|
Surface Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an medical instrument, instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cell (biology), cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In computer science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrography (other)
Electrography may refer to electrophotography, that is, Kirlian photography. Electrography may also refer to: * Measurement and recording of electrophysiology, electrophysiologic activity for diagnostic purposes ** Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG), electrography of heart electrical activity and rhythm ** Electromyography (EMG), electrography of other muscle action potentials throughout the body ** Electroencephalography (EEG), electrography of brain waves (from outside the skull) *** Electrocorticography or intracranial EEG (iEEG or ECoG), EEG with direct contact to the cerebral cortex ** Electrooculography (EOG), electrography of intraocular potential differences ** Electro-olfactography, Electroolfactography (EOG), electrography of olfaction (smell) ** Electroretinography (ERG), electrography of retinal cell action potentials ** Electronystagmography (ENG), electrography of eye muscle movements ** Electrocochleography (ECOG), electrography of cochlear auditory activity ** Elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Conduction Study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical test, medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of action potential, electrical conduction, of the motor nerve, motor and sensory nerves of the human body. These tests may be performed by Specialty (medicine), medical specialists such as clinical neurophysiology, clinical neurophysiologists, physical therapy, physical therapists, physiatry, physiatrists (physical medicine and rehabilitation physicians), and neurology, neurologists who subspecialize in electrodiagnostic medicine. In the United States, neurologists and physiatrists receive training in electrodiagnostic medicine (performing needle electromyography (EMG and NCSs) as part of residency training and, in some cases, acquire additional expertise during a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology, electrodiagnostic medicine, or neuromuscular medicine. Outside the US, clinical neurophysiologists learn needle EMG and NCS testing. Purpose and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Fat
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Some types are also associated with problems in other human organs, organs. Over 30 different disorders are classified as muscular dystrophies. Of those, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) accounts for approximately 50% of cases and affects males beginning around the age of four. Other relatively common muscular dystrophies include Becker muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, and myotonic dystrophy, whereas limb–girdle muscular dystrophy and congenital muscular dystrophy are themselves groups of several – usually extremely rare – genetic disorders. Muscular dystrophies are caused by mutations in genes, usually those involved in making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, drooping eyelids, and difficulties in talking and walking. Onset can be sudden. Those affected often have a large thymus or develop a thymoma. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease of the neuromuscular junction which results from antibodies that block or destroy nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChR) at the junction between the nerve and muscle. This prevents nerve impulses from triggering muscle contractions. Most cases are due to immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG3 antibodies that attack AChR in the postsynaptic membrane, causing complement-mediated damage and muscle weakness. Rarely, an inherited genetic defect in the neuromuscular junction results in a similar condition known as congenital myasthenia. Babies of mothers wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
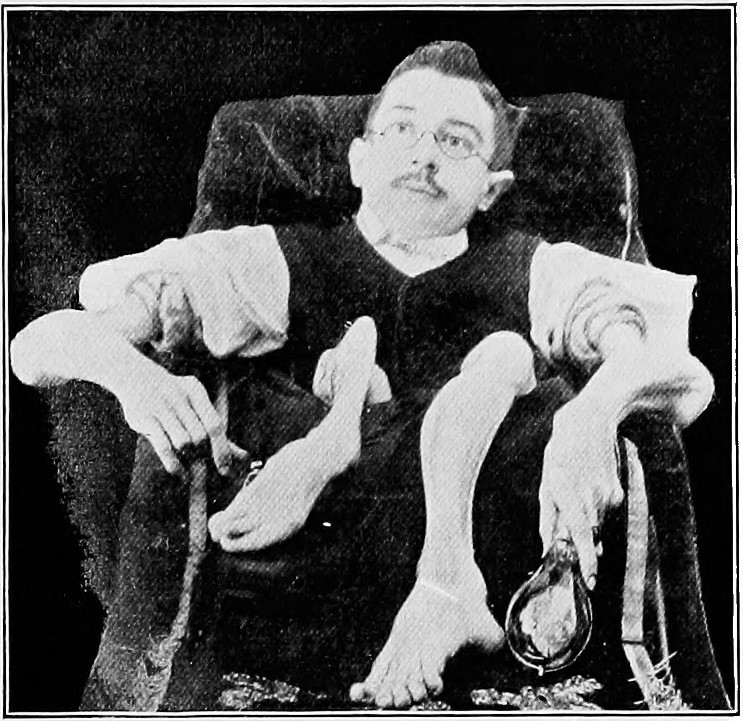
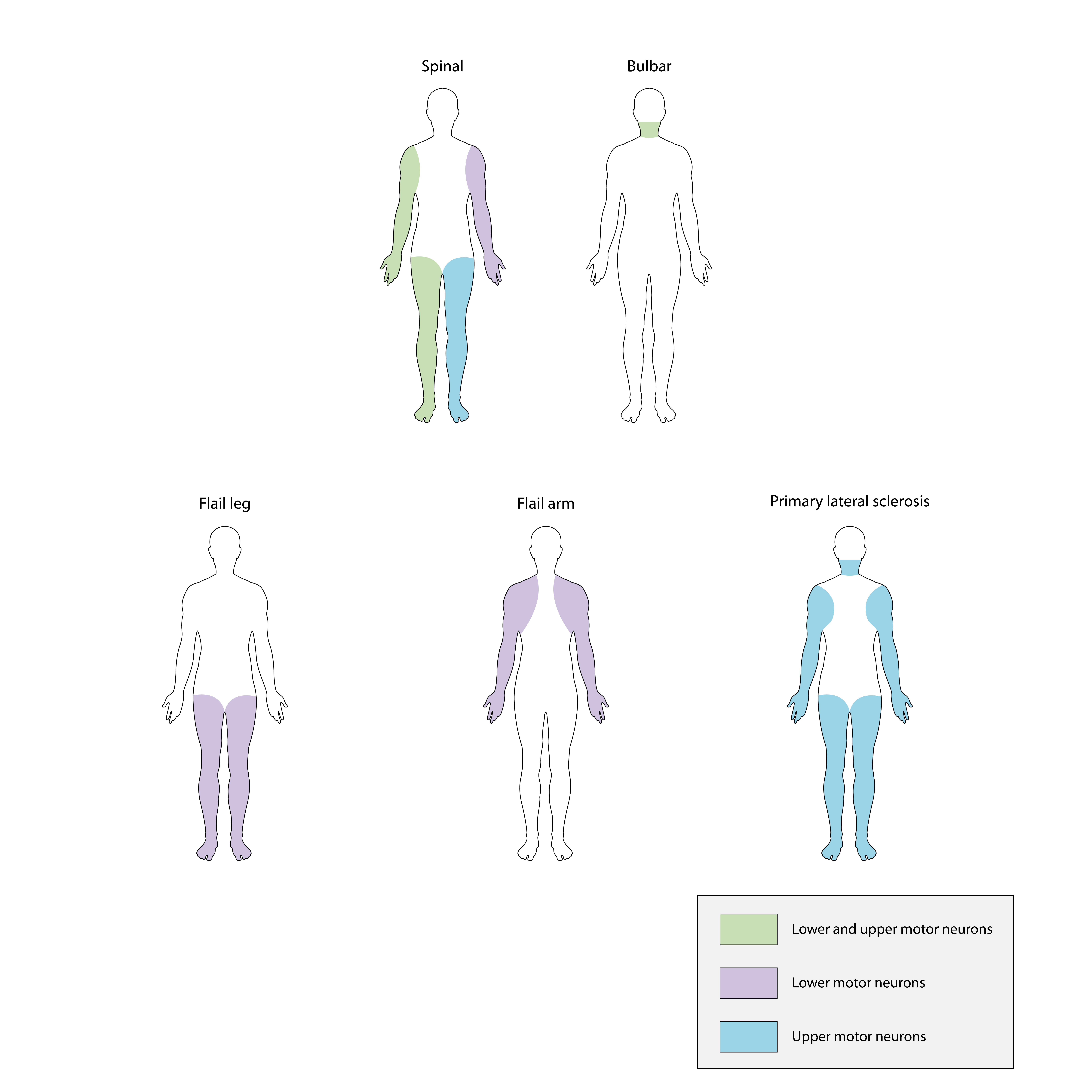
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control Skeletal muscle, voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle Spasticity, stiffness, Fasciculation, twitches, Muscle weakness, weakness, and Muscle atrophy, wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with cognitive disorder, thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as ''limb-onset'' (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
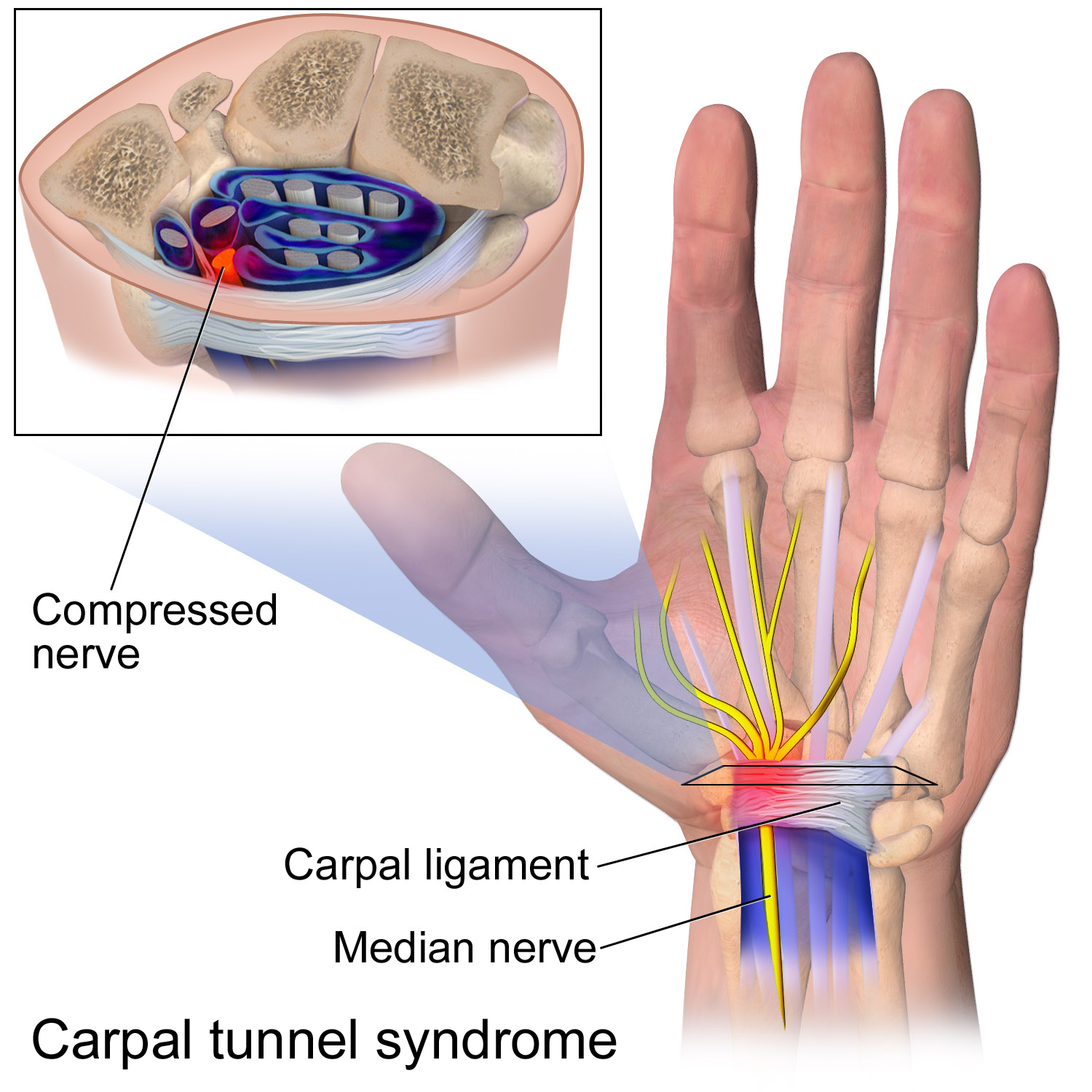
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome usually has no known cause, but there are environmental and medical risk factors associated with the condition.> CTS can affect both wrists. Other conditions can cause CTS such as wrist fracture or rheumatoid arthritis. After fracture, the resulting swelling, bleeding, and deformity compress the median nerve. With rheumatoid arthritis, the enlarged synovial membrane, synovial lining of the tendons causes compression. The main symptoms are numbness and Paresthesia, tingling of the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and the thumb side of the ring finger, as well as pain in the hand and fingers. Symptoms are typically most troublesome at night. Many people sleep with their wrists bent, and the ensuing symptoms may lead to awake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
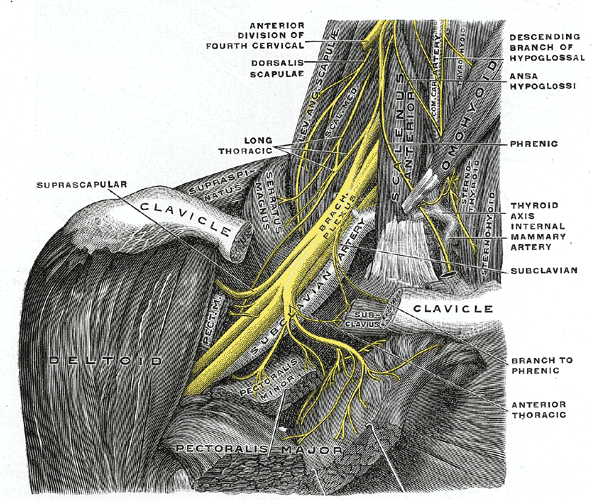
Cervical Spine Disorder
Cervical spine disorders are illnesses that affect the cervical spine, which is made up of the upper first seven vertebrae, encasing and shielding the spinal cord. This fragment of the spine starts from the region above the shoulder blades and ends by supporting and connecting the skull. The cervical spine contains many different anatomic compositions, including muscles, bones, ligaments, and joints. All of these structures have nerve endings that can detect painful problems when they occur. Such nerves supply muscular control and sensations to the skull and arms while correspondingly providing our bodies with flexibility and motion. However, if the cervical spine is injured it can cause many minor or traumatic problems, and although these injuries vary specifically they are more commonly known as "cervical spine disorders" as a whole. Symptoms It is through upper frontal chest discomfort (also known as cervical angina) and scapular pains which signs of cervical spine disorders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Back Pain
Low back pain or wiktionary:lumbago#Etymology, lumbago is a common musculoskeletal disorders, disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling. Low back pain may be classified by Pain#Chronic versus acute, duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks). The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain. The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people recovered by six weeks. In most episodes of low back pain a specific underlying cause is not identified or even looked for, with the pain believed to be due to mechanical problems such as muscle strain, muscle or joint strain. If the pain does not go away with conservative treatmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burr Ridge, Illinois
Burr Ridge (formerly Harvester) is a village in Cook and DuPage counties in the U.S. state of Illinois. Per the 2020 census, the population was 11,192. Geography Burr Ridge is located at (41.753030, -87.919998). According to the 2021 census gazetteer files, Burr Ridge has a total area of , of which (or 98.15%) is land and (or 1.85%) is water. Burr Ridge lies in both Du Page and Cook counties. The village is bordered by Hinsdale to the north, Western Springs to the northeast, Indian Head Park to the east, Willow Springs to the south and southeast, and Willowbrook to the west, along with several unincorporated areas. History Burr Ridge's gently rolling hills were carved by glaciers at the end of the last ice age, and most of the village lies on the Valparaiso Moraine. Flagg Creek, a tributary of the Des Plaines River, runs through town. Joseph Vial erected a log cabin near Wolf and Plainfield roads in 1834. Vial also ran a hotel on the stagecoach line, and the Vial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency For Healthcare Research And Quality
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ; pronounced "ark" by initiates and often "A-H-R-Q" by the public) is one of twelve agencies within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The agency is headquartered in North Bethesda, Maryland, a suburb of Washington, D.C. (with a Rockville mailing address). It was established as the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR) in 1989 as a constituent unit of the Public Health Service (PHS) to enhance the quality, appropriateness, and effectiveness of health care services and access to care by conducting and supporting research, demonstration projects, and evaluations; developing guidelines; and disseminating information on health care services and delivery systems. As part of the announced 2025 HHS reorganization, AHRQ is planned to be integrated into the new HHS Office of Strategy. History AHRQ's earliest predecessor was the National Center for Health Services Research and Development, establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |