|
Spring Triangle (Stellarium)
The Spring Triangle is an astronomical asterism involving an imaginary triangle drawn upon the celestial sphere, with its defining vertices at Arcturus, Spica, and Regulus. This triangle connects the constellations of Boötes, Virgo, and Leo. It is visible in the evening rising in the southeastern sky of the Northern Hemisphere between March and May and setting until August, while at morning rising and setting from November to the end of February. George Lovi of Sky & Telescope magazine had a slightly different Spring Triangle, including the tail of Leo, with Denebola replacing Regulus. Although Denebola is dimmer, this triangle is more nearly equilateral. These stars, together with Cor Caroli, form parts of a larger spring asterism called the Great Diamond. The stars of the Spring Triangle Arcturus (α Boötes) Arcturus is a giant orange star in the constellation Boötes. Located only 37 light years away, it has an apparent magnitude of -0.04. It is the brightest star i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
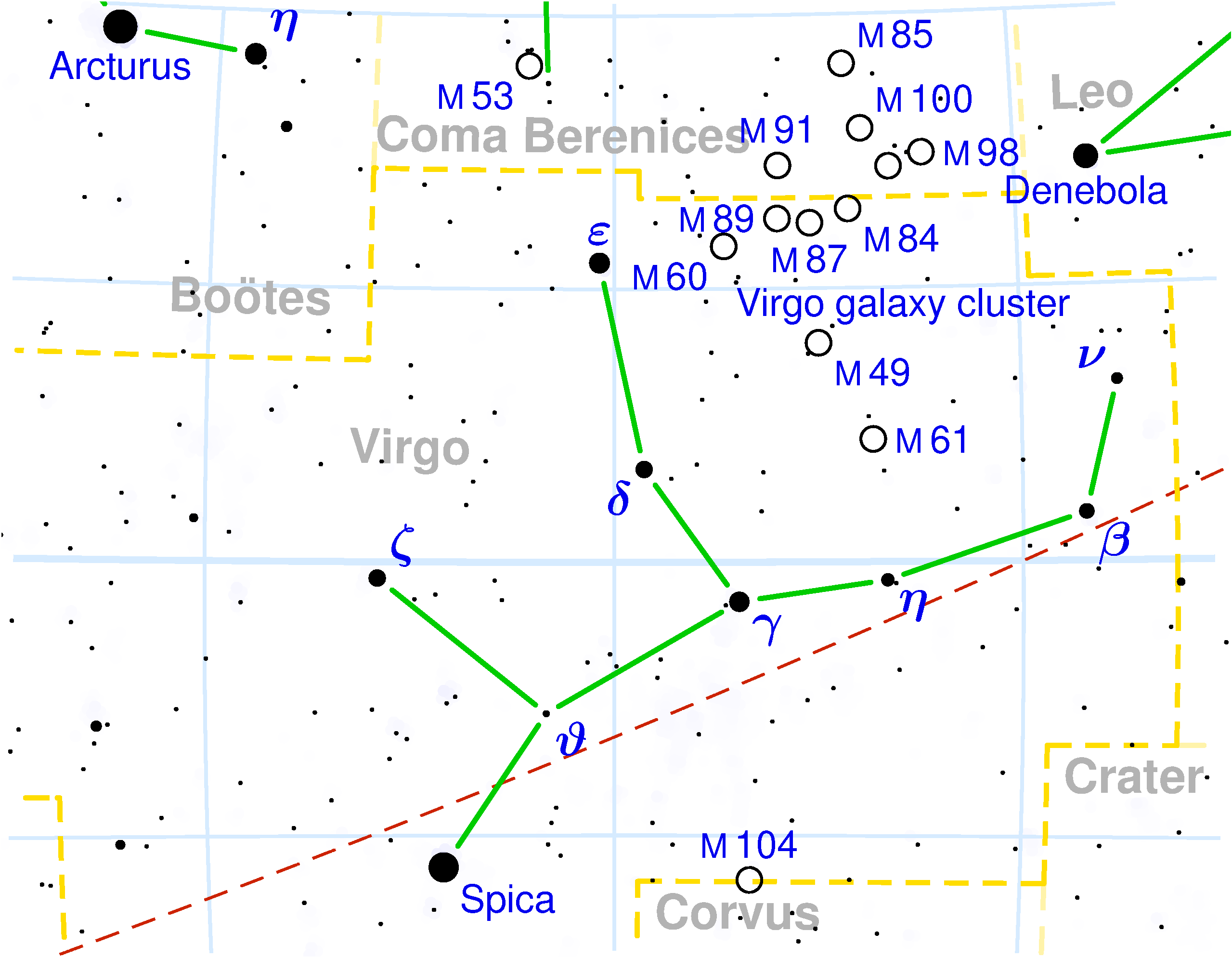
Satellite Galaxy
A satellite galaxy is a smaller companion galaxy that travels on bound orbits within the gravitational potential of a more massive and Luminosity, luminous host galaxy (also known as the primary galaxy). Satellite galaxies and their constituents are bound to their host galaxy, in the same way that planets within the Solar System are gravitationally bound to the Sun. While most satellite galaxies are dwarf galaxies, satellite galaxies of large galaxy clusters can be much more massive. The Milky Way is orbited by about fifty satellite galaxies, the largest of which is the Large Magellanic Cloud. Moreover, satellite galaxies are not the only astronomical objects that are gravitationally bound to larger host galaxies (see globular clusters). For this reason, astronomers have defined galaxies as gravitationally bound collections of stars that exhibit properties that cannot be explained by a combination of Baryon, baryonic matter (i.e. ordinary matter) and Newton's law of gravity, Newt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable reference such as the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF). Patterns in proper motion reveal larger structures like stellar streams, the general rotation of the Milky Way disk, and the random motions of stars in the Galactic halo. The components for proper motion in the equatorial coordinate system (of a given epoch, often J2000.0) are given in the direction of right ascension (''μ''α) and of declination (''μ''δ). Their combined value is computed as the ''total proper motion'' (''μ''). It has dimensions of angle per time, typically arcseconds per year or milliarcseconds per year. Knowledge of the proper motion, distance, and radial velocity allows calculations of an object's motion from the Solar System's frame of reference an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcturus Moving Group
In astronomy, the Arcturus moving group or Arcturus stream is a moving group or stellar stream, discovered by Olin J. Eggen (1971), comprising 53 stars moving at 275,000 miles per hour, which includes the nearby bright star Arcturus. It comprises many stars which share similar proper motion and so appear to be physically associated. This group of stars is not in the plane of the Milky Way galaxy, and has been proposed as a remnant of an ancient dwarf satellite galaxy, long since disrupted and assimilated into the Milky Way. It consists of old stars deficient in heavy elements. However, Bensby and colleagues, in analysing chemical composition of F and G dwarf stars in the solar neighbourhood, found there was no difference in chemical makeup of stars from the stream, suggesting an intragalactic rather than extragalactic origin. One possibility is that the stream appeared in a manner similar to the Hercules group, which is hypothesized to have formed due to Outer Lindblad Resonanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galactic poles'' usually refer specifically to the plane and poles of the Milky Way, in which Planet Earth is located. Some irregular galaxy, galaxies are irregular and do not have any well-defined disk. Even in the case of a barred spiral galaxy like the Milky Way, defining the galactic plane is slightly imprecise and arbitrary since the stars are not perfectly coplanar. In 1959, the International Astronomical Union, IAU defined the position of the Milky Way's north galactic pole as exactly right ascension, RA = , declination, Dec = in the then-used B1950 epoch (astronomy), epoch; in the currently-used J2000 epoch, after precession is taken into account, its position is RA , Dec . This position is in Coma Berenices, near the bright star Arctu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD) is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities and their stellar classifications or effective temperatures. The diagram was created independently in 1911 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and by Henry Norris Russell in 1913, and represented a major step towards an understanding of stellar evolution. Historical background In the nineteenth century large-scale photographic spectroscopic surveys of stars were performed at Harvard College Observatory, producing spectral classifications for tens of thousands of stars, culminating ultimately in the Henry Draper Catalogue. In one segment of this work Antonia Maury included divisions of the stars by the width of their spectral lines. Hertzsprung noted that stars described with narrow lines tended to have smaller proper motions than the others of the same spectral classification. He took this as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (, contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern celestial hemisphere, northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a Ladle (spoon), ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by Sailor, mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star. Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging in apparent magnitude from 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa Minor, the lesser bear. In antiquity, it was one of the original 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, drawing on earlier works by Greek, Egyptian, Babylonian, and Assyrian astronomers. Today it is the third largest of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Major is primarily known from the asterism of its main seven stars, which has been called the "Big Dipper", "the Wagon", "Charles's Wain", or "the Plough", among other names. In particular, the Big Dipper's stellar configuration mimics the shape of the " Little Dipper". Two of its stars, named Dubhe and Merak ( α Ursae Majoris and β Ursae Majoris), can be used as the navigational pointer towards the place of the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Mino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boötes Constellation Map
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from , which comes from 'herder, herdsman' or 'plowman' (literally, 'ox-driver'; from ''boûs'' 'cow'). One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the List of brightest stars, fourth-brightest star in the night sky, the orange giant Arcturus. Epsilon Boötis, or Izar, is a colourful multiple star popular with amateur astronomers. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye. History and mythology In ancient Babylon, the stars of Boötes were known as SHU.PA. They were apparently depicted as the god Enlil, who was the leader of the Babylonian religion, Babyloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |