|
Sunil Bajpai
Sunil Bajpai (born 30 September 1961) is the Chair Professor of Vertebrate Paleontology in the Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee. He is in service as a professor at IIT Roorkee since 1st January 1996 till 30 September 2026. He also served as the director of the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences from January 2013 to July 2018. Sunil Bajpai predominantly works on the Cenozoic vertebrates of India with focus on marine mammals, such as whales and sea cows. Bajpai and his collaborators fossil discoveries from the Eocene of Kutch (Gujarat) and the Himalayas have helped in understanding how whales have evolved. Bajpai also works on land mammals, which includes the early representatives of horses, artiodactyls, and primates, such as the stem perissodactyl family Cambaytheriidae, artiodactyl ''Gujaratia,'' and primates such as the adapoid '' Marcgodinotius'' and the omomyid Vastanomys'' Additionally, he has worked on many other fossil vertebrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panjab University, Chandigarh
Panjab University (PU) is an Indian collegiate public state university located in Chandigarh. Funded through both State and Union governments, it is considered a state university. It traces its origins to the University of the Punjab in Lahore, which was founded in 1882. After the partition of India, the university was established on 1 October 1947, and called East Punjab University. Initially housed primarily at a cantonment in Solan, it later relocated to a newly built campus in Chandigarh, and was renamed Panjab University. It is accredited by NAAC A++ grade. The university has 78 teaching and research departments and 10 centres/chairs for teaching and research at the main campus located at Chandigarh. It has 201 affiliated colleges spread over the eight districts of Punjab state and union-territory of Chandigarh, with Regional Centres at Sri Muktsar Sahib, Ludhiana and Hoshiarpur. It is one of the well-ranked universities in India. The campus is residential, spread ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaisalmer Formation
The Jaisalmer Formation is a Middle to Late Jurassic-aged geologic formation located in India near the city of Jaisalmer that consists mainly of marine deposits. The formation was first identified and defined by geologist Richard Dixon Oldham in 1886. Dinosaur remains are among the known fossils recovered from this formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, Asia)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): ''The Dinosauria'', 2nd, ''Berkeley: University of California Press''. Pp. 593–600. . '' Strophodus jaisalmerensis'', a hybodont, was named after this formation and the Jaisalmer District where its holotype was found. Sub-units The Badabag, Fort, Joyan and Hamira members represent the Middle Jurassic Bajocian and Bathonian stages, while the Jajiya and Kuldhar members represent the Middle Jurassic Callovian and the Late Jurassic Oxfordian stages. The Fort Member is the most extensively studied and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panjab University
Panjab University (PU) is an Indian collegiate public state university located in Chandigarh. Funded through both State and Union governments, it is considered a state university. It traces its origins to the University of the Punjab in Lahore, which was founded in 1882. After the partition of India, the university was established on 1 October 1947, and called East Punjab University. Initially housed primarily at a cantonment in Solan, it later relocated to a newly built campus in Chandigarh, and was renamed Panjab University. It is accredited by NAAC A++ grade. The university has 78 teaching and research departments and 10 centres/chairs for teaching and research at the main campus located at Chandigarh. It has 201 affiliated colleges spread over the eight districts of Punjab state and union-territory of Chandigarh, with Regional Centres at Sri Muktsar Sahib, Ludhiana and Hoshiarpur. It is one of the well-ranked universities in India. The campus is residential, spread over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Vertebrate Paleontology
The ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1980 by Jiri Zidek (University of Oklahoma). It covers all aspects of vertebrate paleontology, including vertebrate origins, evolution, functional morphology, taxonomy, biostratigraphy, paleoecology, paleobiogeography, and paleoanthropology. The journal is published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.190. References External links * Paleontology journals Academic journals established in 1980 Quarterly journals English-language journals Taylor & Francis academic journals {{Oklahoma- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertrappean Beds
The Intertrappean Beds are a Late Cretaceous and early Paleogene geologic unit in India. These beds are found as interbeds between Deccan Traps layers, including the slightly older Lameta Formation. They consist a number of different subgroups and formations, and span the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. Many mostly fragmentary fossils, especially of small vertebrates, are known from the formation. Indeterminate theropod and pterosaur remains have been recovered from the formation, as well as dinosaur eggs.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. The mammal genera '' Deccanolestes'', '' Sahnitherium'', '' Bharattherium'', '' Indoclemensia, Indotriconodon'' and'' Kharmerungulatum'' have been recovered from several localities. The Early Eocene-aged Bamanbor locality in Gujarat preserves articulated freshwater fish specimens. A rich plant flora is known from the formation. Stratigraphy Although often thought of as a contemporaneous unit that was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indotriconodon
''Indotriconodon magnus'' is an extinct mammal from the Late Cretaceous of India. A eutriconodont, it represents the geologically youngest of the group dating to the Maastrichtian just a few thousand years before the KT event (a record previously held by '' Alticonodon lindoei'' from the Campanian of Canada), as well as a relatively large sized Mesozoic mammal. Description ''Indotriconodon magnus'' is known only from a single lower molar. It is about 20% smaller than that of ''Repenomamus giganticus'' but larger than that of other eutriconodonts, making it a badger-sized mammal. Phylogeny In its 2024 description it nests deeply within Eutriconodonta, being sister taxa to Volaticotherini. Palaeoceology Found in the Intertrappean Beds, it co-existed with at least other ten mammal genera as well various squamates, turtles and dinosaur Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor 3.8. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
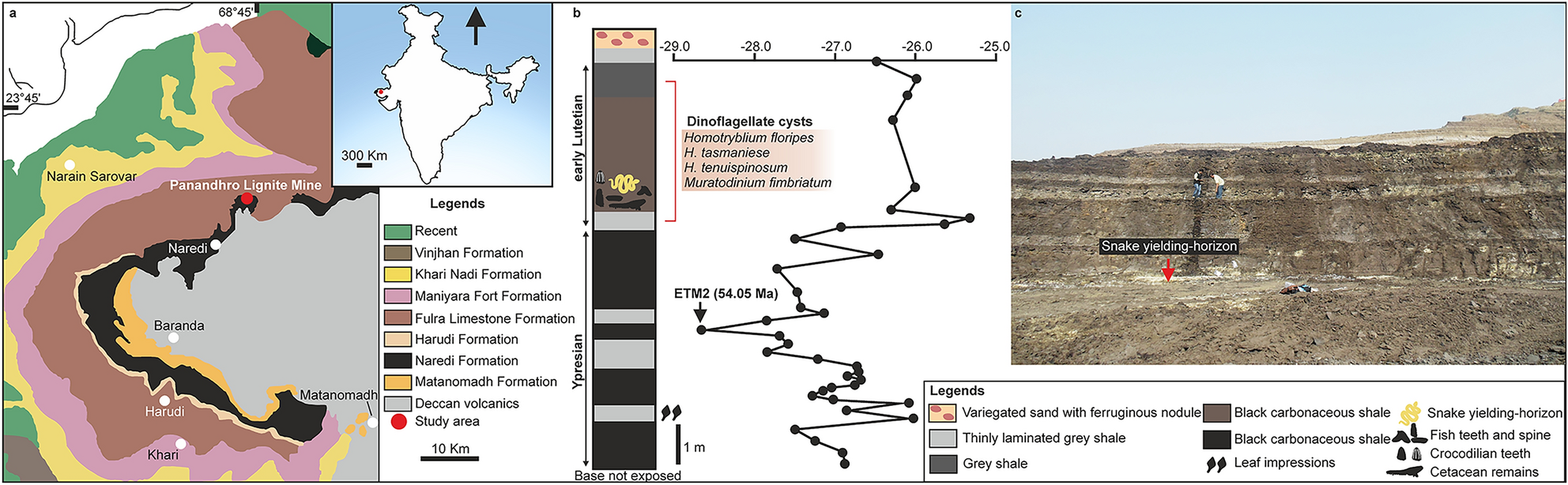
Naredi Formation
The Naredi Formation is a Cenozoic geologic formation in India. Remains of large snakes such as ''Vasuki'' are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, as well as other flora and fauna Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively .... Paleobiota Mammals ;Cetacea Reptiles Pseudosuchians Snakes Turtles Fishes Mollusca References {{reflist Eocene Asia Geologic formations of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasuki Indicus
''Vasuki indicus'' is an extinct snake species in the family Madtsoiidae that lived during the Middle Eocene of what is now India. ''V. indicus'' is the Monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Vasuki'', known from several vertebrae found in the Naredi Formation. It has an estimated body length between , making it the largest known madtsoiid. The highest length estimates place ''Vasuki'' among the longest snakes ever discovered. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen of ''Vasuki'', IIT Roorkee, IITR/VPL/SB 3102-1-21, was discovered in 2005 within the sedimentary layers of the Naredi Formation in the Panadhro Lignite Mine in the Kutch district of Gujarat State, western India. The specimen consists of 27 pre-cloacal vertebrae, some of which were found in Joint, articulation. The fossil material was found some time after 2004, and preliminary analyses suggested crocodilian affinities for the fossil material without further review. In 2024, ''Vasuki indicus'' was Species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |