|
Streptomyces Spectabilis
''Streptomyces'', from στρεπτός (''streptós''), meaning "twisted", and μύκης (''múkés''), meaning "fungus", is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC-content, GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the same species may colonize very diverse environments. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. Between 5-23% (average: 12%) of the protein-coding genes of each ''Streptomyces'' species are implicated in secondary metabolism. Streptomycetes produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as research tools in molecular biology. The term ''culture'' can also refer to the microorganisms being grown. Microbial cultures are used to determine the type of organism, its abundance in the sample being tested, or both. It is one of the primary diagnostic methods of microbiology and used as a tool to determine the cause of infectious disease by letting the agent multiply in a predetermined medium. For example, a throat culture is taken by scraping the lining of tissue in the back of the throat and blotting the sample into a medium to be able to screen for harmful microorganisms, such as '' Streptococcus pyogenes'', the causative agent of strep throat. Furthermore, the term culture is more generally used informal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neomycin
Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against Gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic Gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. Neomycin received approval for medical use in 1952. Rutgers University was granted the patent for neomycin in 1957. Discovery Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by the microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. It is produced naturally by the bacterium '' Streptomyces fradiae''. Synthesis req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Turgidiscabies
''Streptomyces turgidiscabies'' is a streptomycete bacterium species, causing scab in potatoes. It has flexuous spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ..., the latter which are cylindrical and smooth. The type strain is SY9113T (= ATCC 700248T = IFO 16080T). It is almost identical to '' Streptomyces reticuliscabiei''; however, they are considered distinct species given the diseases they cause are different. References Further reading *Joshi, Madhumita V., and Rosemary Loria. "Streptomyces turgidiscabies possesses a functional cytokinin biosynthetic pathway and produces leafy galls." Molecular plant-microbe interactions 20.7 (2007): 751–758. * *Thwaites, R., et al. "Streptomyces turgidiscabies and S. acidiscabies: two new causal agents of common scab of potato (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Acidiscabies
''Streptomyces acidiscabies'' is a streptomycete bacterium species, causing a scab disease of potatoes. Its type strain is RL-110 (= ATCC 49003). References Further reading * *Zhao, W. Q., X. M. Yu, and D. Q. Liu. "First report of Streptomyces acidiscabies causing potato scab in China." New Disease Reports 19 (2009): 29. * * External links *LPSN acidiscabies Bacteria described in 1989 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Caviscabies
''Streptomyces griseus'' is a species of bacteria in the genus '' Streptomyces'' commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, ''S. griseus'' strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of ''S. griseus''. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed. The taxonomic history of ''S. griseus'' and its phylogenetically related strains has been turbulent. ''S. griseus'' was first described in 1914 by Krainsky, who called the species '' Actinomyces griseus''. The name was changed in 1948 by Waksman and Henrici to ''Streptomyces griseus''. The interest in these strains stems f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Sudanensis
''Streptomyces sudanensis'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from patients with actinomycosis infections in Sudan Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi .... See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References sudanensis Bacteria described in 2008 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Somaliensis
''Streptomyces somaliensis'' is a proteolytic bacterium species from the genus of '' Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from a mycetoma from the foot of a man in Somalia Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th .... ''Streptomyces somaliensis'' is a human pathogen and can cause actinomycosis. See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References Further reading * * * * * * External linksType strain of ''Streptomyces somaliensis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase somaliensis Bacteria described in 1948 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
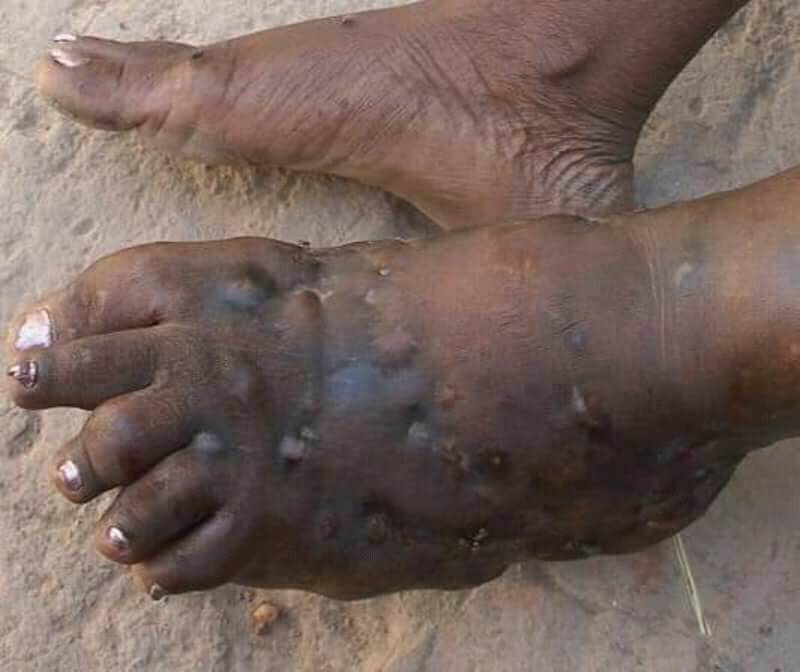
Eumycetoma
Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent Mycoses, fungal infection of the skin and the tissues subcutaneous tissue, just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet Nodule (medicine), nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from Sinus (anatomy), sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity. Several fungi can cause eumycetoma, including: ''Madurella mycetomatis'', ''Madurella grisea'', ''Curvularia lunata'', ''Scedosporium species'', ''Acremonium'' and ''Fusarium'' species. Diagnosis is by biopsy, visualising the fungi microscopy, under the microscope and microbiological culture, culture. Medical imaging may reveal extent of bone involvement. Other tests include ELISA, immunodiffusion, and DNA Barcoding. Treatment includes Surgical debridement, surgical removal of affected tissue and Antifungal, antifungal medicines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogens
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ. The term ''pathogen'' came into use in the 1880s. Typically, the term ''pathogen'' is used to describe an ''infectious'' microorganism or agent, such as a virus, bacterium, protozoan, prion, viroid, or fungus. Small animals, such as helminths and insects, can also cause or transmit disease. However, these animals are usually referred to as parasites rather than pathogens. The scientific study of microscopic organisms, including microscopic pathogenic organisms, is called microbiology, while parasitology refers to the scientific study of parasites and the organisms that host them. There are several pathways through which pathogens can invade a host. The principal pathways have different episodic time frames, but soil has the longest or most pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical Society Transactions
''Biochemical Society Transactions'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal which publishes the transactions of the annual conference and focused meetings of the Biochemical Society, together with independent meetings supported by the society. The society's annual symposium, previously published only in '' Biochemical Society Symposium'', was first published in the ''Transactions'' in 2008. The journal was established in 1973 and is published by Portland Press, the Society's publishing arm. The journal was issued quarterly until 1999. Since 2004, issues have been made up entirely of full papers, having previously alternated between an issue of abstracts and an issue of full papers. Transactions take the form of short papers, usually of 3–4 pages; the journal also publishes longer papers from the society's award lectures. Since 2005, David J. Richardson (University of East Anglia) has been honorary editor. Colin Bingle is the editor-in-chief in 2020. According to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague (disease), plague, cholera, and typhoid fever. Its use by mouth or by injection is only recommended when safer antibiotics cannot be used. Monitoring both blood levels of the medication and blood cell levels every two days is recommended during treatment. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, nausea, and diarrhea. The bone marrow suppression may result in death. To reduce the risk of side effects treatment duration should be as short as possible. People with liver or kidney problems may need lower doses. In young infants, a condition known as gray baby syndrome may occur which results in a swollen stomach and Hypotension, low blood pressure. Its use near the end of pregnancy and during breastfeeding is typically not re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
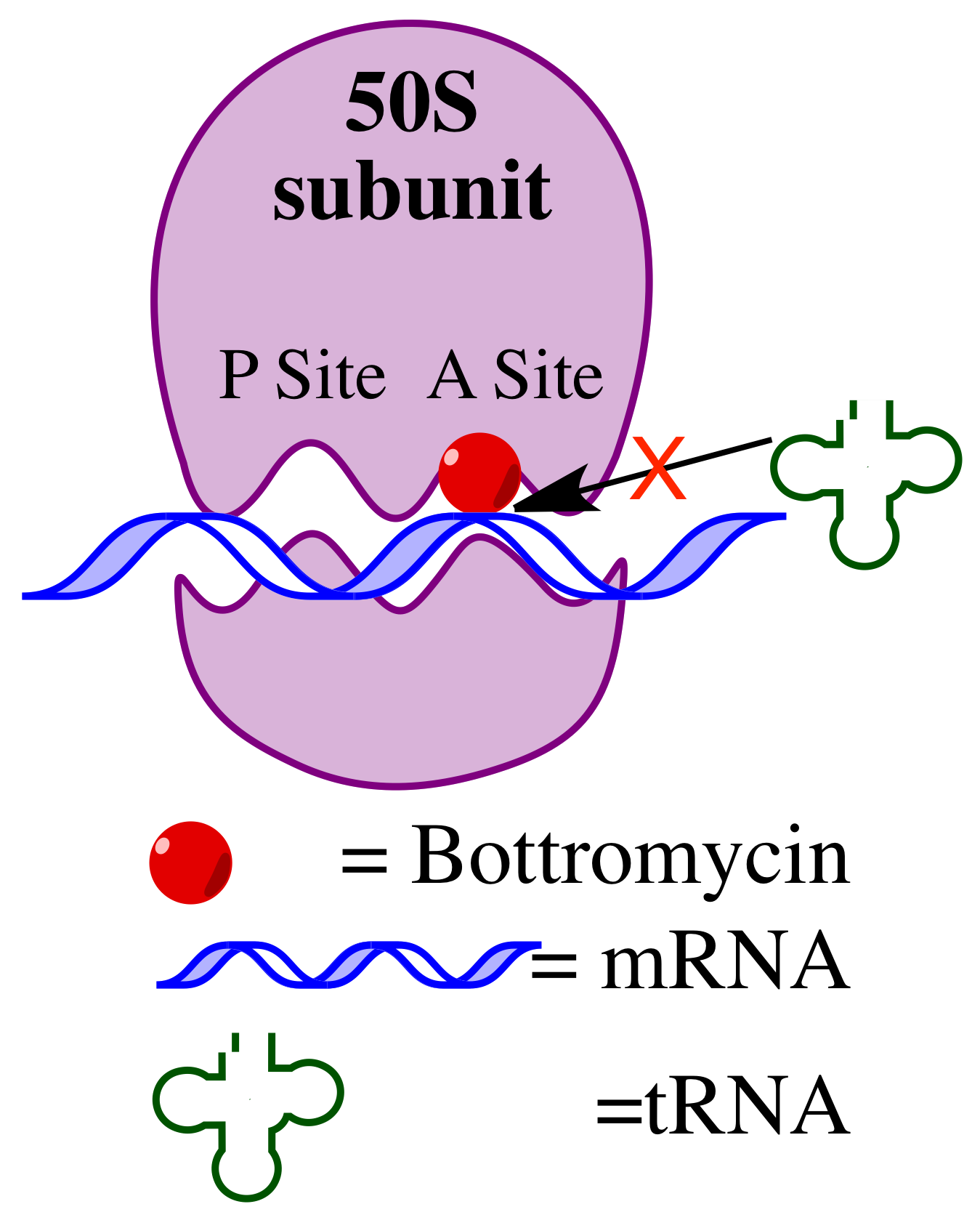
Bottromycin
Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from ''Streptomyces bottropensis''. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic. Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, aminoacyl-''t''RNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity ''in vitro'', it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability ''in vivo'', some bottromycin derivatives have been explored. The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |