|
Suhl Card Reader Case
The Suhl card reader case deals with the 1956 verdict on Charlotte Marquardt (born 1902 in Berlin, died 1975 in Suhl, East Germany). A court in Eastern Germany had condemned Marquardt, an amateur psychic and cartomancy practitioner, to twelve years' imprisonment. The verdict referred to so called ''Kriegs- und Boykotthetze'', incitement to war and boycott: Marquardt had provided favorable forecasts for families preparing to leave East Germany, and when arrested, was in possession of an astrological handbook including a horoscope with a positive outlook on Western Germany. The judgment has been deemed barbaric and was mentioned several times in documentations about ''Unrechtsjustiz'', systematic injustice in the East Germany, GDR. Background of Marquardt Charlotte Marquardt was born 1902 in Berlin and grew up in the family of a metal worker in Weissensee (Berlin), Berlin-Weißensee. She worked as a telephone operator and typist, and in 1927 married an officer of the Schutzpolizei, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella-Mehlis, Suhl forms the largest urban area in the Thuringian Forest with a population of 46,000. The region around Suhl is marked by up to 1,000-meter-high mountains, including Thuringia's highest peak, the Großer Beerberg (983 m), approximately NE of the city centre. Suhl was first mentioned in 1318 and stayed a small mining and metalworking town, until industrialization broke through in late 19th century and Suhl became a centre of Germany's arms production, specialized on rifles and guns with companies such as Sauer & Sohn. Furthermore, the engineering industry was based in Suhl with Simson, a famous car and moped producer. In 1952, Suhl became one of East Germany's 14 district capitals, which led to a government-directed period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
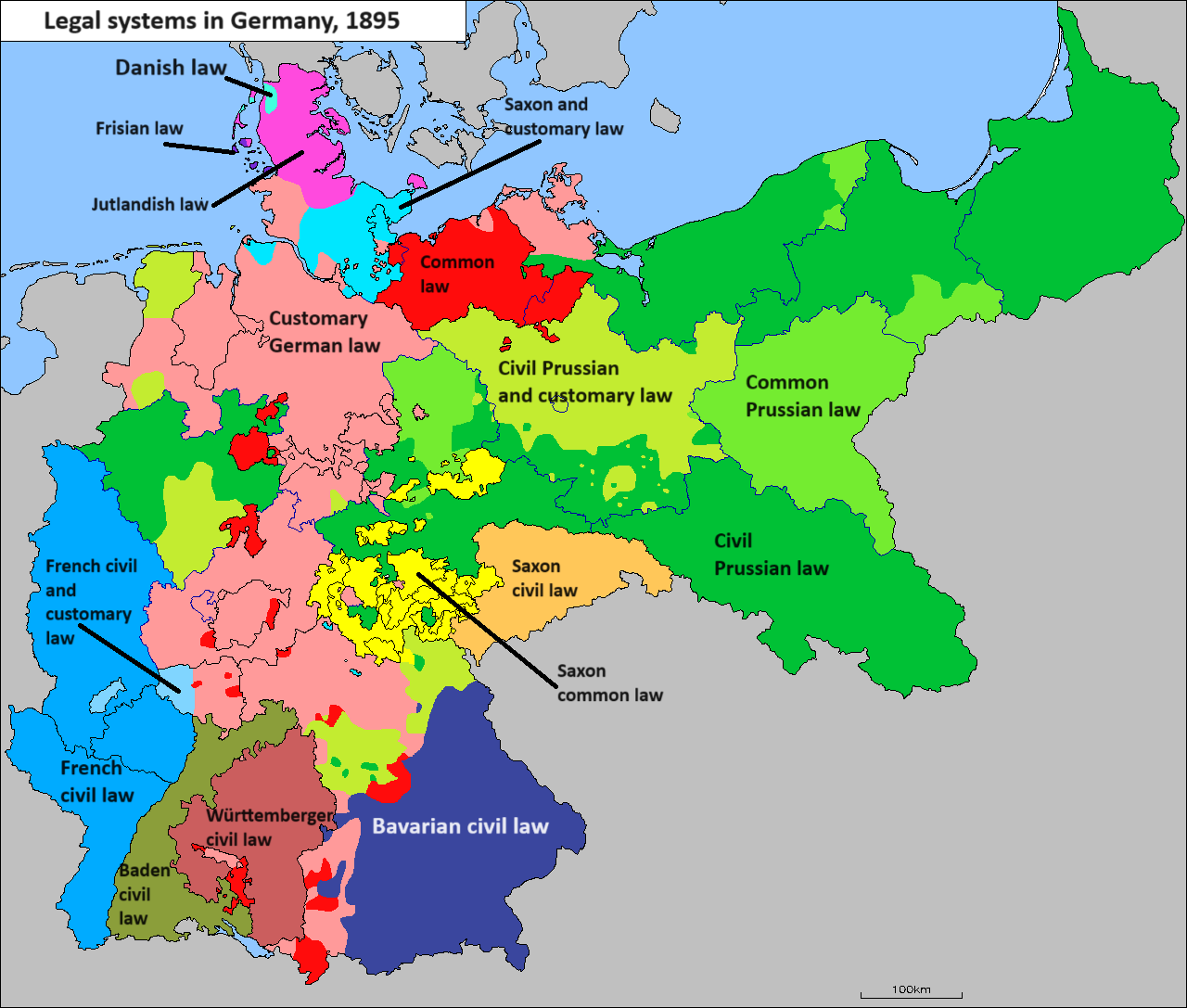
Legal History Of Germany
The law of Germany (), that being the modern German legal system (), is a system of civil law which is founded on the principles laid out by the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, though many of the most important laws, for example most regulations of the civil code (''Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch'', or BGB) were developed prior to the 1949 constitution. It is composed of public law (''öffentliches Recht''), which regulates the relations between a citizen/person and the state (including criminal law) or two bodies of the state, and the private law, (''Privatrecht'') which regulates the relations between two people or companies. It has been subject to a wide array of influences from Roman law, such as the Justinian Code the Corpus Juris Civilis, and to a lesser extent the Napoleonic Code. History German law has been subject to many influences over the centuries. Until Medieval times the Early Germanic Law, derived from the Salic Law of the Salian Franks and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania State University Press
The Penn State University Press, also known as The Pennsylvania State University Press, is a non-profit publisher of scholarly books and journals. Established in 1956, it is the independent publishing branch of the Pennsylvania State University and is a division of the Penn State University Library system. Penn State University Press publishes books and journals of interest to scholars and general audiences. As a part of a land-grant university with a mandate to serve the citizens of the commonwealth of Pennsylvania, it also specializes in works about Penn State University, Pennsylvania, and the mid-Atlantic region. The areas of scholarship the Press is best known for are art history, medieval studies, Latin American studies, rhetoric and communication, religious studies, and graphic medicine. The press produces about 80 books a year and over 60 journals. The Press employs 25 to 30 people, and has several internship programs for Penn State students interested in a publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteen Eighty-Four
''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (also published as ''1984'') is a dystopian novel and cautionary tale by the English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and final completed book. Thematically, it centres on the consequences of totalitarianism, mass surveillance and repressive regimentation of people and behaviours within society. Orwell, a democratic socialist and an anti-Stalinist, modelled Britain under authoritarian socialism in the novel on the Soviet Union in the era of Stalinism and the practices of censorship and propaganda in Nazi Germany. More broadly, the book examines the role of truth and facts within societies and the ways in which they can be manipulated. The story takes place in an imagined future. The current year is uncertain, but believed to be 1984. Much of the world is in perpetual war. Great Britain, now known as Airstrip One, has become a province of the totalitarian superstate Oceania, which is led b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950) was an English novelist, poet, essayist, journalist, and critic who wrote under the pen name of George Orwell. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to all totalitarianism (both authoritarian communism and fascism), and support of democratic socialism. Orwell is best known for his allegorical novella ''Animal Farm'' (1945) and the Utopian and dystopian fiction, dystopian novel ''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (1949), although his works also encompass literary criticism, poetry, fiction and polemical journalism. His non-fiction works, including ''The Road to Wigan Pier'' (1937), documenting his experience of working-class life in the industrial north of England, and ''Homage to Catalonia'' (1938), an account of his experiences soldiering for the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republican faction of the Spanish Civil War (1936–1939), are as critically respected as George Orwell bibliograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stasi Records Agency
The Stasi Records Agency () was the organisation that administered the archives of Ministry of State Security (Stasi) of the former German Democratic Republic (East Germany). It was a government agency of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was established when the Stasi Records Act came into force on 29 December 1991. Formally it was called the Federal Commissioner for the Records of the State Security Service of the former German Democratic Republic (); the official German abbreviation was BStU. On June 17, 2021, the BStU was absorbed into the German Federal Archives (''Bundesarchiv''). The Stasi was established on 8 February 1950. It functioned as the GDR's secret police, intelligence agency and crime investigation service. It grew to have around 270,000 people working for it, including about 180,000 informers, or " unofficial collaborators". It was renamed the "Office for National Security" () on 17 November 1989. It was dissolved on 13 January 1990. The Stasi spied on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (, ) was a guarded concrete Separation barrier, barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and the East Germany, German Democratic Republic (GDR; East Germany). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government of the GDR on 13 August 1961. It included guard towers placed along large concrete walls, accompanied by a wide area (later known as the "death strip") that contained anti-vehicle trenches, beds of nails and other defenses. The primary intention for the Wall's construction was to prevent East Germany, East German citizens from Emigration from the Eastern Bloc, fleeing to the West. The Eastern Bloc, Soviet Bloc propaganda portrayed the Wall as protecting its population from "Fascist (insult), fascist elements conspiring to prevent the will of the people" from building a Communism, communist state in the GDR. The authorities officially referred to the Berlin Wall as the ''Anti-Fascist Protection Ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stollberg
Stollberg is a town in Saxony, Germany, in the district Erzgebirgskreis. It is situated 20 km east of Zwickau and 17 km southwest of Chemnitz. It was the site of the Hoheneck women's prison until 2001. References Erzgebirgskreis {{Erzgebirgskreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoheneck Women's Prison
Hoheneck Women's Prison (German: ''Frauengefängnis Hoheneck'') was a women's correctional facility in operation between 1862 and 2001 in Stollberg, Germany. It became most notable as a detention facility for female political prisoners in East Germany. The prison was designed to hold up to 600 inmates, however, as many as 1,600 were detained there. The short film ''Broken: The Women’s Prison at Hoheneck'' examines forced labour in Hoheneck Prison. Notable inmates * Erika Bergmann: Nazi war criminal and Ravensbrück concentration camp guard * Ulla Jürß: Nazi war criminal and Ravensbrück concentration camp guard * Erna Petri: Nazi war criminal * Jutta Fleck: Attempted escapee from the German Democratic Republic See also * Berlin-Hohenschönhausen Memorial * Memorial and Education Centre Andreasstrasse References Further reading * Rodewill, Rengha (2014) ''Hoheneck – Das DDR-Frauenzuchthaus: Dokumentarische Erkundung in Fotos mit Zeitzeugenberichten und einem Vorw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This metropolitan area, Germany's largest, is also the second largest in the European Union by GDP, with over 11 million residents. Bonn served as the capital of West Germany from 1949 until 1990 and was the seat of government for reunified Germany until 1999, when the government relocated to Berlin. The city holds historical significance as the birthplace of Germany's current constitution, the Basic Law. Founded in the 1st century BC as a settlement of the Ubii and later part of the Roman province Germania Inferior, Bonn is among Germany's oldest cities. It was the capital city of the Electorate of Cologne from 1597 to 1794 and served as the residence of the Archbishops and Prince-electors of Cologne. The period during which Bonn was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrological Aspect
In astrology, an aspect is an angle that Planets in astrology, planets make to each other in the horoscope; as well as to the Ascendant, Midheaven, descendant (astrology), Descendant, Imum coeli, Lower Midheaven, and other points of astrological interest. As viewed from Earth, aspects are measured by the angular distance in degrees and minutes of ecliptic longitude between two points. According to astrological tradition, they indicate the timing of transitions and developmental changes in the lives of people and affairs relative to the Earth. For example, if an astrologer creates a Horoscope that shows the apparent positions of the celestial bodies at the time of a person's birth (Natal astrology, Natal Chart), and the angular distance between Planets in astrology#Mars, Mars and Planets in astrology#Venus, Venus is 92° ecliptic longitude, the chart is said to have the aspect "Venus #Square, Square Mars" with an Celestial orb, orb of 2° (i.e., it is 2° away from being an exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |