah Curtiss (1880-1923), a wealthy business man who was the son and heir of Frank Curtiss former president of New York's Sixth Street Elevated Railway Society and Ethel Grace Quinn (1885-1974). His parents had married in 1907 and Roy was the oldest of their four boys. The family had an estate near Sheffield, Massachusetts and a town house on Eleventh Avenue near the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). A precocious boy, Curtiss developed an early interest in natural history, encouraged by his mother and his well traveled maternal grandmother who as well as having studied medicine wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe (biology)
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxa ranked above species are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe. In zoology, the standard ending for the name of a zoological tribe is "-ini". Examples include the tribes Caprini (goat-antelopes), Hominini (hominins), Bombini (bumblebees), and Thunnini (tunas). The tribe Hominini is divided into subtribes by some scientists; subtribe Hominina then comprises "humans". The standard ending for the name of a zoological subtribe is "-ina". In botany, the standard ending for the name of a botanical tribe is "-eae". Examples include the tribes Acalypheae and Hyacintheae. The tribe Hyacintheae is divided into subtribes, including the subtribe Massoniinae. The standard ending for the name of a botanical subtribe is "-inae". In bacteriology, the form of tribe names is as in botany, e.g., Pseudomonadeae, based on the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea, Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 280 million people, Indonesia is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fourth-most-populous country and the most populous Islam by country, Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia operates as a Presidential system, presidential republic with an elected People's Consultative Assembly, legislature and consists of Provinces of Indonesia, 38 provinces, nine of which have Autonomous administrative divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
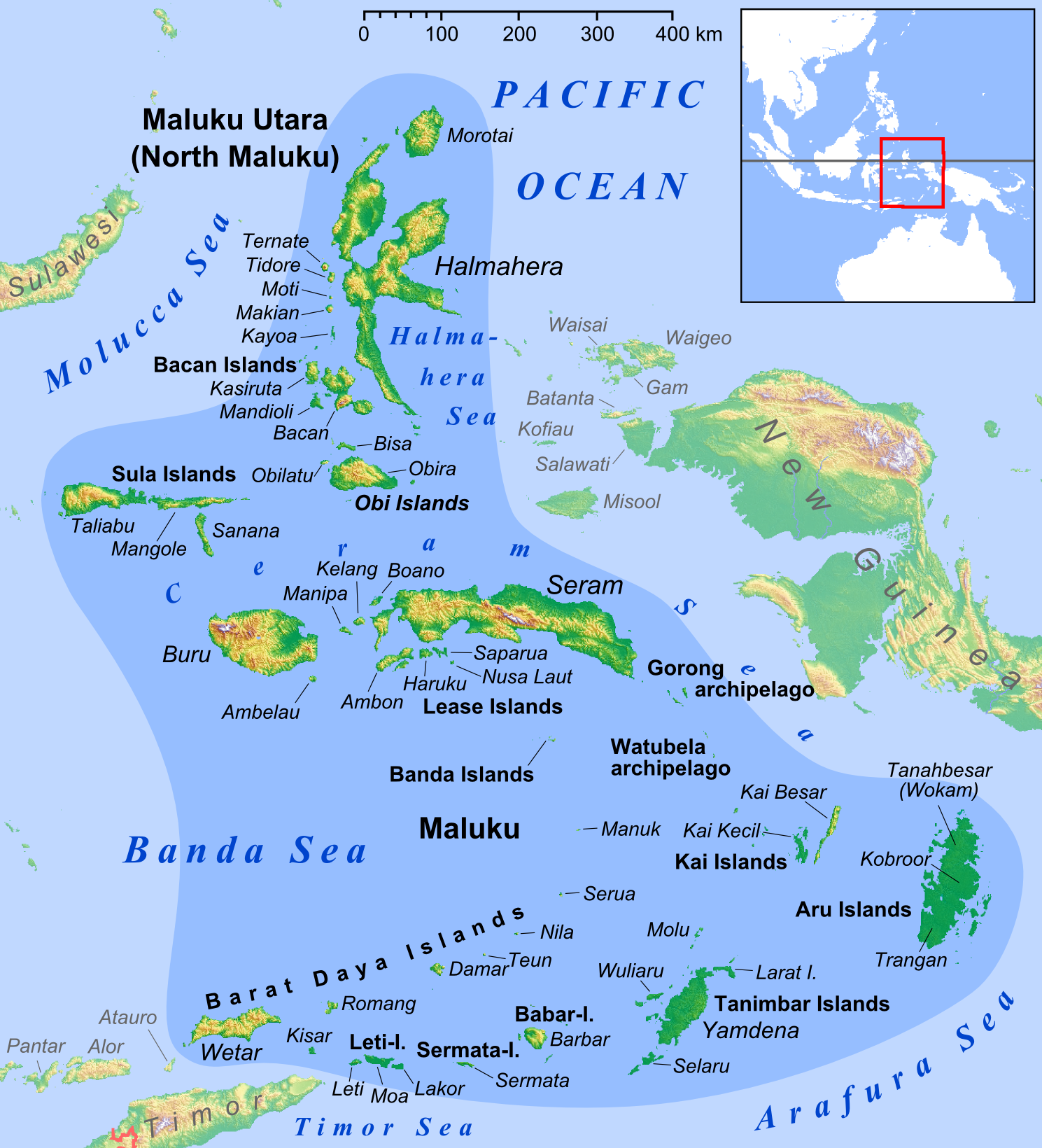
Ambon Island
Ambon Island is part of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island has an area of and is mountainous, well watered, and fertile. Ambon Island consists of two territories: the city of Ambon, Maluku, Ambon to the south, and three districts (''kecamatan'') of the Central Maluku Regency to the north. The main city and seaport is Ambon, Maluku, Ambon (with a 2020 Census population of 347,288), which is also the capital of Maluku (province), Maluku Provinces of Indonesia, province, while those districts of Maluku Tengah Regency situated on Ambon Island had a 2020 Census population of 128,069. By mid 2023 those populations were estimated to have become 354,052 and 128,754 respectively, resulting in an all-island population of 482,806. Ambon has an Pattimura Airport, airport and is home to the Pattimura University and Open University (Universitas Terbuka), state universities, and a few private universities, which include Darussalam University (Universitas Darussalam, UNDAR) and Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |