|
Symphony No. 83 (Haydn)
Symphony No. 83 in G minor, Hoboken I/83, is the second of the six Paris Symphonies (numbers 82–87) written by Joseph Haydn in 1785. It was published by Artaria in Vienna in December 1787. It is popularly known as The Hen (). Nickname (the Hen) The nickname comes from the clucking second subject in the first movement, which reminded listeners of the jerky back-and-forth head motion of a walking hen.Ethan Mordden, ''A Guide to Orchestral Music: The Handbook for Non-Musicians''. New York: Oxford University Press (1980): 82. Movements The symphony is in standard four movement form and scored for flute, two oboes, two bassoons, two horns and strings. #Allegro spiritoso, # Andante, in E major #Menuet: Allegretto – Trio, in G major #Finale: Vivace, in G major The symphony opens in stormy G minor with the minor triad further intensified by the added dissonance of the C. The dotted rhythms that answer are transformed into fanfares later in the first theme group of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Minor
G minor is a minor scale based on G, consisting of the pitches G, A, B, C, D, E, and F. Its key signature has two flats. Its relative major is B-flat major and its parallel major is G major. The G natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The G harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of G minor are: * Tonic – G minor * Supertonic – A diminished * Mediant – B-flat major * Subdominant – C minor * Dominant – D minor * Submediant – E-flat major * Subtonic – F major Mozart's use of G minor G minor has been considered the key through which Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart best expressed sadness and tragedy, and many of his minor key works are in G minor, such as Piano Quartet No. 1 and String Quintet No. 4. Though Mozart touched on various minor keys in his symphonies, G minor is the only minor key he used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Flat Major
E-flat major is a major scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has three flats. Its relative minor is C minor, and its parallel minor is E minor, (or enharmonically D minor). The E-flat major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The E-flat harmonic major and melodic major scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of E-flat major are: * Tonic – E-flat major * Supertonic – F minor * Mediant – G minor * Subdominant – A-flat major * Dominant – B-flat major * Submediant – C minor * Leading-tone – D diminished Characteristics The key of E-flat major is often associated with bold, heroic music, in part because of Ludwig van Beethoven's usage. His ''Eroica Symphony'', ''Emperor Concerto'' and ''Grand Sonata'' are all in this key. Beethoven's (hypothetical) 10th Symphony is also in E-flat. But even before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphonies By Joseph Haydn
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning common today: a work usually consisting of multiple distinct sections or movements, often four, with the first movement in sonata form. Symphonies are almost always scored for an orchestra consisting of a string section (violin, viola, cello, and double bass), brass, woodwind, and percussion instruments which altogether number about 30 to 100 musicians. Symphonies are notated in a musical score, which contains all the instrument parts. Orchestral musicians play from parts which contain just the notated music for their own instrument. Some symphonies also contain vocal parts (e.g., Beethoven's Ninth Symphony, or Mahler's Second Symphony). Etymology and origins The word ''symphony'' is derived from the Greek word (), meaning "agreement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Symphonies By Name
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acciaccatura
In music, ornaments or embellishments are musical flourishes—typically, added notes—that are not essential to carry the overall line of the melody (or harmony), but serve instead to decorate or "ornament" that line (or harmony), provide added interest and variety, and give the performer the opportunity to add expressiveness to a song or piece. Many ornaments are performed as "fast notes" around a central, main note. There are many types of ornaments, ranging from the addition of a single, short grace note before a main note to the performance of a virtuosic and flamboyant trill. The amount of ornamentation in a piece of music can vary from quite extensive (it was often extensive in the Baroque period, from 1600 to 1750) to relatively little or even none. The word ''agrément'' is used specifically to indicate the French Baroque style of ornamentation. Improvised vs. written In the Baroque period, it was common for performers to improvise ornamentation on a given mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Flat Major
B-flat major is a major scale based on B, with pitches B, C, D, E, F, G, and A. Its key signature has two flats. Its relative minor is G minor and its parallel minor is B-flat minor. The B-flat major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B-flat harmonic major and melodic major scales are: Many transposing instruments are pitched in B-flat major, including the clarinet, trumpet, tenor saxophone, and soprano saxophone. As a result, B-flat major is one of the most popular keys for concert band compositions. Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of B-flat major are: * Tonic – B-flat major * Supertonic – C minor * Mediant – D minor * Subdominant – E-flat major * Dominant – F major * Submediant – G minor * Leading-tone – A diminished History Joseph Haydn's Symphony No. 98 is often credited as the first symphony written in that key, including trumpet and ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonata Form
The sonata form (also sonata-allegro form or first movement form) is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical music era, Classical period). While it is typically used in the first Movement (music), movement of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement. The teaching of sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the form—a definition that arose in the second quarter of the 19th century. There is little disagreement that on the largest level, the form consists of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation; however, beneath this general structure, sonata form is difficult to pin down to a single model. The standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Major
G major is a major scale based on G (musical note), G, with the pitches G, A (musical note), A, B (musical note), B, C (musical note), C, D (musical note), D, E (musical note), E, and F♯ (musical note), F. Its key signature has one sharp (music), sharp. Its relative key, relative minor is E minor and its parallel key, parallel minor is G minor. The G major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The G Harmonic major scale, harmonic major and Melodic major scale, melodic major scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of G major are: * Tonic (music), Tonic – G major * Supertonic – A minor * Mediant – B minor * Subdominant – C major * Dominant (music), Dominant – D major * Submediant – E minor * Leading-tone – Diminished triad, F-sharp diminished Notable compositions Baroque period In Baroque music, G major was regarded as the "key of benediction". Of Domen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ternary Form
Ternary form, sometimes called song form, is a three-part musical form consisting of an opening section (A), a following section (B) and then a repetition of the first section (A). It is usually schematized as A–B–A. Prominent examples include the da capo aria "The trumpet shall sound" from Handel's '' Messiah'', Chopin's Prelude in D-Flat Major "Raindrop", ( Op. 28) and the opening chorus of Bach's '' St John Passion''. Simple ternary form In ternary form each section is self-contained both thematically as well as tonally (that is, each section contains distinct and complete themes), and ends with an authentic cadence. The B section is generally in a contrasting but closely related key, usually a perfect fifth above or the parallel minor of the home key of the A section (V or i); however, in many works of the Classical period, the B section stays in tonic but has contrasting thematic material. It usually also has a contrasting character; for example section A might ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
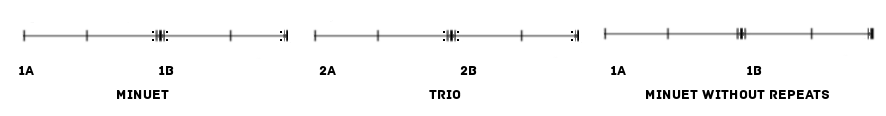
Menuet
A minuet (; also spelled menuet) is a social dance of French origin for two people, usually written in time. The English word was adapted from the Italian ''minuetto'' and the French ''menuet''. The term also describes the musical form that accompanies the dance, which subsequently developed more fully, often with a longer musical form called the minuet and trio, and was much used as a movement in the early classical symphony. While often stylized in instrumental forms, composers of the period would have been familiar with the popular dance. Dance The name may refer to the short steps, ''pas menus'', taken in the dance, or else be derived from the ''branle à mener'' or ''amener'', popular group dances in early 17th-century France. The minuet was traditionally said to have descended from the ''bransle de Poitou'', though there is no evidence making a clear connection between these two dances. The earliest treatise to mention the possible connection of the name to the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |