|
Sugar Pine Lumber Company
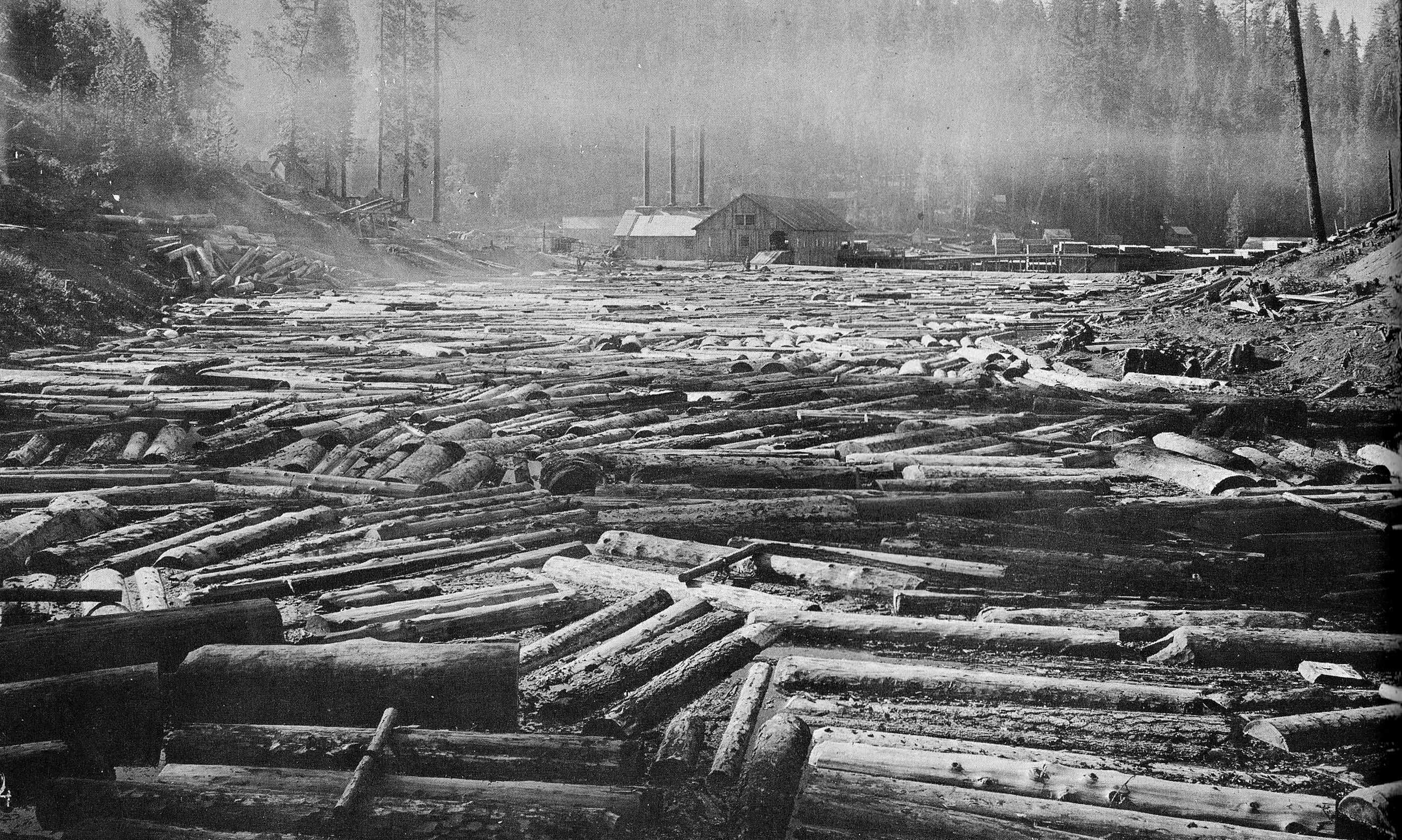
The Sugar Pine Lumber Company was an early 20th century logging operation and railroad in the Sierra Nevada. Unable to secure water rights to build a log flume, the company operated the “crookedest railroad ever built." They later developed the Minarets-type locomotive, the largest and most powerful saddle tank locomotive ever made. The company was also a pioneer in the electrification of logging where newly plentiful hydroelectric power replaced the widespread use of steam engines. The company founded two towns. They built Central Camp, a permanent logging camp with lavish amenities, and Pinedale, site of the company lumber mill. They operated two railroads: the Sugar Pine Railroad, which connected Central Camp to the switching yard in Bass Lake, and the Minarets and Western Railway, a client carrier that transported whole logs from the Sierra Nevada to the company lumber mill. The Sugar Pine Lumber Company became one of the most notable boom-and-bust stories of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Lake (Madera County, California)
Bass Lake, formerly known as Crane Valley Reservoir, is a man-made lake located in Madera County, California, within the Sierra National Forest, approximately 14 miles (23 km) south of Yosemite National Park. The lake was formed by the construction of Crane Valley Dam on Willow Creek, a tributary of the San Joaquin River The San Joaquin River ( ; ) is the longest river of Central California. The long river starts in the high Sierra Nevada and flows through the rich agricultural region of the northern San Joaquin Valley before reaching Suisun Bay, San Francis .... Completed in 1910, the 145-foot (44 m) concrete gravity dam was built to generate hydroelectric power. Today, Bass Lake supports energy production, recreation, and diverse ecological habitats. History The name "Crane Valley" dates back to 1851, when early explorers misidentified great blue herons as cranes in the region’s wetlands. Hydroelectric development began in 1895 under the San Joaquin Electric Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
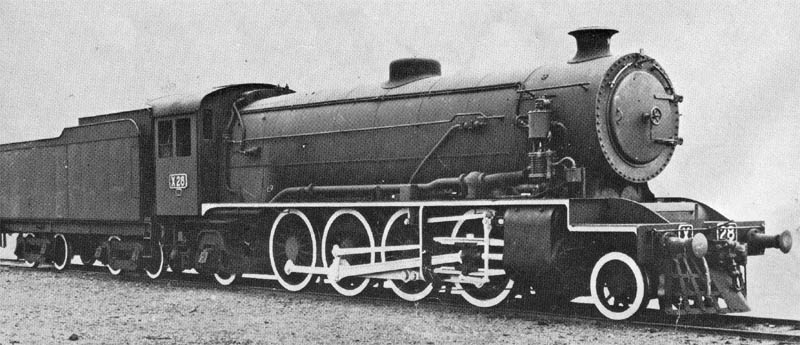
2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, frequently shortened to Mike. It was also at times referred to on some railroads in the United States as the McAdoo Mikado and, during World War II, the MacArthur. The notation 2-8-2T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, the "T" suffix indicating a locomotive on which the water is carried in tanks mounted on the engine rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-8-2 wheel arrangement allowed the locomotive's firebox to be placed behind instead of above the driving wheels, thereby allowing a larger firebox that could be both wide and deep. This supported a greater rate of combustion and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginger Rogers
Ginger Rogers (born Virginia Katherine McMath; July 16, 1911 – April 25, 1995) was an American actress, dancer and singer during the Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood. She won an Academy Award for Best Actress for her starring role in Kitty Foyle (film), ''Kitty Foyle'' (1940), and performed during the 1930s in RKO's musical films with Fred Astaire. Her career continued on stage, radio and television throughout much of the 20th century. Rogers was born in Independence, Missouri, and raised in Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City. She and her family moved to Fort Worth, Texas, when she was nine years old. In 1925, she won a Charleston dance contest that helped her launch a successful vaudeville career. After that, she gained recognition as a Broadway theatre, Broadway actress for her stage debut in ''Girl Crazy''. This led to a contract with Paramount Pictures, which ended after five films. Rogers had her first successful film roles as a supporting actress in '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Boyd (actor)
William Lawrence Boyd (June 5, 1895 – September 12, 1972) was an American film actor who is known for portraying the cowboy hero Hopalong Cassidy. Biography Boyd was born in Hendrysburg, Ohio and reared in Cambridge, Ohio and Tulsa, Oklahoma, where he lived from 1909 to 1913. He was the son of day laborer Charles William Boyd and his wife Lida (née Wilkens). Following his father's death, Boyd moved to California and worked as an orange picker, surveyor, tool dresser and auto salesman. In Hollywood, Boyd found work as an Extra (acting), extra in ''Why Change Your Wife?'' and other films. During World War I, he enlisted in the army but was exempt from military service because of a heart condition. More prominent film roles followed, including his breakout role as Jack Moreland in Cecil B. DeMille's ''The Road to Yesterday'' (1925), which earned critical praise. DeMille soon cast him as the leading man in the highly acclaimed silent drama film ''The Volga Boatman''. anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnival Boat
''Carnival Boat'' is a 1932 American Pre-Code adventure film directed by Albert S. Rogell and written by James Seymour. The film stars William Boyd, Ginger Rogers, Fred Kohler, and Hobart Bosworth. The film was released on March 21, 1932, by RKO Pictures. Plot With production down and his health failing, Jim Gannon has only one logging season to groom his son Buck to replace him as the logging camp boss. However, Buck is more interested in courting Honey, a singer and dancer on a carnival boat that travels from camp to camp. Against orders from his father, he takes his crew to the boat where he proposes to Honey and promises her that he will quit his job and move to the city. Meanwhile, head loader Hack Logan wants to be promoted to boss after Jim retires. After Jim is injured in an accident, Buck is too busy with work to see Honey and she begins to doubt their relationship. When she visits Jim, he convinces Honey that Buck wants to continue logging. Before Honey can leave town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RKO Pictures
RKO Radio Pictures Inc., commonly known as RKO Pictures or simply RKO, is an American film production and distribution company, historically one of the major film studios, "Big Five" film studios of Cinema of the United States, Hollywood's Classical Hollywood cinema#1927–1960: Sound era and the Golden Age of Hollywood, Golden Age. The business was formed after the Keith-Albee-Orpheum theater chain and Joseph P. Kennedy, Joseph P. Kennedy's Film Booking Offices of America studio were studio system, brought together under the control of the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) in October 1928. RCA executive David Sarnoff engineered the merger to create a market for the company's sound-on-film technology, RCA Photophone, and in early 1929 production began under the RKO name (an initialism of Radio-Keith-Orpheum). Two years later, another Kennedy concern, the Pathé Exchange, Pathé studio, was folded into the operation. By the mid-1940s, RKO was controlled by investor Floyd Odlum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loggersports
Lumberjack is a mostly North American term for workers in the logging industry who perform the initial harvesting and transport of trees. The term usually refers to loggers in the era before 1945 in the United States, when trees were felled using hand tools and dragged by oxen to rivers. The work was difficult, dangerous, intermittent, low-paying, and involved living in primitive conditions. However, the men built a traditional culture that celebrated strength, masculinity, confrontation with danger, and resistance to modernization. Term The term lumberjack is of Canadian derivation. The first attested use of the term combining its two components comes from an 1831 letter to the Cobourg, Ontario, ''Star and General Advertiser'' in the following passage: "my misfortunes have been brought upon me chiefly by an incorrigible, though perhaps useful, race of mortals called lumberjacks, whom, however, I would name the Cossacks of Upper Canada, who, having been reared among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log Pond
A log pond is a small natural lake or reservoir used for storage of wooden logs in readiness for milling at a sawmill. Although some mill ponds served this purpose for water-powered sawmills, steam-powered sawmills used log ponds for transportation of logs near the mill; and did not require the elevation drop of watermill reservoirs. Background The earliest mechanized sawmills of the industrial revolution were built on navigable rivers, lakes, or estuaries where logs could be floated to the sawmill and lumber could be carried to markets aboard ships or barges. Early steam sawmills included a hoist to lift logs out of the water onto a carriage which moved the log past a stationary powered saw. Men could relatively easily push floating logs into position to be lifted by the hoist. Forests distant from navigable water became accessible with the development of railroads. Sawmills adjacent to navigable waters were termed cargo mills, in contrast to interior rail mills relying up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willamette Iron And Steel Works
Willamette Iron Works (also known as Willamette Iron and Steel Company or WISCO) was a general foundry and machine business established in 1865 in Portland, Oregon, originally specializing in the manufacture of steamboat boilers and engines. In 1904, the company changed its name to Willamette Iron and Steel Works, under which name it operated continually until its close in 1990. The works was very busy during the World War I shipbuilding boom, building boilers for Northwest Steel and Albina Engine & Machine Works in Portland, G. M. Standifer Construction in Vancouver, Alameda Works Shipyard, Union Iron Works, Western Pipe and Steel, Schaw-Batcher and the Moore Dry Dock Company in San Francisco, Southwestern Shipbuilding Company, Southwestern Shipbuilding and the Long Beach Shipbuilding Company in Los Angeles, Skinner & Eddy, J. F. Duthie & Company, J. F. Duthie and Ames Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, Ames in Seattle and Todd Dry Dock and Construction Company, Todd Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerator Car
A refrigerator car (or "reefer") is a Refrigeration, refrigerated boxcar (U.S.), a piece of railroad rolling stock designed to carry perishable freight at specific temperatures. Refrigerator cars differ from simple Thermal insulation, insulated boxcars and Ventilation (architecture), ventilated boxcars (commonly used for transporting fruit), neither of which are fitted with cooling apparatus. Reefers can be ice-Refrigeration, cooled, come equipped with any one of a variety of mechanical refrigeration systems, or use carbon dioxide (as dry ice) or liquid nitrogen as a cooling agent. Milk cars (and other types of "express" reefers) may or may not include a cooling system, but are equipped with high-speed bogie, trucks and other modifications that allow them to travel with train, passenger trains. History Background: North America After the end of the American Civil War, Chicago, Illinois emerged as a major railway center for the Distribution (business), distribution of livestock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatcar
A flatcar (US) (also flat car, or flatbed) is a piece of rolling stock that consists of an open, flat deck mounted on trucks (US) or bogies (UK) at each end. Occasionally, flat cars designed to carry extra heavy or extra large loads are mounted on a pair (or rarely, more) of bogies under each end. The deck of the car can be wood or steel, and the sides of the deck can include pockets for Side stake, stakes or tie-down points to secure loads. Flatcars designed for carrying machinery have sliding chain assemblies recessed in the deck. Flatcars are used for loads that are too large or cumbersome to load in enclosed cars such as boxcars, but which will not be harmed by the weather. They are also often used to transport intermodal containers (shipping containers) or Semi-trailer, trailers as part of intermodal freight transport shipping. Specialized types Aircraft parts flatcars Aircraft parts were hauled via conventional Boxcar, freight cars beginning in World War II. However, gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shay Locomotive
The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a ''geared steam locomotive''. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track. Development Ephraim Shay (1839–1916), was a schoolteacher, a clerk in an American Civil War hospital, a civil servant, a logging, logger, a merchant, a railway owner, and an inventor who lived in Michigan. In the 1860s, he became a logger and wanted a better way to move logs to the sawmill, mill than on winter snow sleds. He built his own Tramway (industrial), tramway in 1875, on gauge rail tracks, track on wooden Railroad tie, ties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |