|
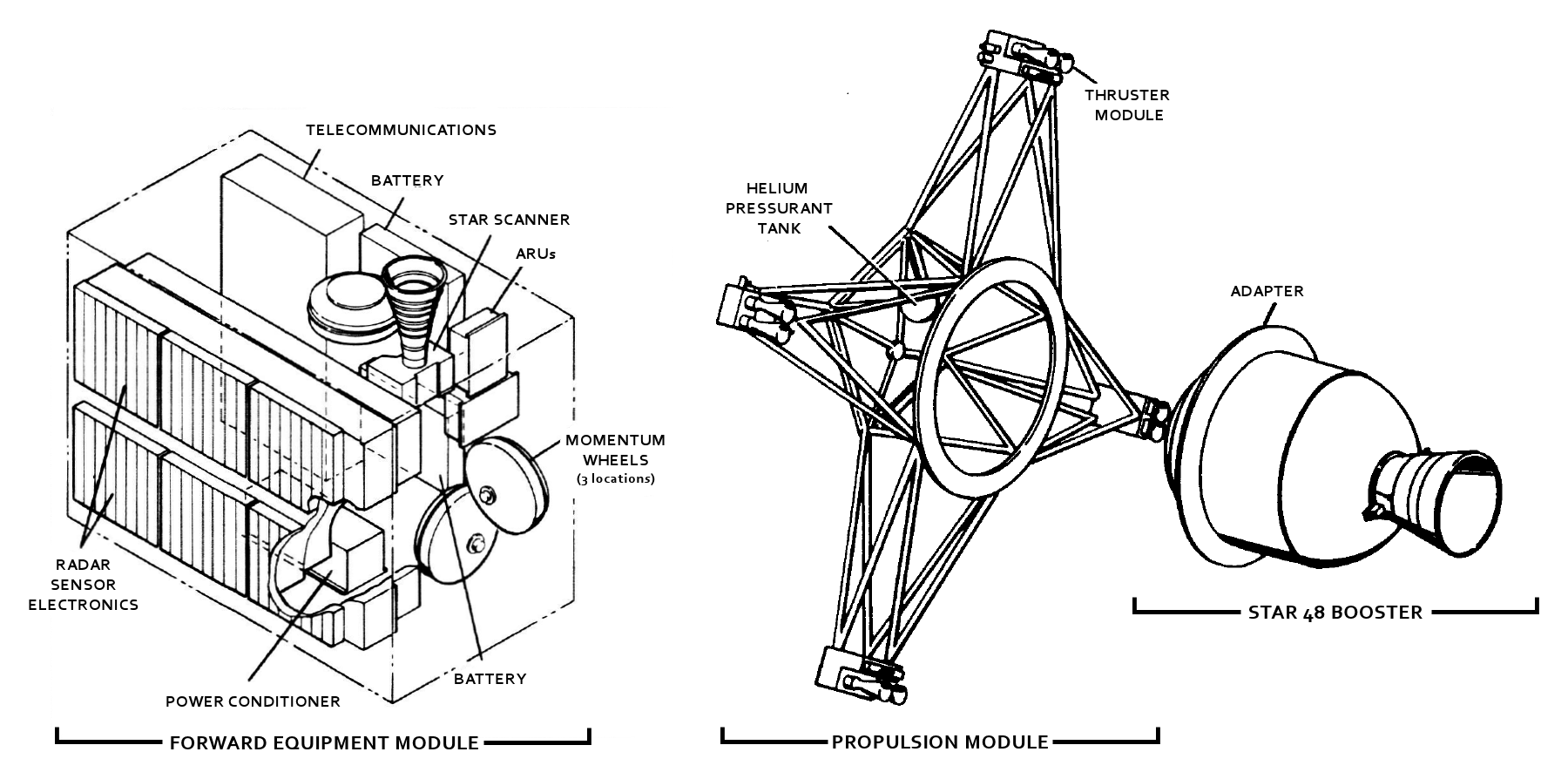
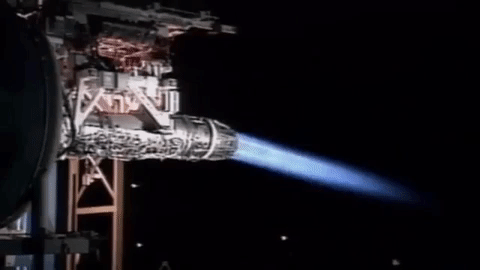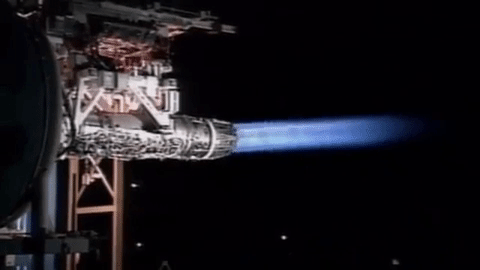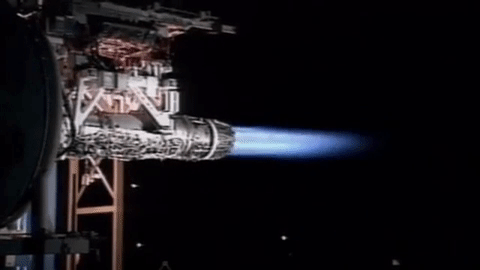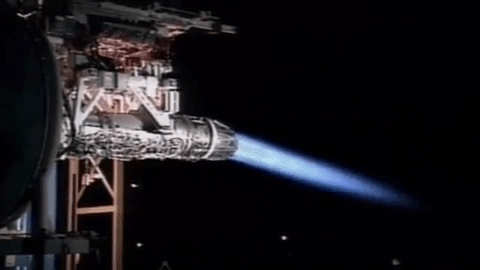
Star 48
The Star 48 is the largest of a family of solid rocket motors used by many space propulsion and launch vehicle stages, almost exclusively as an upper stage. It was developed primarily by Thiokol Propulsion and after several mergers, is manufactured by Northrop Grumman’s Space Systems division. A Star 48B stage is also one of the few man-made items sent on escape trajectories out of the Solar System, although it is derelict since its use. The Star 48B variant was the PAM-D upper stage used on the retired Delta II rocket. The Star 48 has been used as an upper stage in three- and four-stage launch systems. Overview The "48" designation refers to the approximate diameter of the fuel casing in inches (122 cm); Thiokol had also manufactured other motors such as the Star 37 and Star 30. Internally, Thiokol's designation was TE-M-711 for early versions and TE-M-799 for later ones. Subtypes are given one or more letter suffixes after the diameter number, or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiokol
Thiokol was an American corporation concerned initially with rubber and related chemicals, and later with rocket and missile propulsion systems. Its name is a portmanteau of the Greek words for sulfur () and glue (), an allusion to the company's initial product, Thiokol polymer. The Thiokol Chemical Company was founded in 1929. Its initial business was a range of synthetic rubber and polymer sealants. Thiokol was a major supplier of liquid polymer sealants during World War II. When scientists at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that Thiokol's polymers made ideal binders for solid rocket fuels, Thiokol moved into the new field, opening laboratories at Elkton, Maryland, and later production facilities at Elkton and at Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama. Huntsville produced the XM33 Pollux, TX-18 Falcon, and TX-135 Nike-Zeus systems. It closed in 1996. In the mid-1950s the company bought extensive lands in Utah for its rocket test range. Thiokol was involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yo-yo De-spin
A yo-yo de-spin mechanism is a device used to reduce the spin of satellites, typically soon after launch. It consists of two lengths of cable with weights on the ends. The cables are wrapped around the final stage and/or satellite, in the manner of a double yo-yo. When the weights are released, the spin of the rocket flings them away from the spin axis. This transfers enough angular momentum to the weights to reduce the spin of the satellite to the desired value. Subsequently, the weights are often released. De-spin is needed since some final stages are spin-stabilized, and require fairly rapid rotation (now typically 30-60 rpm; some early missions, such as Pioneer, rotated at over 600 rpm) to remain stable during firing. (See, for example, the Star 48, a solid fuel rocket motor.) After firing, the satellite cannot be simply released, since such a spin rate is beyond the capability of the satellite's attitude control. Therefore, after rocket firing but before satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas E/F
The Atlas E/F (or SB-1A) was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket built using parts of decommissioned SM-65 Atlas missiles. It was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets. The first stage was built using parts taken from decommissioned SM-65E Atlas, Atlas-E and SM-65F Atlas, Atlas-F missiles, with various solid rocket, solid propellant upper stages used depending on the requirements of the payload. The Atlas E/F was also used without an upper stage for a series of re-entry vehicle tests. On a single launch, an RM-81 Agena liquid-propellant upper stage was used. Variants Atlas E/F Thirty Atlas E/F rockets were launched without upper stages for ABRES and BMRS re-entry vehicle tests between 1965 and 1974. Three of these launches failed. Five ABRES launches were also conducted while the missiles were still operational, but did not use the Atlas E/F configuration. Atlas E/F-Agena An RM-81 Agena upper stage was used on a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilisation
In aerospace engineering, spin stabilization is a method of stabilizing a satellite or launch vehicle by means of spin, i.e. rotation along the longitudinal axis. The concept originates from conservation of angular momentum as applied to ballistics, where the spin is commonly obtained by means of rifling. For most satellite applications this approach has been superseded by three-axis stabilization. Use Spin-stabilization is used on rockets and spacecraft where attitude control is required without the requirement for on-board 3-axis propulsion or mechanisms, and sensors for attitude control and pointing. On rockets with a solid motor upper stage, spin stabilization is used to keep the motor from drifting off course as they don't have their own thrusters. Usually small rockets are used to spin up the spacecraft and rocket then fire the rocket and send the craft off. Rockets and spacecraft that use spin stabilization: * The Jupiter-C and Minotaur V launch vehicles used spin-stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minotaur IV
Minotaur IV, also known as Peacekeeper SLV and OSP-2 PK is an active expendable launch system derived from the retired LGM-118 Peacekeeper ICBM. It is operated by Northrop Grumman Space Systems, and made its maiden flight on 22 April 2010 carrying the HTV-2a Hypersonic Test Vehicle. The first orbital launch occurred on 26 September 2010 with the SBSS satellite for the United States Air Force. The Minotaur IV vehicle consists of four stages and is capable of placing of payload into a low Earth orbit (LEO). The first three stages are decommissioned Peacekeeper missile motors. On the baseline Minotaur IV, the fourth stage is an Orion 38. The higher-performance Minotaur IV+ variant instead replaces the Orion motor with a Star 48BV fourth stage. A three-stage configuration (no Orion 38 or Star 48), designated the Minotaur IV Lite, is available for suborbital trajectories. A five-stage derivative, the Minotaur V, made its maiden flight on 7 September 2013. Minotaur IV launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Vectoring
Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control (TVC), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine(s) or motor(s) to Aircraft flight control system, control the Spacecraft attitude control, attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle. In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic Flight control surfaces, control surfaces are ineffective, so thrust vectoring is the primary means of Flight dynamics (fixed-wing aircraft), attitude control. Exhaust vanes and Gimbaled thrust, gimbaled engines were used in the 1930s by Robert H. Goddard, Robert Goddard. For aircraft, the method was originally envisaged to provide upward vertical thrust as a means to give aircraft vertical (VTOL) or short (STOL) takeoff and landing ability. Subsequently, it was realized that using vectored thrust in combat situations enabled aircraft to perform various maneuvers not available to conventional-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta IV Heavy
The Delta IV Heavy (Delta 9250H) was an expendable heavy-lift launch vehicle, the largest type of the Delta IV family. It had the highest capacity of any operational launch vehicle in the world after the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011 until the Falcon Heavy debuted in 2018, and it was the world's third highest-capacity launch vehicle in operation at the time of its retirement in 2024. It was manufactured by United Launch Alliance (ULA) and was first launched in 2004. Delta IV Heavy was the last operating member of the Delta IV family, and its final flight was on 9 April 2024. It is succeeded by the Vulcan Centaur rocket. The Delta IV Heavy first stage consisted of a central Common Booster Core (CBC), with two additional CBCs as liquid rocket boosters instead of the GEM-60 solid rocket motors used by the Delta IV Medium+ versions. At lift-off, all three rocket engines would operate at full thrust, and 44 seconds later the central engine would throttle down to 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker Solar Probe
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 to make observations of the Stellar corona, Sun's outer corona. It used repeated Gravity assist, gravity assists from Venus to develop an eccentric orbit, approaching within 9.86 solar radius, solar radii (6.9 million km or 4.3 million miles) from the center of the Sun. At its closest approach in 2024, its speed relative to the Sun was or 191 km/s (118.7 mi/s), which is 0.064% the speed of light. It is the fastest object ever built on Earth. The project was announced in the fiscal 2009 budget year. Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory designed and built the spacecraft, which was launched on 12 August 2018. It became the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person, honoring physicist Eugene Parker, Eugene Newman Parker, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago. On 29 October 2018, at about 18:04 UTC, the spacecraft became t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest known trans-Neptunian object by volume by a small margin, but is less massive than Eris (dwarf planet), Eris. Like other Kuiper belt objects, Pluto is made primarily of ice and rock and is much smaller than the inner planets. Pluto has roughly one-sixth the mass of the Moon and one-third its volume. Originally considered a planet, its classification was changed when astronomers adopted a new definition of planet, definition of ''planet''. Pluto has a moderately Orbital eccentricity, eccentric and Inclination, inclined orbit, ranging from from the Sun. Light from the Sun takes 5.5 hours to reach Pluto at its orbital distance of . Pluto's eccentric orbit periodically brings it closer to the Sun than Neptune, but a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), with a team led by Alan Stern, the spacecraft was launched in 2006 with the primary mission to perform a Planetary flyby, flyby study of the Pluto system in 2015, and a secondary mission to fly by and study one or more other Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) in the decade to follow, which became a mission to 486958 Arrokoth. It is the List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System, fifth space probe to achieve the escape velocity needed to leave the Solar System. On January 19, 2006, ''New Horizons'' was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station by an Atlas V rocket directly into an Earth-and-solar Escape velocity, escape trajectory with a speed of about . It was the fastest (average speed w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight in Houston, Texas (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight controller, flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late U.S. president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973. JSC consists of a complex of 100 buildings constructed on in Clear Lake (region), Clear Lake. The center is home to NASA Astronaut Corps, NASA's astronaut corps, and is responsible for training astronauts from both the U.S. and its international partners. It also houses the Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, which has provided the flight controller, flight control function for every NASA human spaceflight since Gemini 4 (including Apollo program, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo–Soyuz, and Space Shuttle program, Space Shuttle). It is popularly known by its radio call signs "Mission Contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |