|
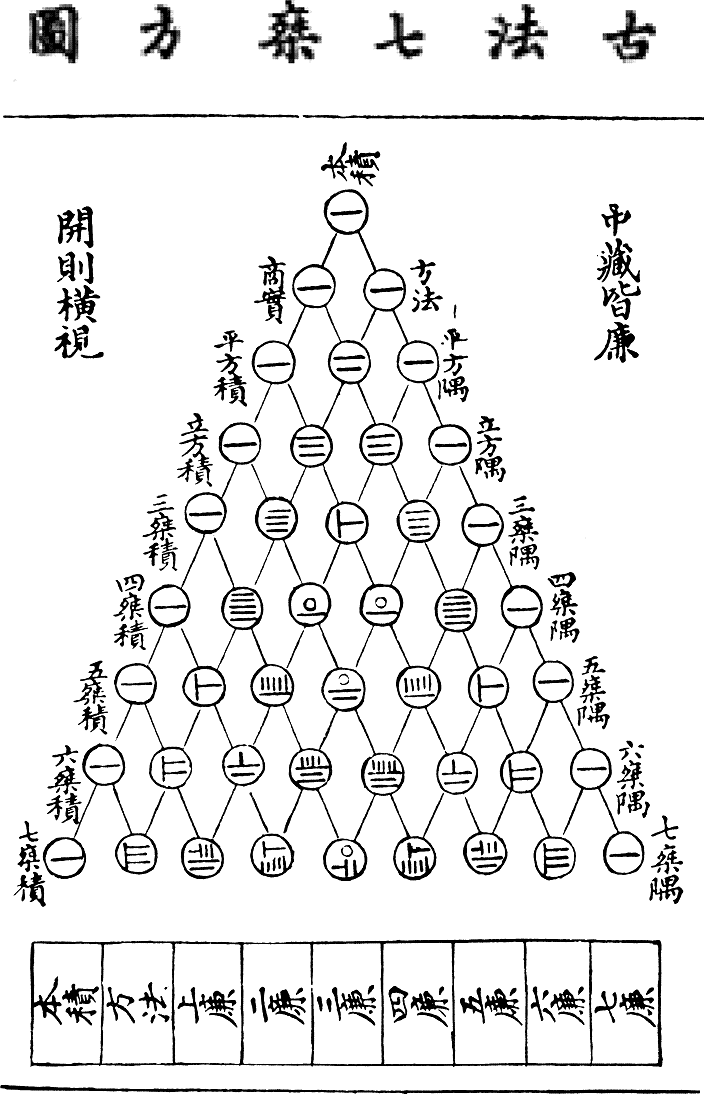
Sunzi Suanjing
''Sunzi Suanjing'' () was a mathematical treatise written during 3rd to 5th centuries CE which was listed as one of the Ten Computational Canons during the Tang dynasty. The specific identity of its author Sunzi (lit. "Master Sun") is still unknown but he lived much later than his namesake Sun Tzu, author of ''The Art of War''. From the textual evidence in the book, some scholars concluded that the work was completed during the Southern and Northern Dynasties. Besides describing arithmetic methods and investigating Diophantine equations, the treatise touches upon astronomy and attempts to develop a calendar. Contents The book is divided into three chapters. Chapter 1 Chapter 1 discusses measurement units of length, weight and capacity, and the rules of counting rods. Although counting rods were in use in the Spring and Autumn period and there were many ancient books on mathematics such as '' Book on Numbers and Computation'' and ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Zi Suanjing
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot Plasma (physics), plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. The Sun has been an The Sun in culture, object of veneration in many cultures. It has been a central subject for astronomical research since Ancient history, antiquity. The Sun orbits the Galactic Center at a distance of 24,000 to 28,000 light-years. Its distance from Earth defines the astronomical unit, which is about or about 8 light-minutes. Solar radius, Its diameter is about (), 109 times that of Earth. solar mass, The Sun's mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth, making up about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. The mass of outer layer of the Sun's atmosphere, its ''photosphere'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE). They flourished during the Han period (202 BCE – 220 CE) and subsequent dynasties with the publication of star catalogues. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Remainder Theorem
In mathematics, the Chinese remainder theorem states that if one knows the remainders of the Euclidean division of an integer ''n'' by several integers, then one can determine uniquely the remainder of the division of ''n'' by the product of these integers, under the condition that the divisors are pairwise coprime (no two divisors share a common factor other than 1). The theorem is sometimes called Sunzi's theorem. Both names of the theorem refer to its earliest known statement that appeared in '' Sunzi Suanjing'', a Chinese manuscript written during the 3rd to 5th century CE. This first statement was restricted to the following example: If one knows that the remainder of ''n'' divided by 3 is 2, the remainder of ''n'' divided by 5 is 3, and the remainder of ''n'' divided by 7 is 2, then with no other information, one can determine the remainder of ''n'' divided by 105 (the product of 3, 5, and 7) without knowing the value of ''n''. In this example, the remainder is 23. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Calculus
Rod calculus or rod calculation was the mechanical method of algorithmic computation with counting rods in China from the Warring States to Ming dynasty before the counting rods were increasingly replaced by the more convenient and faster abacus. Rod calculus played a key role in the development of Chinese mathematics to its height in the Song dynasty and Yuan dynasty, culminating in the invention of polynomial equations of up to four unknowns in the work of Zhu Shijie. Hardware The basic equipment for carrying out rod calculus is a bundle of counting rods and a counting board. The counting rods are usually made of bamboo sticks, about 12 cm- 15 cm in length, 2mm to 4 mm diameter, sometimes from animal bones, or ivory and jade (for well-heeled merchants). A counting board could be a table top, a wooden board with or without grid, on the floor or on sand. In 1971 Chinese archaeologists unearthed a bundle of well-preserved animal bone counting rods stored in a silk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Nine Chapters On The Mathematical Art
''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE. This book is one of the earliest surviving mathematical texts from China, the others being the '' Suan shu shu'' (202 BCE – 186 BCE) and ''Zhoubi Suanjing'' (compiled throughout the Han until the late 2nd century CE). It lays out an approach to mathematics that centres on finding the most general methods of solving problems, which may be contrasted with the approach common to ancient Greek mathematicians, who tended to deduce propositions from an initial set of axioms. Entries in the book usually take the form of a statement of a problem, followed by the statement of the solution and an explanation of the procedure that led to the solution. These were commented on by Liu Hui in the 3rd century. The book was later included in the early Tang collection, the '' Ten Computational C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book On Numbers And Computation
The ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' (), or the ''Writings on Reckoning'', is one of the earliest known Chinese mathematical treatises. It was written during the early Western Han dynasty, sometime between 202 BC and 186 BC.Liu et al. (2003), 9. It was preserved among the Zhangjiashan Han bamboo texts and contains similar mathematical problems and principles found in the later Eastern Han period text of ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art''. Discovery The text was found in tomb M247 of the burial grounds near Zhangjiashan, Jiangling County, in Hubei province, excavated in December–January 1983–1984. This tomb belonged to an anonymous civil servant in early West Han dynasty. In the tomb were 1200 bamboo strips written in ink. Originally the strips were bound together with string, but the string had rotted away and it took Chinese scholars 17 years to piece together the strips. As well as the mathematical work the strips covered government statutes, law repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject to the Zhou exercised increasing political autonomy. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 481 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, local polities negotiated their own alliances, waged wars against one another, up to defying the king's court in Luoyang, Luoyi. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, is generally considered to mark the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. The periodization dates to the late Western Han (). Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng (state), Zeng and Shen (state), Shen— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counting Rods
Counting rods (筭) are small bars, typically 3–14 cm (1" to 6") long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number. The written forms based on them are called rod numerals. They are a true Positional notation, positional numeral system with numerical digit, digits for 1–9 and a blank for 0, from the Warring States period, Warring states period (circa 475 BCE) to the 16th century. History Chinese arithmeticians used counting rods well over two thousand years ago. In 1954, forty-odd counting rods of the Warring States period (5th century BCE to 221 BCE) were found in Zuǒjiāgōngshān (左家公山) Chu (state), Chu Grave No.15 in Changsha, Hunan. In 1973, archeologists unearthed a number of wood scripts from a tomb in Hubei dating from the period of the Han dynasty (206 BCE to 220 CE). On one of the wooden scripts was written: "当利二月定算� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunzi Sqrt
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the author of ''The Art of War'', a Classical Chinese text on military strategy from the Warring States period, though the earliest parts of the work probably date to at least a century after his purported death. Sun Tzu is revered in Chinese and East Asian culture as a legendary historical and military figure; however, his historical existence is uncertain. The Han dynasty historian Sima Qian and other traditional Chinese historians placed him as a minister to King Helü of Wu and dated his lifetime to 544–496 BC. The name ''Sun Tzu''by which he is more popularly knownis an honorific which means "Master Sun". His birth name was said to be Sun Wu ( zh, t=孫武, s=孙武, first=t) and he is posthumously known by his courtesy name Changqing ( zh, t=� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunzi Division
Sun Tzu (; zh, t=孫子, s=孙子, first= t, p=Sūnzǐ) may have been a Chinese military general, strategist, philosopher, and writer who lived during the Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC). Sun Tzu is traditionally credited as the author of ''The Art of War'', a Classical Chinese text on military strategy from the Warring States period, though the earliest parts of the work probably date to at least a century after his purported death. Sun Tzu is revered in Chinese and East Asian culture as a legendary historical and military figure; however, his historical existence is uncertain. The Han dynasty historian Sima Qian and other traditional Chinese historians placed him as a minister to King Helü of Wu and dated his lifetime to 544–496 BC. The name ''Sun Tzu''by which he is more popularly knownis an honorific which means "Master Sun". His birth name was said to be Sun Wu ( zh, t=孫武, s=孙武, first=t) and he is posthumously known by his courtesy name Changqing ( zh, t=� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |