|
Suetonius Grant Heatly
Suetonius Grant Heatly (sometimes spelled as ''Heatley''; 1751–1793) was a judge employed by the British East India Company and, with John Sumner, established what is considered to be the first coal mine in India.Manners & Williamson (1920), pp. 180–181. Heatly was born in Newport, Rhode Island, in what is now the United States, to a family that had a Scottish heritage.and was loyal to the British Crown. That loyalty caused them to move to England around the time of the American Revolution. His connections and ability were useful in his career with the East India Company, which he joined in 1766 and for which he held various offices. Grant and his colleague, Sumner, saw potential in the extraction of coal in India and attempted to capitalise on that and their relationship with the East India Company, which they envisaged as being a significant purchaser. Their project involved several mine workings, the precise location of which has been debated. It was beset by problems, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magistrate
The term magistrate is used in a variety of systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. In ancient Rome, a '' magistratus'' was one of the highest ranking government officers, and possessed both judicial and executive powers. In other parts of the world, such as China, magistrate is a word applied to a person responsible for administration over a particular geographic area. Today, in some jurisdictions, a magistrate is a judicial officer who hears cases in a lower court, and typically deals with more minor or preliminary matters. In other jurisdictions (e.g., England and Wales), magistrates are typically trained volunteers appointed to deal with criminal and civil matters in their local areas. Original meaning In ancient Rome, the word '' magistratus'' referred to one of the highest offices of state. Analogous offices in the local authorities, such as '' municipium'', were subordinate only to the legislature of which they generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta (List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary Financial centre, financial and Commercial area, commercial centre of Eastern India, eastern and Northeast India, northeastern India. Kolkata is the list of cities in India by population, seventh most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 4.5 million (0.45 crore) while its metropolitan region Kolkata Metropolitan Area is the List of million-plus agglomerations in India, third most populous metropolitan region of India with a metro population of over 15 million (1.5 crore). Kolkata is regarded by many sources as the cultural capital of India and a historically and culturally significant city in the historic Bengal, region of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Ton
The long ton, also known as the imperial ton, displacement ton,Dictionary.com - ''"a unit for measuring the displacement of a vessel, equal to a long ton of 2240 pounds (about 1016 kg) or 35 cu. ft. (1 cu. m) of seawater."'' or British ton, is a measurement unit equal to 2,240 pounds (1,016.0 kg). It is the name for the unit called the " ton" in the avoirdupois system of weights or Imperial system of measurements. It was standardised in the 13th century. It is used in the United States for bulk commodities. It is not to be confused with the short ton, a unit of weight equal to used in the United States, and Canada before metrication, also referred to simply as a "ton". Unit definition A long ton is defined as exactly 2,240 pounds. The long ton arises from the traditional British measurement system: A long ton is 20 long hundredweight (cwt), each of which is 8 stone Thus, a long ton is Unit equivalences A long ton, also called the weight ton (W/T), imperial ton, or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maunds
The maund (), mun or mann (Bengali: ; Urdu: ) is a traditional unit of mass used in British India, and also in Afghanistan, Persia, and Arabia:. the same unit in the Mughal Empire was sometimes written as ''mann'' or ''mun'' in English, while the equivalent unit in the Ottoman Empire and Central Asia was called the ''batman''. At different times, and in different South Asian localities, the mass of the maund has varied, from as low as 25 pounds (11 kg) to as high as 160 pounds (72 kg): even greater variation is seen in Persia and Arabia... One maund in Pakistan is measured as 40kg. History In British India, the maund was first standardized in the Bengal Presidency in 1833, where it was set equal to 100 Troy pounds (82.28 lbs. av.). This standard spread throughout the British Raj.. After the independence of India and Pakistan, the definition formed the basis for metrication, one maund becoming exactly 37.3242 kilograms.. A similar metric defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Hastings
Warren Hastings (6 December 1732 – 22 August 1818) was a British colonial administrator, who served as the first governor of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), the head of the Supreme Council of Bengal, and so the first governor-general of Bengal in 1772–1785. He and Robert Clive are credited with laying the foundation of the British Empire in India. He was an energetic organizer and reformer. In 1779–1784 he led forces of the East India Company against a coalition of native states and the French. In the end, the well-organized British side held its own, while France lost influence in India. In 1787, he was accused of corruption and impeached, but he was eventually acquitted in 1795 after a long trial. He was made a privy councillor in 1814. Early life and education Warren Hastings was born in Churchill, Oxfordshire, in 1732 to Reverend Penyston Hastings and his wife Hester (née Warren), who died soon after he was born.Gloucestershire, England, Church of Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birbhum District
Birbhum district () is an administrative unit in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the northernmost district of Burdwan division—one of the five administrative divisions of West Bengal. The district headquarters is in Suri. Other important cities are Bolpur, Rampurhat and Sainthia. Jamtara, Dumka and Pakur districts of the state of Jharkhand lie at the western border of this district; the border in other directions is covered by the districts of Bardhaman of Purba Bardhaman, Paschim Bardhaman and Murshidabad of West Bengal. Often called "the land of red soil",Rahim, Kazi MB, and Sarkar, Debasish, ''Agriculture, Technology, Products and Markets of Birbhum District'', ''Paschim Banga'', Birbhum Special Issue, pp. 157–166, Information and Cultural Department, Government of West Bengal. Birbhum is noted for its topography and its cultural heritage which is somewhat different from the other districts in West Bengal. The western part of Birbhum is a bushy region, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethora
Ethora is a rural suburb of Asansol, located in the Salanpur CD block in the Asansol Sadar subdivision of the Paschim Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It was a site of the first attempts at commercial coal extraction in the country. The area presently is a coal-mining area. It is in Raniganj Coalfield and lies in the Salanpur Area of Eastern Coalfields. History In 1774, two employees of the East India Company, Suetonius Grant Heatly and John Sumner, proposed to establish six mines in an area which they defined as A site at Ethora was among the six selected and was probably the first to operate. According to the anthropologist Morton Klass, by 1963 it "had become a sleepy village of mud houses scattered among the ruins of once much grander buildings." However, until the independence of India from British rule in 1947 it had been of local significance as it was home to a zamindar successor to the Maharajah of Kasipur and to both religious centres and schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajay River
The Ajay (/ˈədʒɑɪ/) is a river which flows through the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal. The catchment area of Ajay River is . See also List of rivers of India With a land area of consisting of diverse ecosystems, India has many river systems and perennial streams. The rivers of India can be classified into four groups – Himalayan, Deccan, Coastal, and Inland drainage. The Himalayan rivers, mainl ... References Bibliography * https://riversgraphy.com/ajay-river/ Rivers of Bihar Rivers of Jharkhand Rivers of West Bengal {{India-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
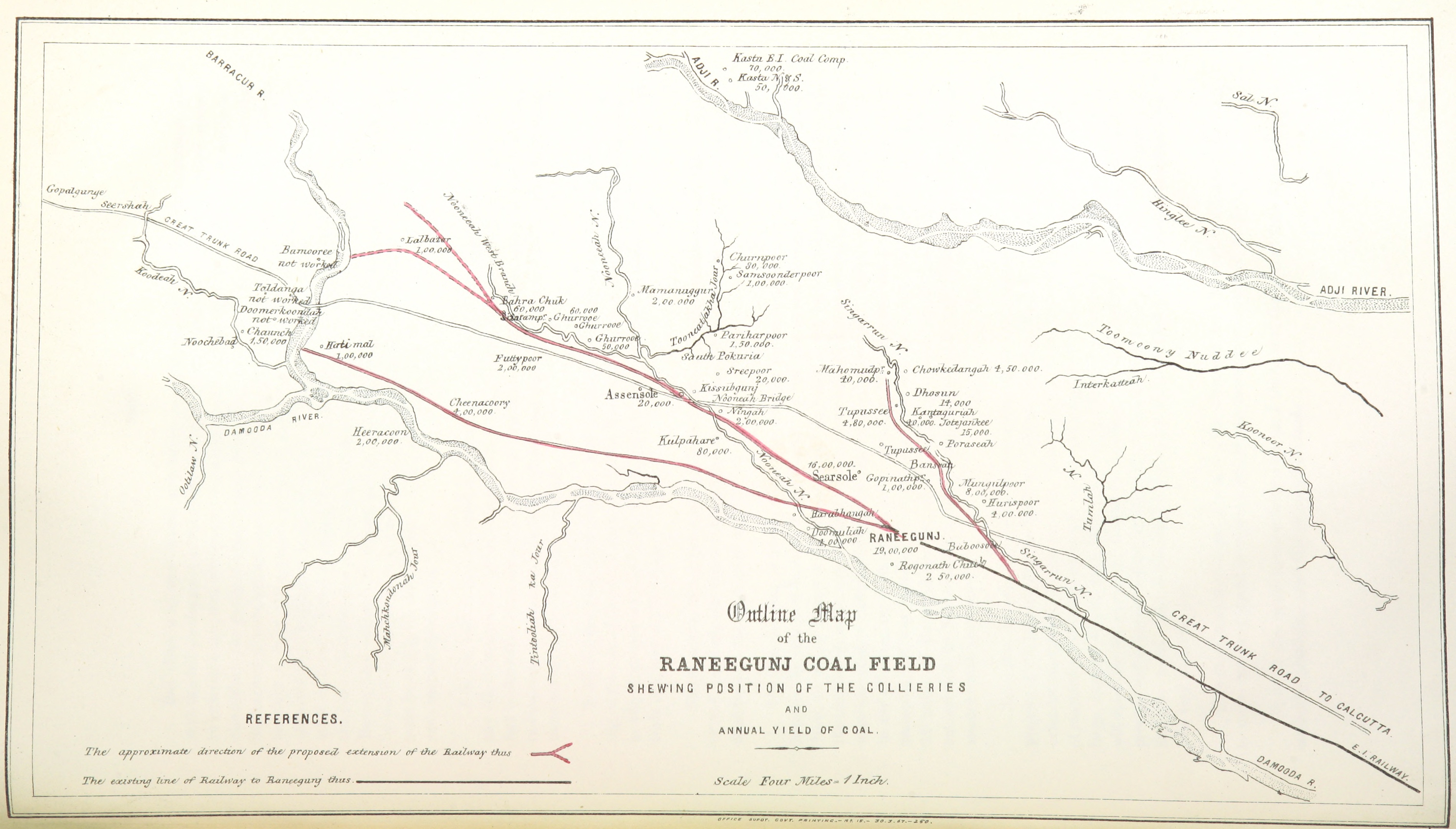
Raniganj Coalfield
Raniganj Coalfield is primarily located in the Asansol and Durgapur subdivisions of Paschim Bardhaman district of West Bengal. It spreads over to the neighboring districts of Birbhum, Bankura, Purulia and to Dhanbad district of Jharkhand. Mainly, cooking coal is found here. History Coalmining in India first started in the Raniganj Coalfield. In 1774, John Sumner and Suetonius Grant Heatly of the British East India Company found coal near Ethora, presently in Salanpur community development block. The early exploration and mining operations were carried out in a haphazard manner.Akkori Chattopadhyay, ''Bardhaman Jelar Itihas O Lok Sanskriti'' , Vol I, pp. 46-51, Radical, 2001, Regular mining started in 1820, led by an agency house, Alexander & Co. In 1835, Prince Dwarkanath Tagore bought over the collieries and Carr, Tagore and Company led the field. For the entire 19th century and a major part of the 20th century, Raniganj coalfields was the major producer of coal in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damodar River
Damodar River (Pron: /ˈdʌmoˌdaː/) is a river flowing across the Indian states of Jharkhand and West Bengal. The valley is rich in mineral resources and is known for large-scale mining and industrial activity. It was also known as the Sorrow of Bengal because of the ravaging floods it caused in the plains of West Bengal. The construction of several dams on the Damodar and its tributaries has helped control some of the flooding. Etymology Damodar means "rope around the belly", derived from Sanskrit दाम (dama) "rope" and उदर (udara) "belly". Damodar is also another name given to the Hindu god Krishna because his foster-mother, Yashoda, had tied him to a large urn.Chattopadhyay, Akkori, ''Bardhaman Jelar Itihas O Lok Sanskriti'' (History and Folk lore of Bardhaman District.), , Vol I, pp. 21- 26, Radical Impression. Course The Damodar is a rain-fed river. It originates in Khamarpat Hill on Chotanagpur Plateau in Jharkhand. It travels before joining the Hooghly Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |