|
Supratrochlear Nerve
The supratrochlear nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) from the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It provides sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead and the upper eyelid. Structure Origin The supratrochlear nerve is the smaller of the two terminal branches of the frontal nerve (the other being the supraorbital nerve). It arises midway between the base and apex of the orbit where the frontal nerve splits into said terminal branches. Course The supratrochlear nerve passes medially above the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle. It then travels anteriorly above the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. It exits the orbit through the supratrochlear notch or foramen. It then ascends onto the forehead beneath the corrugator supercilii muscle and frontalis muscle. It finally divides into sensory branches. The supratrochlear nerve travels with the supratrochlear artery, a branch of the ophthalmic artery. Branches Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Nerve
The frontal nerve is the largest branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It supplies sensation to the skin of the forehead, the mucosa of the frontal sinus, and the skin of the upper eyelid. It may be affected by schwannoma. Structure The frontal nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1), itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). The frontal nerve branches immediately before entering the superior orbital fissure. In then travels superolateral to the annulus of Zinn between the lacrimal nerve and inferior ophthalmic vein. After entering the orbit it travels anteriorly between the roof periosteum and the levator palpebrae superioris. Midway between the apex and base of the orbit it divides into two branches, the supratrochlear nerve and supraorbital nerve. Functions The two branches of the frontal nerve provide sensory innervation to the skin of the forehead, mucosa of the frontal sinus (an air sinus), and the skin of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmic Artery
The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions. Structure The ophthalmic artery emerges from the internal carotid artery. This is usually just after the internal carotid artery emerges from the cavernous sinus. In some cases, the ophthalmic artery branches just before the internal carotid exits the carotid sinus. The ophthalmic artery emerges along the medial side of the anterior clinoid process. It runs anteriorly, passing through the optic canal inferolaterally to the optic nerve. It can also pass superiorly to the optic nerve in a minority of cases. In the posterior third of the cone of the orbit, the ophthalmic artery turns sharply and med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders (publisher)
Saunders is an American academic publisher based in the United States. It is currently an imprint of Elsevier. Formerly independent, the W. B. Saunders company was acquired by CBS in 1968, who added it to their publishing division Holt, Rinehart & Winston. When CBS left the publishing field in 1986, it sold the academic publishing units to Harcourt Brace Jovanovich. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001. . Northern Illinois University Libraries. Retrieved May 2, 2015. W. B. Saunders published the |
Mosby (imprint)
Mosby is an academic publisher of textbooks and academic journals based in the United States. The C.V. Mosby Company was incorporated in 1906 in St. Louis, Missouri. Formerly independent, C.V. Mosby, Inc. was acquired by Times Mirror in 1967. In 1989, Times Mirror merged C.V. Mosby with Year Book Medical Publishers, Wolfe Publishing Ltd. and PSG Publishing Company. Harcourt General acquired Mosby in 1998. The company was purchased by Reed Elsevier in 2001, and the company became an imprint of Elsevier Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, .... See also * :Mosby academic journals References External links * Book publishing companies based in Missouri Publishing companies established in 1906 Elsevier imprints 1906 establishments in Missouri {{publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
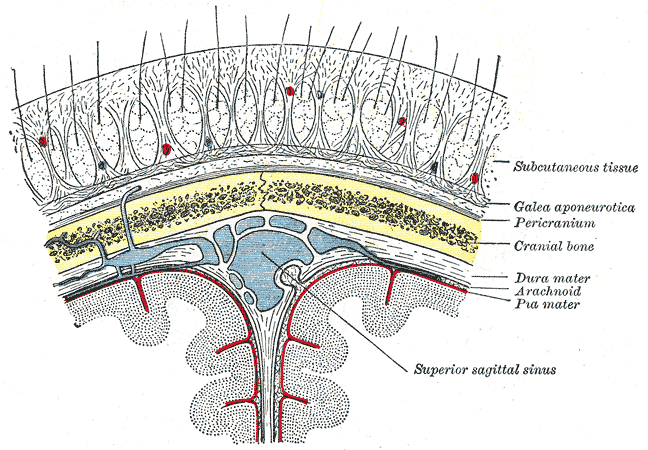
Scalp
The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology. Structure Layers The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can be remembered using the mnemonic 'SCALP': * S: Skin. The skin of the scalp contains numerous hair follicles and sebaceous glands. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: Aponeurosis. The epicranial aponeurosis or galea aponeurotica is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which anchors the above layers in place. It runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Livingstone
Churchill Livingstone is an academic publisher. It was formed in 1971 from the merger of Longman's medical list, E & S Livingstone (Edinburgh, Scotland) and J & A Churchill (London, England) and was owned by Pearson. Harcourt acquired Churchill Livingstone in 1997. It is now integrated as an imprint in Elsevier's health science The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences: Health sciences – those sciences that focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple ... division after Elsevier acquired Harcourt in 2001. In the past it published a number of classic medical texts, including Sir William Osler's textbook '' The Principles and Practice of Medicine, Gray's Anatomy,'' and '' Myles' Textbook for Midwives.'' In the 1980s, in addition to new texts in all areas of clinical medicine, it published an extensive list of medical and nursing textbooks in low-cost e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. (At the joints of long bones the bone's outer surface is lined with "articular cartilage", a type of hyaline cartilage.) Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner ''cambium layer'' (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone (the length of a long bone is controlled by the epiphyseal plate) and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral" (and "blepharal") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies. A set of specialized hairs known as lashes grow from the upper and lower eyelid margins to further protect the eye from dust and debris. The appearance of the human upper eyelid often varies between different populations. The prevalence of an epicanthic fold covering the inner corner of the eye account for the majority of East Asian and Southeast Asian populations, and is also found in varying degrees among other populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly Angiogenesis, vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |